A Comprehensive Look at Mexico’s Agricultural Landscape: Unveiling the Map of Bounty
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Look at Mexico’s Agricultural Landscape: Unveiling the Map of Bounty
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Look at Mexico’s Agricultural Landscape: Unveiling the Map of Bounty. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Look at Mexico’s Agricultural Landscape: Unveiling the Map of Bounty
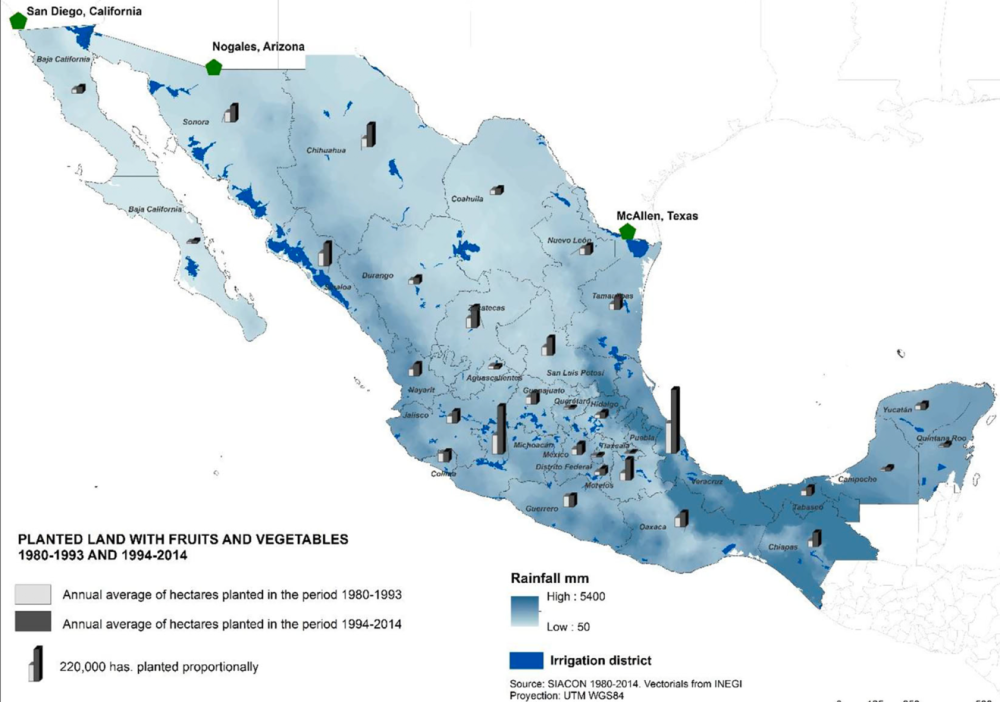
Mexico’s diverse geography and climate create a vibrant tapestry of agricultural landscapes, nurturing a wide array of crops and livestock that play a vital role in the nation’s economy and food security. This article delves into the intricate map of Mexican agriculture, exploring its key features, challenges, and the profound impact it has on the lives of millions.
A Mosaic of Agricultural Regions:
Mexico’s agricultural map is a vibrant mosaic of distinct regions, each with its own unique characteristics and contributions:
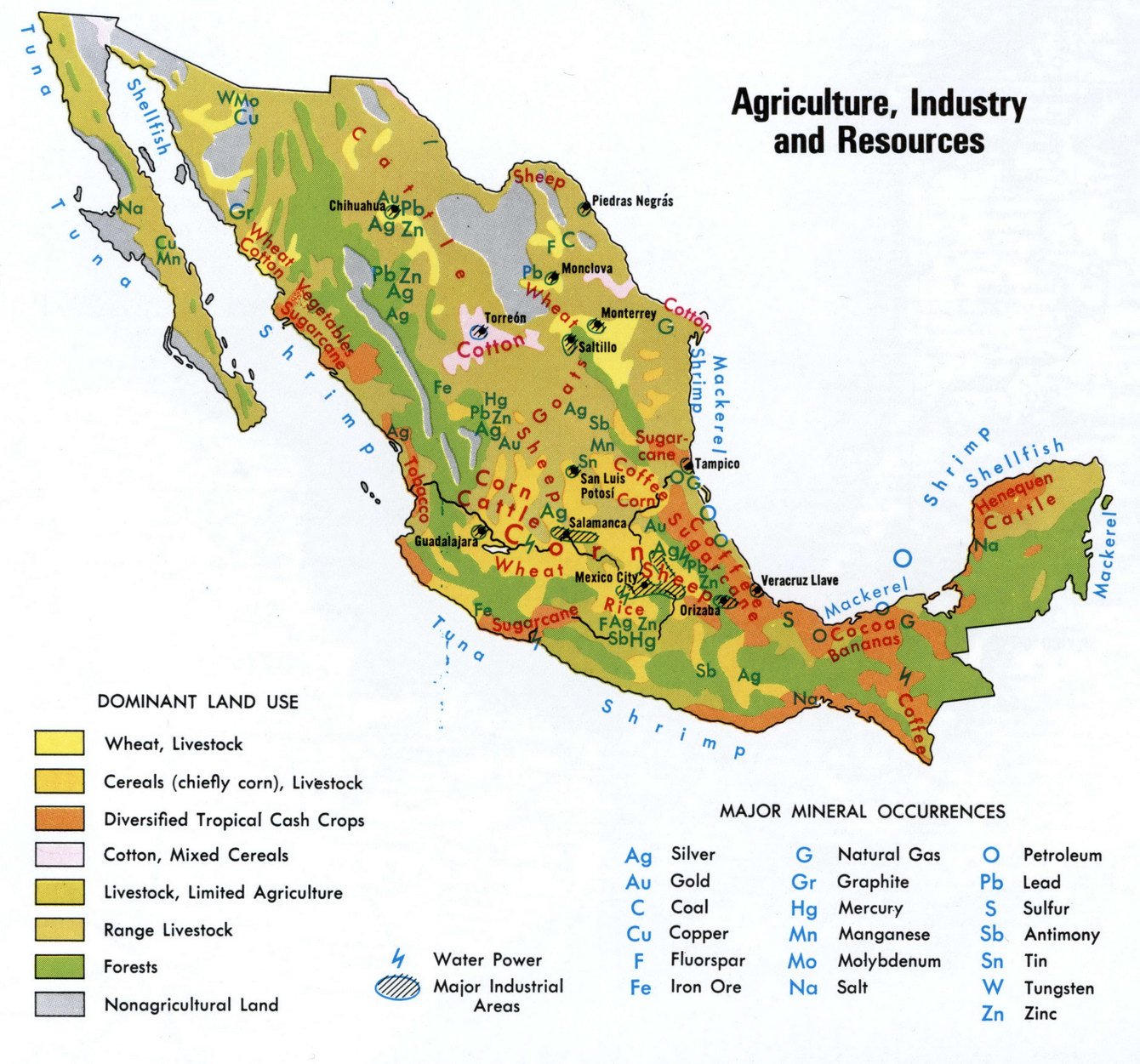
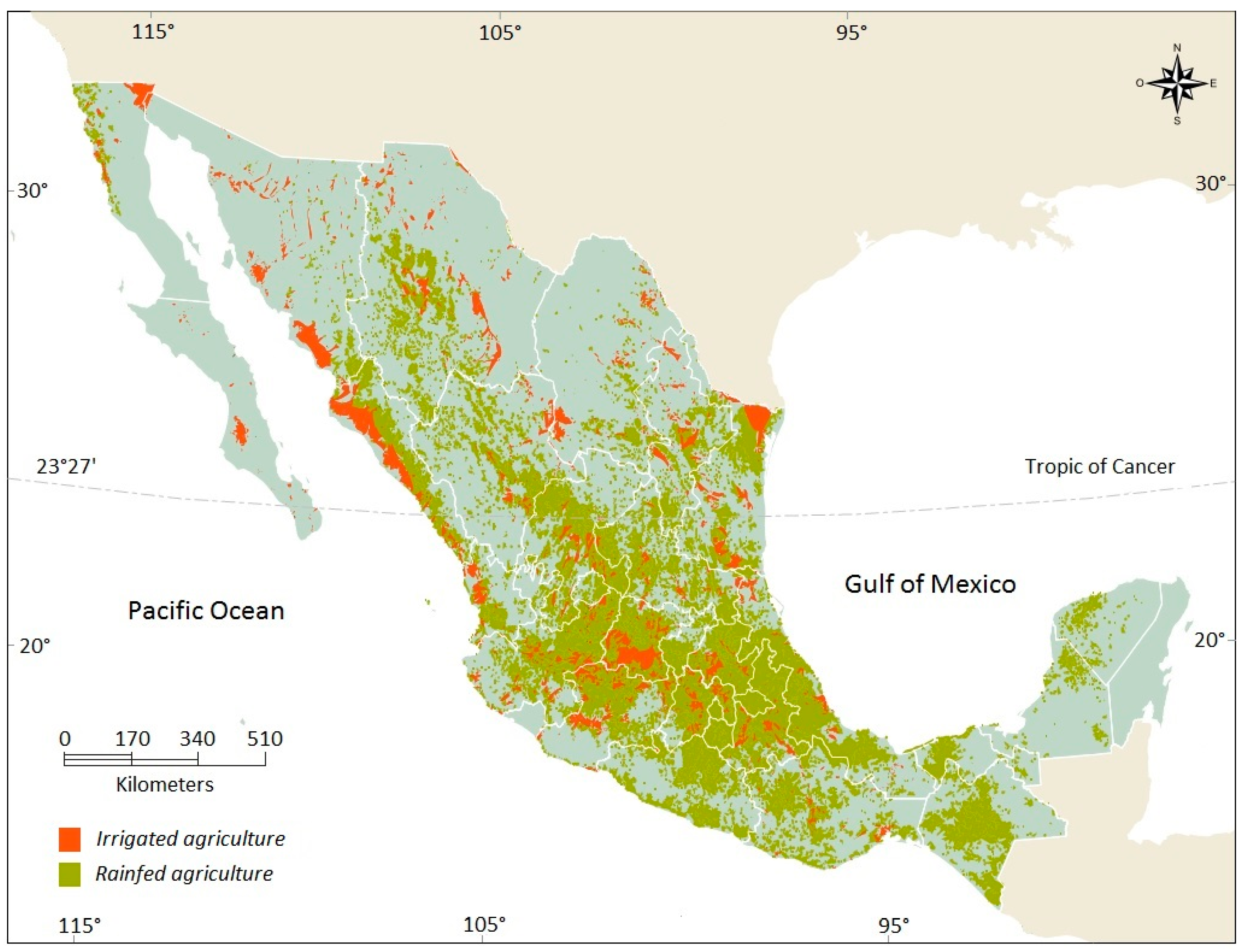
- The North: Characterized by arid and semi-arid conditions, this region is primarily known for its vast expanses of irrigated farmland, producing staple crops like wheat, corn, and beans, alongside important commodities like cotton and livestock.
- The Central Plateau: This region boasts fertile volcanic soils and a temperate climate, making it ideal for cultivating a wide range of crops, including corn, beans, wheat, and fruits like avocado and mango. The Central Plateau also serves as a significant producer of dairy and livestock.
- The Gulf Coast: With its humid subtropical climate and fertile coastal plains, the Gulf Coast is a major producer of fruits, vegetables, and sugarcane. This region also plays a significant role in Mexico’s aquaculture industry, producing shrimp and other seafood.
- The Pacific Coast: Blessed with a diverse climate and fertile soils, the Pacific Coast is a major producer of coffee, bananas, mangoes, and other tropical fruits. This region also boasts a thriving fishing industry.
- The Yucatan Peninsula: Characterized by its tropical climate and karst terrain, the Yucatan Peninsula is renowned for its production of henequen (a fiber used in rope and twine), chicle (a natural gum), and tropical fruits like citrus and mangoes.
Key Crops and Commodities:
Mexico’s agricultural landscape is rich in diversity, producing a wide array of crops and commodities that contribute significantly to the nation’s food supply and economy:
- Corn: A staple food for millions of Mexicans, corn is widely cultivated across the country, with the Central Plateau and the North being major production centers.
- Beans: Another essential part of the Mexican diet, beans are grown throughout the country, particularly in the Central Plateau and the North.
- Wheat: A significant component of Mexico’s breadbasket, wheat is primarily grown in the North and the Central Plateau.
- Avocado: Mexico is the world’s leading producer of avocados, with the Michoacán region being particularly renowned for its high-quality fruit.
- Mango: A popular fruit in Mexico, mangoes are grown extensively along the Pacific Coast and the Gulf Coast.
- Coffee: Mexico is a significant producer of coffee, with the Chiapas region being particularly known for its Arabica beans.
- Sugarcane: A major agricultural commodity, sugarcane is grown primarily in the Gulf Coast region.
- Livestock: Cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs are raised throughout Mexico, with the North and the Central Plateau being major production centers.
- Seafood: Mexico’s extensive coastline supports a thriving fishing industry, producing a wide range of seafood, including shrimp, tuna, and snapper.
Challenges Facing Mexican Agriculture:
Despite its rich agricultural heritage, Mexican agriculture faces several challenges:
- Climate Change: Increasing temperatures, erratic rainfall patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events pose significant threats to agricultural production.
- Water Scarcity: Many regions of Mexico experience water scarcity, particularly in the North and the Central Plateau, making irrigation a critical challenge.
- Soil Degradation: Decades of intensive farming practices have led to soil degradation, reducing soil fertility and productivity.
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in global commodity prices and trade policies can significantly impact the profitability of Mexican farmers.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Limited access to irrigation systems, transportation infrastructure, and agricultural technology hinders the growth of the sector.
The Importance of Mexican Agriculture:
Despite the challenges, Mexican agriculture remains a vital sector of the economy, contributing significantly to the nation’s food security, employment, and rural development:
- Food Security: Mexican agriculture provides food for millions of citizens, ensuring a steady supply of staple crops and essential nutrients.
- Economic Growth: The agricultural sector employs a significant portion of the workforce and contributes to national GDP.
- Rural Development: Agriculture plays a crucial role in supporting rural communities, providing livelihoods and stimulating economic activity in remote areas.
- Cultural Heritage: Agriculture is deeply intertwined with Mexican culture, shaping traditions, cuisine, and the country’s identity.
FAQs: Unveiling Insights into Mexico’s Agricultural Map
1. What are the major agricultural regions in Mexico?
Mexico’s agricultural map is divided into five distinct regions: the North, the Central Plateau, the Gulf Coast, the Pacific Coast, and the Yucatan Peninsula.
2. What are the key crops and commodities produced in Mexico?
Mexico produces a wide range of crops and commodities, including corn, beans, wheat, avocado, mango, coffee, sugarcane, livestock, and seafood.
3. What are the main challenges facing Mexican agriculture?
Mexican agriculture faces challenges such as climate change, water scarcity, soil degradation, market volatility, and a lack of infrastructure.
4. Why is Mexican agriculture important?
Mexican agriculture is vital for the country’s food security, economic growth, rural development, and cultural heritage.
5. What are some of the initiatives being taken to support Mexican agriculture?
The Mexican government is implementing programs to address challenges such as water conservation, soil health improvement, and access to technology.
Tips for Navigating the Mexican Agricultural Landscape:
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on the latest agricultural trends, market conditions, and policy developments.
- Embrace Technology: Utilize technology to improve farming practices, increase efficiency, and access new markets.
- Promote Sustainable Practices: Adopt sustainable farming methods to conserve resources and protect the environment.
- Support Local Farmers: Patronize local farmers’ markets and buy locally produced goods to support the agricultural sector.
- Invest in Research and Development: Encourage research and development to enhance agricultural productivity and address challenges.
Conclusion: A Future of Bounty and Sustainability
Mexico’s agricultural map is a testament to the resilience and resourcefulness of its people. Despite the challenges, the sector continues to play a vital role in the nation’s economy, food security, and cultural identity. By embracing innovation, promoting sustainable practices, and fostering collaboration, Mexico can ensure a future of agricultural bounty that benefits generations to come.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Look at Mexico’s Agricultural Landscape: Unveiling the Map of Bounty. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!