Delving into the Mason-Dixon Line: A Historical and Geographical Divide
Related Articles: Delving into the Mason-Dixon Line: A Historical and Geographical Divide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Mason-Dixon Line: A Historical and Geographical Divide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Mason-Dixon Line: A Historical and Geographical Divide

The Mason-Dixon Line, a boundary etched onto the landscape of the United States, holds a unique place in American history. It transcends its role as a mere geographical marker, serving as a tangible symbol of a complex past, a dividing line between North and South, and a testament to the enduring influence of human endeavor.
Tracing the Line’s Origins:
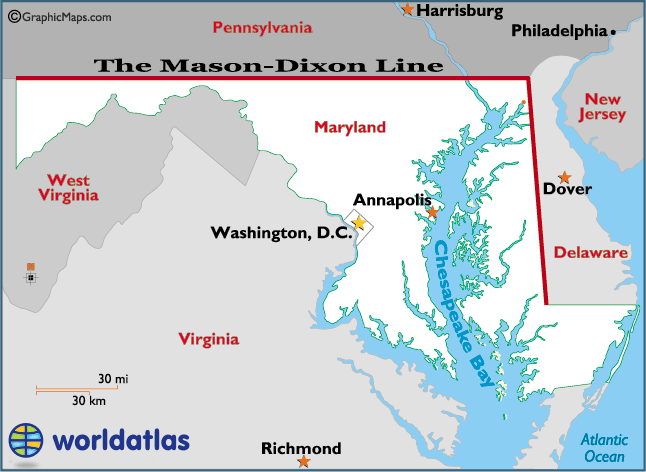
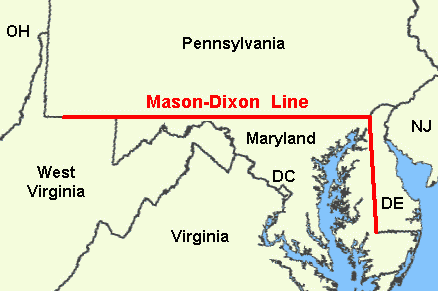
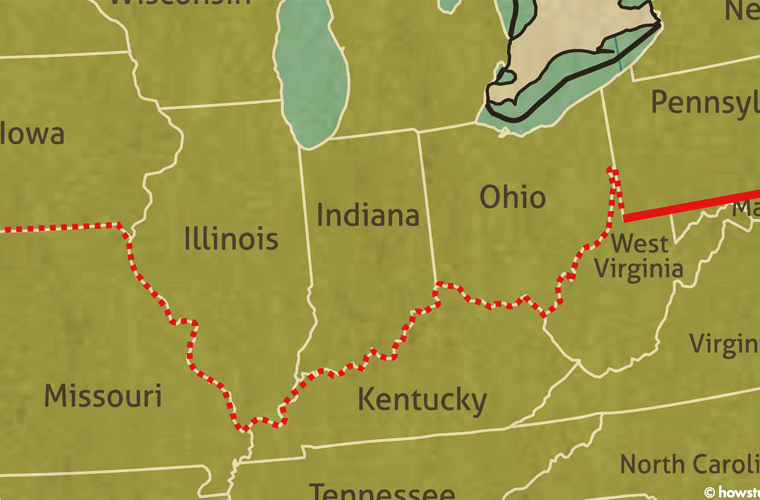
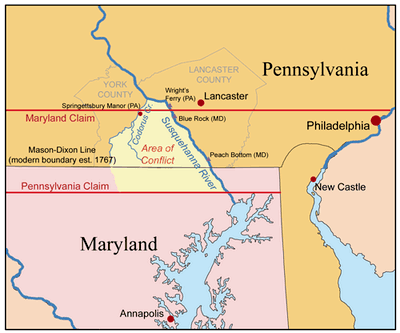
The Mason-Dixon Line originated in the 18th century as a result of a boundary dispute between the British colonies of Pennsylvania and Maryland. In 1763, Charles Mason and Jeremiah Dixon, two English surveyors, were commissioned to determine the precise location of the boundary between the two colonies. Their meticulous work, utilizing astronomical observations and rigorous surveying techniques, resulted in the creation of a line that extended 233 miles, starting at the Delaware River and running westward across the Appalachian Mountains.
The Line’s Significance:
The Mason-Dixon Line, established in 1767, became more than just a colonial border. It evolved into a symbolic dividing line between the North and South, reflecting the growing differences in culture, economy, and social values.
- The North: Above the line, the economy was largely based on industry and agriculture, with a strong emphasis on abolitionism and the growing movement against slavery.
- The South: Below the line, the economy was heavily reliant on plantation agriculture, primarily cotton, with a strong dependence on slave labor. This reliance on slavery fostered a deeply entrenched culture that defended the institution, leading to significant political and social tensions.
The Line’s Evolution:
The Mason-Dixon Line’s significance continued to grow as the United States matured. It became a focal point during the tumultuous period leading up to the Civil War, symbolizing the deep divisions between North and South. While the line itself did not cause the war, it served as a stark reminder of the growing chasm between the two regions.
Beyond the Civil War:
The Mason-Dixon Line remained a significant marker even after the Civil War, serving as a reminder of the nation’s fractured past. Although the line is no longer legally recognized as a boundary, its historical and cultural significance persists.
Understanding the Line’s Impact:
The Mason-Dixon Line’s enduring influence can be seen in various aspects of American life:
- Cultural Identity: The line continues to hold symbolic weight, often used to delineate regional differences in dialect, cuisine, and cultural practices.
- Political Landscape: The line’s historical significance continues to resonate in American politics, influencing voting patterns and political discourse.
- Literary and Artistic Expression: The Mason-Dixon Line has inspired numerous works of literature, art, and music, serving as a backdrop for exploring themes of division, reconciliation, and the complexities of American identity.
Mapping the Line:
The Mason-Dixon Line can be found on various maps, including:
- Historical Maps: Maps depicting the original 13 colonies and the early United States will typically include the Mason-Dixon Line.
- Modern Maps: While the line is not a formal boundary, it is often included on modern maps as a historical reference point.
- Online Mapping Tools: Websites like Google Maps and ArcGIS offer interactive maps that allow users to view the Mason-Dixon Line’s path.
FAQs about the Mason-Dixon Line:
1. Where is the Mason-Dixon Line located geographically?
The Mason-Dixon Line runs for 233 miles, starting at the Delaware River and extending westward across the Appalachian Mountains. It passes through parts of Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware, and West Virginia.
2. Is the Mason-Dixon Line still a legal boundary?
No, the Mason-Dixon Line is no longer a legally recognized boundary. It was primarily a colonial boundary and has been superseded by modern state borders.
3. Why is the Mason-Dixon Line important?
The Mason-Dixon Line holds significant historical and cultural importance. It served as a dividing line between North and South during the pre-Civil War era, reflecting the growing differences between the two regions. It continues to serve as a symbol of division and reconciliation in American history.
4. What states does the Mason-Dixon Line pass through?
The Mason-Dixon Line passes through parts of Pennsylvania, Maryland, Delaware, and West Virginia.
5. What is the significance of the Mason-Dixon Line in relation to slavery?
The Mason-Dixon Line became a symbolic dividing line between free states in the North and slave states in the South. This division played a significant role in the escalation of tensions leading up to the Civil War.
Tips for Understanding the Mason-Dixon Line:
- Consult historical maps: Examine maps from the 18th and 19th centuries to visualize the line’s original context and its significance in the context of colonial boundaries.
- Explore historical resources: Read about the lives and experiences of people who lived along the Mason-Dixon Line during different historical periods.
- Visit historical sites: Explore locations along the Mason-Dixon Line, such as the Mason-Dixon Line Monument in Maryland, to gain a deeper understanding of its historical significance.
- Engage with contemporary discussions: Participate in discussions about the enduring legacy of the Mason-Dixon Line in modern society, including its role in understanding regional differences and the complexities of American history.
Conclusion:
The Mason-Dixon Line, a product of colonial surveying and a symbol of historical division, remains a powerful reminder of the complexities of American history. It serves as a testament to the enduring influence of human endeavor, the impact of geographical boundaries, and the enduring legacy of a nation grappling with its past. Understanding the Mason-Dixon Line’s history and significance provides valuable insights into the evolution of the United States, its cultural landscape, and the ongoing conversation about identity and division.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1279px-1864_Johnsons_Map_of_Maryland_and_Delaware_-_Geographicus_-_DEMD-j-64-5c44f8c046e0fb00019310dd.jpg)



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Mason-Dixon Line: A Historical and Geographical Divide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!