Exploring Florida’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geographic Regions
Related Articles: Exploring Florida’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geographic Regions
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Exploring Florida’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geographic Regions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring Florida’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geographic Regions
Florida, the Sunshine State, is renowned for its diverse landscape, encompassing everything from pristine beaches and lush wetlands to sprawling forests and vast agricultural fields. Understanding the geographic regions of Florida provides a deeper appreciation for its unique ecosystems, cultural heritage, and economic activities. This comprehensive guide delves into the state’s diverse regions, offering insights into their defining characteristics, notable features, and the factors that make each area unique.
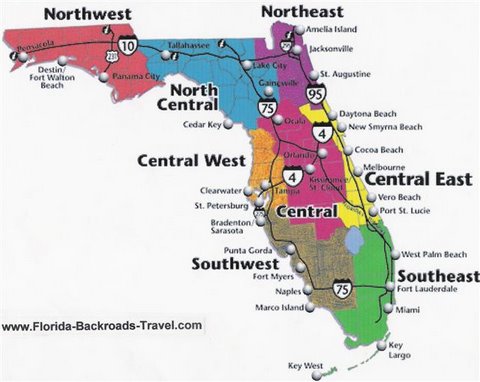
1. The Panhandle:
The Florida Panhandle, nestled along the Gulf Coast in the northwestern part of the state, is a region of rolling hills, coastal plains, and abundant natural resources. Characterized by its proximity to the Gulf of Mexico, the Panhandle boasts pristine beaches, picturesque coastal towns, and a rich history rooted in maritime traditions.
Key Features:
- Coastal Beaches: The Panhandle’s coastline is adorned with sugar-white sand beaches, offering tranquil escapes and opportunities for water sports.
- Emerald Coast: Renowned for its emerald-green waters, the Panhandle’s coastline is a popular destination for swimming, sunbathing, and fishing.
- Natural Resources: The region is rich in natural resources, including timber, seafood, and oil and gas deposits.
- Historical Significance: The Panhandle holds a significant place in Florida’s history, with its role in the Civil War and the development of Pensacola as a major port.
2. The Big Bend:
Stretching along the northern coast of the state, the Big Bend region is a transition zone between the Panhandle’s coastal plains and the central Florida peninsula. Known for its diverse ecosystems, the Big Bend offers a unique blend of coastal beauty, inland forests, and agricultural lands.
Key Features:
- Apalachicola Bay: A vast estuary, Apalachicola Bay is a vital ecosystem for numerous species, including oysters, shrimp, and redfish.
- Tallahassee: The state capital, Tallahassee, is a center for government, education, and culture.
- Agricultural Lands: The Big Bend region is home to extensive agricultural lands, particularly for cotton, peanuts, and cattle.
- Riverine Landscapes: The region’s rivers, including the Apalachicola and the Suwannee, offer scenic beauty and recreational opportunities.
3. North Central Florida:
Located in the heart of the state, North Central Florida is a region of rolling hills, freshwater springs, and dense forests. This area is known for its natural beauty, vibrant agricultural industry, and historical significance.
Key Features:
- Ocala National Forest: A vast expanse of protected wilderness, the Ocala National Forest is home to numerous springs, lakes, and hiking trails.
- Silver Springs: A world-renowned attraction, Silver Springs is a crystal-clear spring that flows into a network of underground caves.
- Agricultural Hub: North Central Florida is a major agricultural center, producing citrus, cattle, and other crops.
- Historical Sites: The region boasts numerous historical sites, including the Ocala Historic District and the Fort King National Historic Landmark.
4. Central Florida:
The heart of Florida, Central Florida is a diverse region encompassing the Orlando metropolitan area, the Space Coast, and the Kissimmee Chain of Lakes. This area is renowned for its theme parks, space exploration, and natural beauty.
Key Features:
- Orlando Theme Parks: Home to world-famous theme parks, including Walt Disney World, Universal Studios, and SeaWorld, Orlando is a global tourist destination.
- Space Coast: Located on the Atlantic coast, the Space Coast is home to the Kennedy Space Center, a hub for space exploration.
- Kissimmee Chain of Lakes: A series of interconnected lakes, the Kissimmee Chain of Lakes offers opportunities for boating, fishing, and water sports.
- Agricultural Production: Central Florida is a significant producer of citrus, vegetables, and other agricultural products.
5. South Central Florida:
Located south of Orlando, South Central Florida is a region of diverse ecosystems, including wetlands, forests, and agricultural lands. This area is known for its natural beauty, its vibrant agricultural industry, and its proximity to major metropolitan areas.
Key Features:
- Everglades National Park: A vast expanse of wetlands, Everglades National Park is a UNESCO World Heritage Site and a haven for diverse wildlife.
- Citrus Production: South Central Florida is a major citrus-producing region, with groves spanning across the landscape.
- Agricultural Lands: The region also produces a variety of other crops, including vegetables, sugarcane, and cattle.
- Proximity to Major Cities: South Central Florida is located within a short distance of major cities like Orlando, Tampa, and Miami, offering convenient access to urban amenities.
6. Southwest Florida:
Located on the Gulf Coast, Southwest Florida is a region of pristine beaches, coastal wetlands, and diverse ecosystems. This area is known for its laid-back atmosphere, its abundance of wildlife, and its thriving tourism industry.
Key Features:
- Gulf Coast Beaches: Southwest Florida boasts some of the most beautiful beaches in the state, with white sand, clear waters, and abundant marine life.
- Everglades National Park: The southern portion of Everglades National Park extends into Southwest Florida, offering opportunities to explore its unique ecosystem.
- Wildlife Sanctuaries: The region is home to numerous wildlife sanctuaries, including the Rookery Bay National Estuarine Research Reserve and the Corkscrew Swamp Sanctuary.
- Tourism Hub: Southwest Florida is a popular tourist destination, with cities like Naples, Fort Myers, and Sarasota offering a range of attractions and activities.
7. Southeast Florida:
Located on the Atlantic coast, Southeast Florida is a region of bustling cities, pristine beaches, and diverse ecosystems. This area is known for its vibrant culture, its thriving economy, and its diverse population.
Key Features:
- Miami-Dade County: Home to Miami, the region’s largest city, Southeast Florida is a cultural and economic hub.
- Palm Beach County: Known for its luxurious resorts and pristine beaches, Palm Beach County is a popular destination for tourists and residents alike.
- Broward County: Home to Fort Lauderdale, Broward County is a major center for tourism, business, and entertainment.
- Everglades National Park: The northern portion of Everglades National Park extends into Southeast Florida, offering a glimpse into the region’s unique ecosystem.
8. Florida Keys:
An archipelago of islands extending south from the mainland, the Florida Keys are a unique region characterized by their tropical climate, turquoise waters, and abundant marine life.
Key Features:
- Coral Reefs: The Florida Keys are home to the third-largest barrier reef in the world, a vibrant ecosystem teeming with marine life.
- Key West: The southernmost city in the United States, Key West is a popular destination for its laid-back atmosphere, its vibrant nightlife, and its historical significance.
- Fishing and Diving: The Florida Keys are renowned for their excellent fishing and diving opportunities, attracting enthusiasts from around the world.
- Tropical Climate: The Keys enjoy a tropical climate with warm temperatures and abundant sunshine year-round.
The Importance of Understanding Florida’s Geographic Regions:
Understanding the geographic regions of Florida is crucial for a variety of reasons:
- Environmental Conservation: Recognizing the unique characteristics of each region is essential for effective environmental conservation efforts, ensuring the protection of diverse ecosystems and natural resources.
- Economic Development: Understanding the strengths and challenges of each region is vital for informed economic development strategies, promoting sustainable growth and job creation.
- Cultural Understanding: Each region possesses its own unique cultural heritage, shaped by its history, environment, and people. Appreciating these differences fosters a deeper understanding of Florida’s diverse cultural landscape.
- Tourism and Recreation: Knowledge of Florida’s geographic regions empowers visitors to choose destinations that align with their interests, ensuring enjoyable and enriching experiences.
FAQs about Florida’s Geographic Regions:
1. What are the major geographic regions of Florida?
Florida can be divided into eight distinct geographic regions: the Panhandle, the Big Bend, North Central Florida, Central Florida, South Central Florida, Southwest Florida, Southeast Florida, and the Florida Keys.
2. What are some of the key features of each region?
Each region has its own unique characteristics, including coastal beaches, freshwater springs, forests, wetlands, agricultural lands, and urban centers.
3. What are the major industries in each region?
Florida’s industries vary by region, with tourism, agriculture, manufacturing, and technology playing significant roles in different areas.
4. How does the climate vary across Florida’s regions?
Florida’s climate is generally subtropical, but there are regional variations. The Panhandle experiences a more humid subtropical climate, while the Keys enjoy a tropical climate.
5. What are some of the cultural differences between Florida’s regions?
Florida’s regions have distinct cultural identities shaped by their history, environment, and people. The Panhandle is known for its Southern hospitality, while Miami is a melting pot of diverse cultures.
Tips for Exploring Florida’s Geographic Regions:
- Research Your Interests: Before planning a trip, identify the regions that align with your interests, whether it’s pristine beaches, wildlife viewing, or cultural experiences.
- Embrace the Diversity: Florida’s regions offer a wide range of experiences. Embrace the diversity and explore different areas to gain a deeper appreciation for the state’s unique character.
- Respect the Environment: Florida’s ecosystems are fragile. Practice responsible tourism by following Leave No Trace principles and supporting eco-friendly businesses.
- Learn from the Locals: Engage with local communities to gain insights into their culture, history, and perspectives.
- Enjoy the Journey: Florida’s geographic regions offer a wealth of opportunities for exploration and discovery. Embrace the journey and create lasting memories.
Conclusion:
Florida’s geographic regions are a testament to the state’s diverse landscape, rich history, and vibrant culture. By understanding the unique characteristics of each region, we can appreciate the intricate tapestry of Florida’s geography and the factors that shape its identity. From the pristine beaches of the Panhandle to the bustling cities of Southeast Florida, each region offers its own unique charm and allure, inviting visitors to explore and discover the wonders of the Sunshine State.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring Florida’s Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to its Geographic Regions. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!