Exploring the High Altitude Wilderness: A Guide to Alpine Tundra Maps
Related Articles: Exploring the High Altitude Wilderness: A Guide to Alpine Tundra Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Exploring the High Altitude Wilderness: A Guide to Alpine Tundra Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Exploring the High Altitude Wilderness: A Guide to Alpine Tundra Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Exploring the High Altitude Wilderness: A Guide to Alpine Tundra Maps
- 3.1 Unveiling the Landscape: The Importance of Alpine Tundra Maps
- 3.2 Constructing the Maps: A Symphony of Data and Technology
- 3.3 Deciphering the Maps: A Guide to Interpretation
- 3.4 The Benefits of Alpine Tundra Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
- 3.5 FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Alpine Tundra Maps
- 3.6 Tips for Using Alpine Tundra Maps Effectively
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Window into the High Altitude World
- 4 Closure
Exploring the High Altitude Wilderness: A Guide to Alpine Tundra Maps

The alpine tundra, a harsh yet captivating ecosystem, stretches across the world’s highest mountain ranges, painting a vibrant tapestry of life against a backdrop of snow-capped peaks. Understanding the geography and distribution of this unique environment is crucial for conservation, research, and appreciating its ecological significance. This article delves into the world of alpine tundra maps, exploring their construction, interpretation, and the valuable insights they provide.
Unveiling the Landscape: The Importance of Alpine Tundra Maps
Alpine tundra maps serve as essential tools for navigating the high-altitude wilderness, understanding its diverse features, and tracking its delicate balance. They provide a visual representation of:
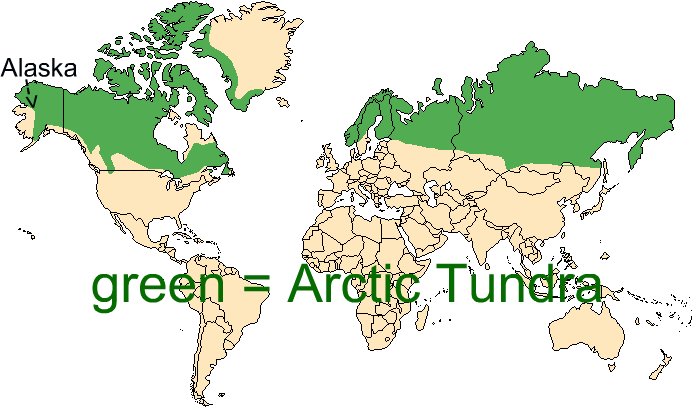
- Geographic Boundaries: Maps clearly delineate the boundaries of the alpine tundra, highlighting its distribution across mountain ranges and continents. This information is vital for understanding the extent and connectivity of this ecosystem.
- Elevation and Topography: Alpine tundra maps often feature elevation contours and topographic features, revealing the rugged and challenging terrain of the high mountains. This information is critical for planning expeditions, assessing ecological conditions, and studying the impact of climate change.
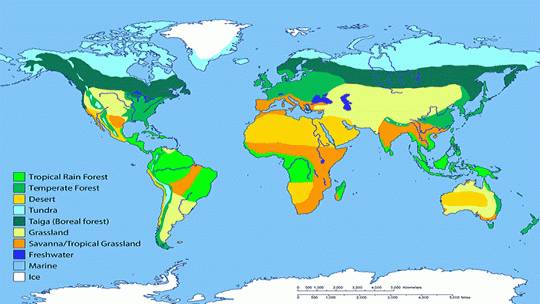
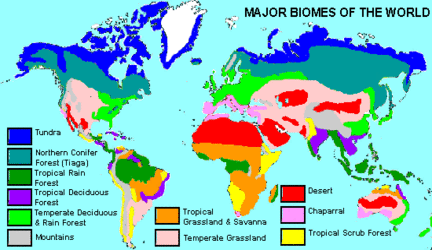
- Vegetation Zones: The maps depict the distribution of various plant communities within the alpine tundra, showcasing the distinct vegetation zones that adapt to different altitudes and microclimates. This allows researchers to track plant diversity, assess the impact of human activities, and monitor the health of these fragile ecosystems.
- Wildlife Habitat: Maps can highlight key wildlife habitats within the alpine tundra, identifying areas of high biodiversity and crucial breeding grounds for endangered species. This information is crucial for conservation efforts, ensuring the survival of these unique and often vulnerable animals.
- Climate Data: Some alpine tundra maps incorporate climate data, including average temperatures, precipitation patterns, and frost-free periods. This information provides crucial insights into the environmental conditions that shape the ecosystem and influence its resilience to climate change.
Constructing the Maps: A Symphony of Data and Technology
The creation of accurate alpine tundra maps involves a complex interplay of data collection, analysis, and visualization. Key steps include:
- Remote Sensing: Satellites and aerial photography provide high-resolution images of the terrain, capturing vegetation patterns, land cover, and topographic features. This data forms the foundation for map creation.
- Field Surveys: Ground-based observations and measurements supplement remote sensing data, providing detailed information on vegetation types, soil conditions, and the presence of specific species. This ensures the accuracy and reliability of the maps.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software is used to integrate and analyze the collected data, generating detailed maps that highlight key features and patterns within the alpine tundra.
- Map Projections: Choosing the appropriate map projection is essential for ensuring accurate representation of the terrain and minimizing distortion.
Deciphering the Maps: A Guide to Interpretation
To effectively utilize alpine tundra maps, understanding their key elements and symbols is crucial:
- Legend: The legend explains the meaning of different colors, symbols, and patterns used on the map, providing a key to understanding the information presented.
- Scale: The scale indicates the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground. Understanding the scale allows for accurate measurements and estimations.
- North Arrow: The north arrow indicates the direction of north, crucial for orientation and navigation.
- Contours: Contour lines connect points of equal elevation, providing a visual representation of the terrain’s shape and slope.
- Symbols: Different symbols represent specific features such as vegetation types, water bodies, settlements, and wildlife habitats.
The Benefits of Alpine Tundra Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
Alpine tundra maps offer a multitude of benefits, supporting various endeavors:
- Scientific Research: Maps provide a framework for studying the ecosystem’s structure, function, and response to climate change. Researchers use them to track vegetation changes, assess habitat suitability for wildlife, and monitor the impact of human activities.
- Conservation Planning: Maps highlight areas of high biodiversity, critical habitats, and vulnerable ecosystems, guiding conservation efforts and ensuring the protection of these precious resources.
- Outdoor Recreation: Hikers, climbers, and other outdoor enthusiasts rely on maps for navigation, identifying trails, and understanding the terrain. They also help to minimize environmental impact by promoting responsible recreation.
- Education and Awareness: Maps serve as powerful tools for educating the public about the importance of alpine tundra ecosystems, their unique characteristics, and the threats they face. This fosters a greater appreciation for these fragile environments and encourages responsible stewardship.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Alpine Tundra Maps
Q: What are the most common types of alpine tundra maps?
A: Alpine tundra maps can be categorized based on their purpose and level of detail. Common types include:
- Topographic Maps: These maps focus on the terrain’s elevation, slope, and features. They are useful for navigation, planning expeditions, and studying the impact of climate change on landforms.
- Vegetation Maps: These maps depict the distribution of different plant communities within the alpine tundra. They are valuable for understanding plant diversity, assessing habitat quality, and monitoring the effects of human activities.
- Wildlife Habitat Maps: These maps highlight areas of high biodiversity and crucial breeding grounds for wildlife. They are essential for conservation efforts and ensuring the survival of endangered species.
- Climate Maps: These maps incorporate climate data, such as average temperatures, precipitation patterns, and frost-free periods. They provide insights into the environmental conditions that shape the ecosystem and influence its resilience to climate change.
Q: How can I access alpine tundra maps?
A: Alpine tundra maps are available from various sources:
- Government Agencies: Organizations like the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the National Park Service (NPS) offer maps of specific regions and parks.
- Research Institutions: Universities and research centers often publish maps as part of their research findings, accessible through online databases and publications.
- Online Mapping Services: Websites like Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, and ArcGIS Online provide interactive maps that can be customized to display various geographic features, including alpine tundra areas.
- Outdoor Recreation Companies: Companies specializing in outdoor recreation often offer maps of popular hiking and climbing destinations, including alpine tundra regions.
Q: What are the limitations of alpine tundra maps?
A: While alpine tundra maps provide valuable information, they also have limitations:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of maps depends on the quality and availability of data. Remote sensing data can be affected by cloud cover and atmospheric conditions, while field surveys may be limited by accessibility and time constraints.
- Map Scale: Large-scale maps may lack detailed information, while small-scale maps may not provide sufficient detail for specific research or conservation purposes.
- Dynamic Ecosystems: Alpine tundra ecosystems are constantly changing due to climate change, natural disturbances, and human activities. Maps may not reflect these dynamic processes, requiring periodic updates and new data collection.
Tips for Using Alpine Tundra Maps Effectively
- Choose the Right Map: Select a map appropriate for your purpose, considering the scale, level of detail, and type of information needed.
- Understand the Legend: Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend to interpret the symbols, colors, and patterns used.
- Consider the Scale: Be aware of the map’s scale to accurately estimate distances and plan your activities.
- Use GPS Technology: Integrate GPS technology with your map for accurate navigation and tracking your location.
- Respect the Environment: Use maps responsibly, minimizing your impact on the fragile alpine tundra ecosystem.
Conclusion: A Window into the High Altitude World
Alpine tundra maps serve as invaluable tools for understanding, exploring, and protecting these unique and delicate ecosystems. They provide a visual representation of the terrain, vegetation, wildlife, and climate conditions, guiding research, conservation efforts, and outdoor recreation. As we continue to face the challenges of climate change and human impact on the environment, the use of accurate and up-to-date alpine tundra maps becomes increasingly crucial for safeguarding these valuable landscapes for future generations.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the High Altitude Wilderness: A Guide to Alpine Tundra Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!