Navigating the Terrain: Deciphering Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: Deciphering Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Terrain: Deciphering Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the Terrain: Deciphering Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the Terrain: Deciphering Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps
- 3.1 Understanding Latitude and Longitude
- 3.2 Identifying Latitude and Longitude on a Topographic Map
- 3.3 Navigating with Latitude and Longitude
- 3.4 Importance of Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Reading Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps
- 3.6 FAQs about Reading Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the Terrain: Deciphering Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps
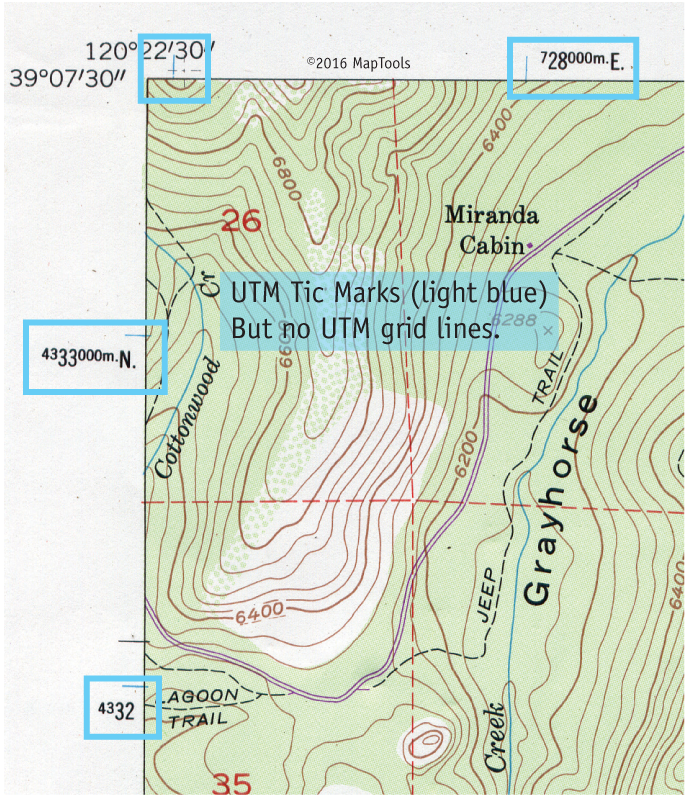
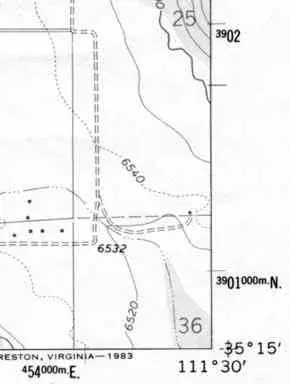
Topographic maps, with their intricate lines and symbols, offer a detailed representation of the Earth’s surface, providing crucial information for hikers, adventurers, and researchers alike. Within this intricate tapestry of data lies a fundamental coordinate system: latitude and longitude. Understanding how to read these coordinates on a topographic map is essential for navigating the terrain accurately and efficiently.
Understanding Latitude and Longitude
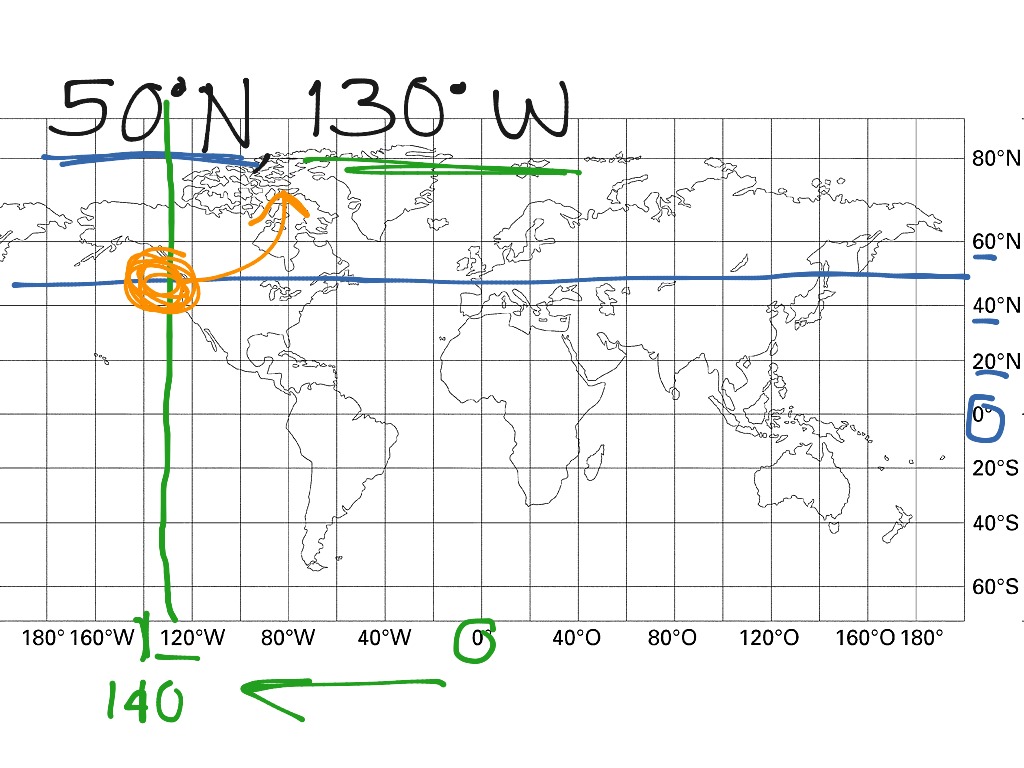
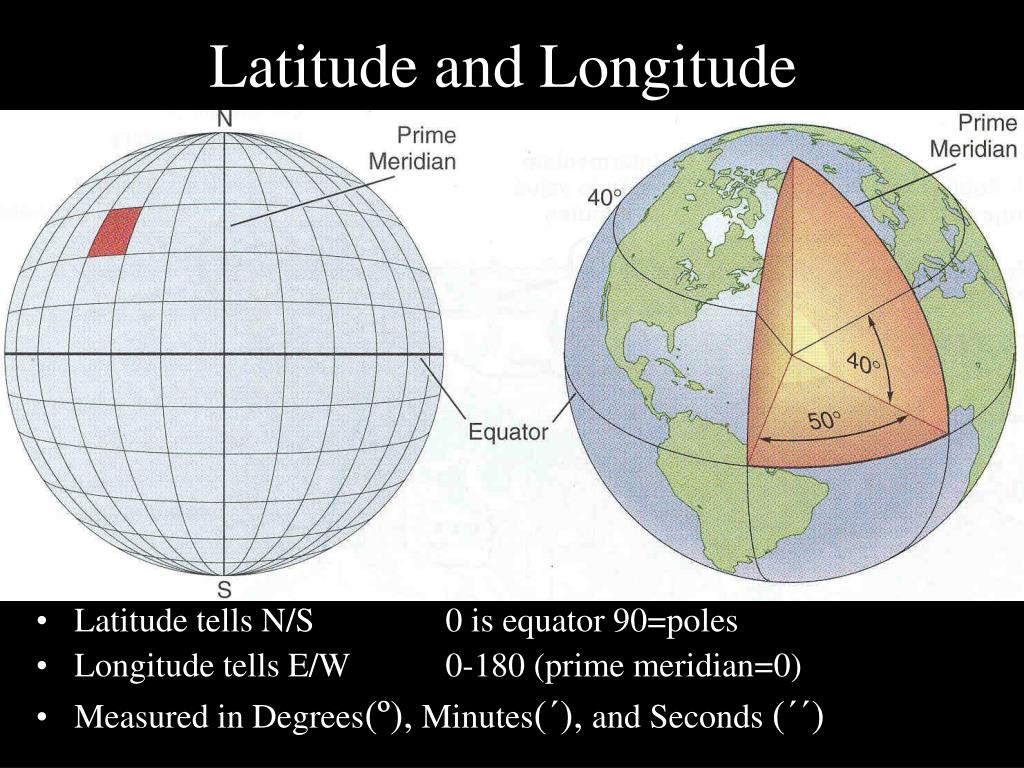
Latitude and longitude form a grid system that covers the entire Earth, allowing for the precise location of any point on the planet. Imagine a series of imaginary lines running horizontally around the Earth, parallel to the equator. These are lines of latitude, measured in degrees north or south of the equator. The equator itself is designated as 0 degrees latitude, while the North Pole is 90 degrees north and the South Pole is 90 degrees south.
Longitude lines, on the other hand, run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, intersecting the equator at right angles. These lines are measured in degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian, which passes through Greenwich, England. The Prime Meridian is designated as 0 degrees longitude, with lines extending eastward to 180 degrees and westward to 180 degrees.
Identifying Latitude and Longitude on a Topographic Map
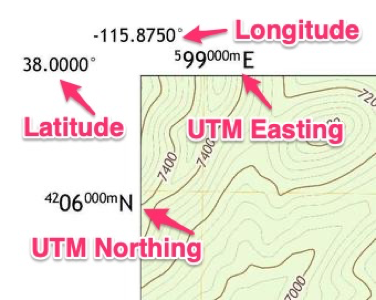
Topographic maps typically include a grid system that represents the latitude and longitude lines. This grid is often presented as a series of parallel lines, with numbers indicating the degrees of latitude and longitude. Here’s a breakdown of how to decipher these lines:
- Latitude Lines: Look for horizontal lines running across the map. The numbers printed along these lines indicate the degrees of latitude. These numbers typically increase as you move north on the map.
- Longitude Lines: Look for vertical lines running up and down the map. The numbers printed along these lines indicate the degrees of longitude. These numbers typically increase as you move east on the map.
Navigating with Latitude and Longitude
Once you’ve identified the latitude and longitude lines on the map, you can use them to pinpoint specific locations. Here’s how:
- Find the intersection: Locate the point on the map that corresponds to the desired location. Identify the latitude and longitude lines that intersect at this point.
- Read the coordinates: Read the values of latitude and longitude at the point of intersection. For example, if the point lies on the 40th degree latitude line and the 75th degree longitude line, its coordinates would be 40° N, 75° W.
Importance of Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps
The ability to read latitude and longitude on topographic maps is crucial for several reasons:
- Precise Location: Latitude and longitude provide a precise way to locate any point on the Earth’s surface, enabling accurate navigation and mapping.
- Understanding Terrain: By referencing latitude and longitude, hikers and explorers can accurately pinpoint their location within the complex topography represented on the map.
- Planning Routes: Latitude and longitude are essential for planning and plotting routes, ensuring efficient and safe travel through unfamiliar terrain.
- Sharing Location: These coordinates allow for easy communication of location information, crucial for rescue operations, emergency services, and collaborative projects.
Tips for Reading Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps
- Study the Map Legend: Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend to understand the symbols, scales, and coordinate system used.
- Practice with Familiar Locations: Start by practicing with known locations, such as your home or a nearby landmark, to build confidence in reading coordinates.
- Use a Ruler or Protractor: For more precise readings, use a ruler or protractor to measure distances and angles on the map.
- Consider the Map’s Projection: Different map projections distort distances and shapes in different ways. Be aware of the projection used for your map to ensure accurate readings.
FAQs about Reading Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps
Q: What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude lines run horizontally around the Earth, measuring degrees north or south of the equator. Longitude lines run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole, measuring degrees east or west of the Prime Meridian.
Q: How do I know which direction is north on a topographic map?
A: Most topographic maps have a north arrow, usually located in the top margin, indicating the direction of true north.
Q: What are the units of measurement for latitude and longitude?
A: Latitude and longitude are typically measured in degrees, with each degree further subdivided into minutes and seconds.
Q: What are the benefits of using latitude and longitude for navigation?
A: Latitude and longitude provide a precise and universally recognized system for pinpointing locations, enabling accurate navigation, route planning, and location sharing.
Q: Can I use a GPS device to find my location on a topographic map?
A: Yes, GPS devices provide accurate latitude and longitude readings, which can be used to locate your position on a topographic map.
Conclusion
Reading latitude and longitude on topographic maps is a fundamental skill for anyone navigating the outdoors. Understanding these coordinates allows for precise location identification, route planning, and safe exploration. By mastering the art of deciphering this grid system, individuals can unlock a world of possibilities, exploring the Earth’s diverse terrain with confidence and accuracy.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Terrain: Deciphering Latitude and Longitude on Topographic Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!