Navigating the Vast Network: An In-Depth Look at the US Railway System Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Vast Network: An In-Depth Look at the US Railway System Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Vast Network: An In-Depth Look at the US Railway System Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Vast Network: An In-Depth Look at the US Railway System Map

The United States boasts a sprawling network of railways, a vital artery for passenger and freight transportation. Understanding this intricate system is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate its vast expanse, whether for business, leisure, or simply out of curiosity. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the US railway system map, exploring its history, structure, key players, and the benefits it provides.
A Historical Perspective:
The foundation of the US railway system was laid in the 19th century, fueled by the need to connect burgeoning cities and facilitate westward expansion. The transcontinental railroad, completed in 1869, marked a pivotal moment, uniting the nation and paving the way for further development. The early 20th century saw the rise of powerful railroad companies, often operating in monopolies and facing government regulation.
Modern Structure and Key Players:
Today, the US railway system is a complex tapestry of private and public entities, each playing a distinct role in the overall network.
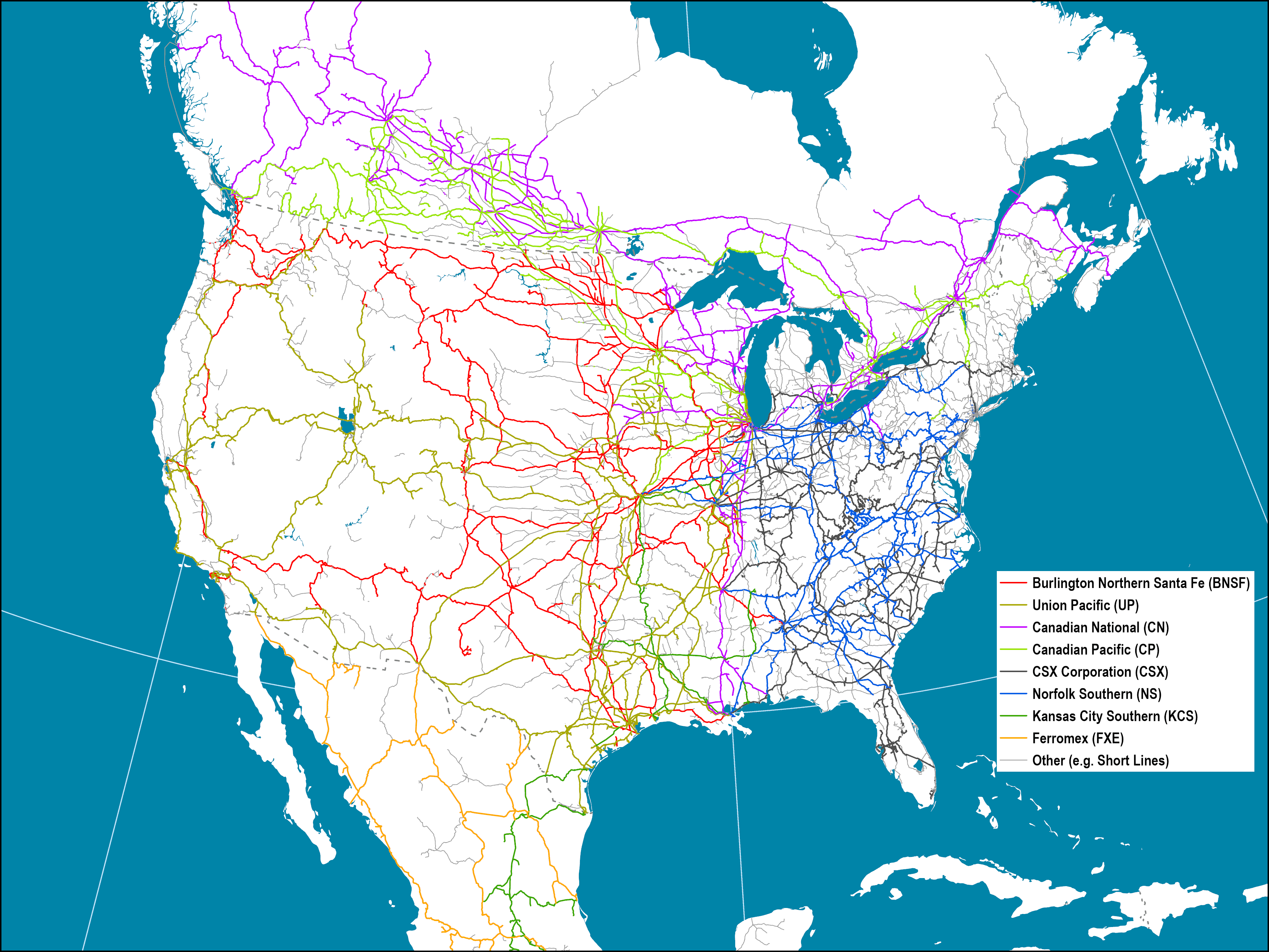
- Class I Railroads: These are the largest freight railroads, operating extensive networks across the country. Examples include Union Pacific, BNSF Railway, CSX Transportation, and Norfolk Southern Railway.
- Regional Railroads: Smaller in scale than Class I railroads, these companies serve specific regions, often connecting with larger lines.
- Short Line Railroads: These typically focus on short-distance freight transportation, connecting industries and communities.
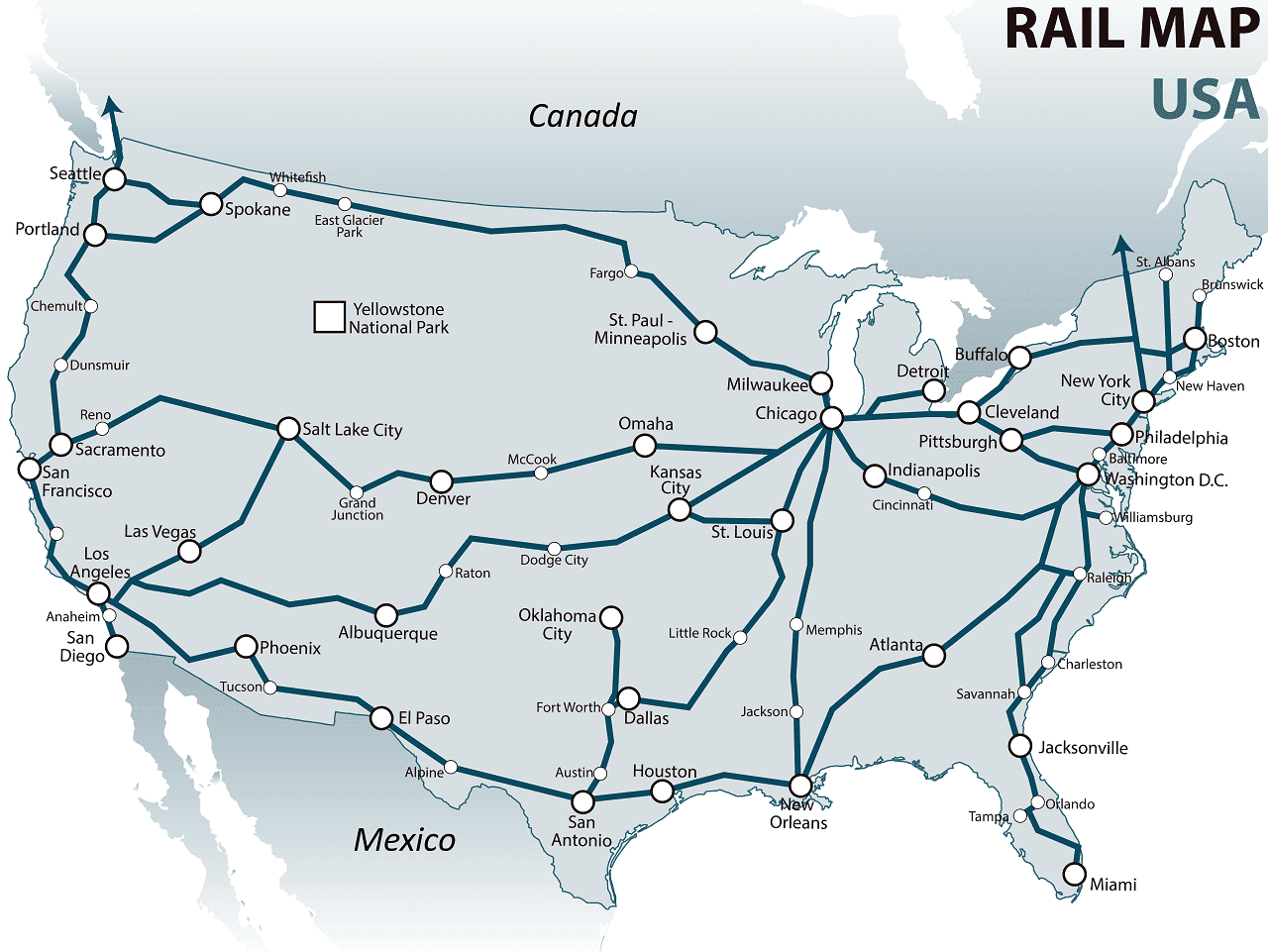
- Passenger Railroads: Amtrak, the national passenger railroad, operates intercity routes across the country, while commuter railroads provide service within metropolitan areas.
- Freight Forwarders: These companies arrange transportation for goods, often utilizing multiple railroads and other modes of transportation.
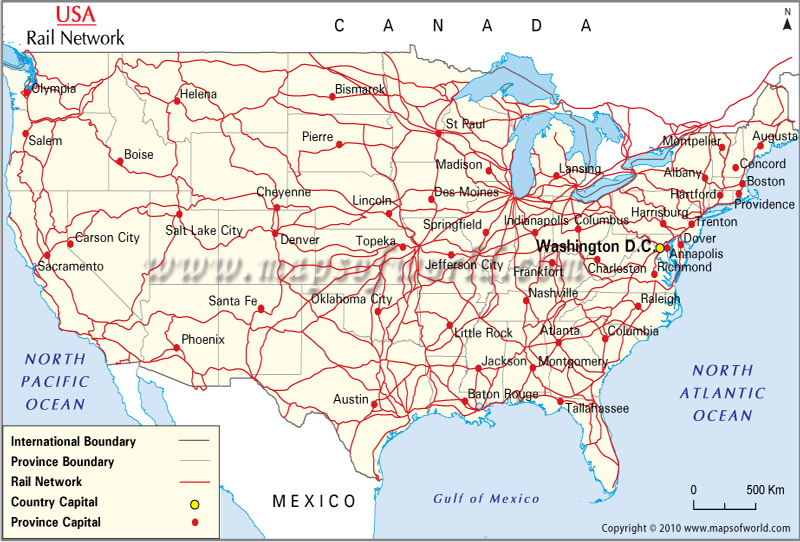
Understanding the Map:
The US railway system map is a valuable tool for visualizing the intricate network of tracks, stations, and connecting lines. It offers a comprehensive overview of:
- Major Rail Lines: The map highlights the primary rail lines, connecting major cities and industrial centers.
- Branch Lines: These lines extend from the main lines, serving smaller towns and industrial sites.
- Passenger Stations: The map pinpoints major passenger stations, facilitating travel planning.
- Freight Yards: These facilities handle the loading, unloading, and sorting of freight cars.
Benefits of the US Railway System:
The US railway system plays a crucial role in the nation’s economy and transportation infrastructure, offering numerous benefits:
- Efficient Freight Transportation: Railroads are highly efficient in transporting large volumes of goods over long distances, contributing significantly to the flow of goods and services.
- Reduced Road Congestion: By moving freight off of roads, railroads help reduce congestion and wear and tear on highways.
- Environmental Sustainability: Compared to trucking, railroads are more energy-efficient and produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
- Economic Development: Railroads stimulate economic growth by facilitating trade, connecting communities, and supporting industries.
- Accessibility for Passengers: Amtrak provides affordable and convenient passenger service, connecting cities and towns across the country.
Navigating the System:
For those planning to travel by rail, the US railway system map offers valuable insights:
- Route Planning: The map helps identify the most efficient routes between destinations, considering connections and travel times.
- Station Information: It provides information on station locations, amenities, and accessibility.
- Connecting Lines: The map highlights connections between different rail lines, facilitating multi-leg journeys.
FAQs about the US Railway System Map:
1. What are the major rail lines in the US?
The major rail lines in the US include the Union Pacific, BNSF Railway, CSX Transportation, and Norfolk Southern Railway lines. These lines traverse vast distances, connecting major cities and industrial centers.
2. How can I find a specific train route on the map?
Most railway system maps are interactive, allowing users to search for specific routes by entering starting and ending points. Some maps also provide detailed information on individual train lines, including schedules and station stops.
3. What are the benefits of using the railway system for freight transportation?
Railroads offer several advantages for freight transportation, including high efficiency for long distances, reduced road congestion, environmental sustainability, and cost-effectiveness.
4. How can I get a copy of the US railway system map?
Several online resources provide downloadable and interactive US railway system maps. Additionally, many rail companies offer maps specific to their lines and services.
5. How does the US railway system compare to other countries?
The US railway system is vast and extensive, but it is less developed for passenger travel compared to some European countries. However, the freight network is highly efficient and plays a crucial role in the nation’s economy.
Tips for Using the US Railway System Map:
- Familiarize yourself with the map’s legend: Understand the symbols and colors used to represent different features, such as rail lines, stations, and connections.
- Consider your travel needs: Determine whether you need to focus on passenger or freight routes, and identify the specific lines and stations relevant to your journey.
- Utilize online resources: Interactive maps and online tools can provide additional information, such as schedules, fares, and station amenities.
- Plan ahead: Allow ample time for your journey, especially if you are traveling long distances or making multiple connections.
- Stay informed: Check for any delays or disruptions before your trip, and be aware of any changes to schedules or routes.
Conclusion:
The US railway system map is an invaluable tool for navigating the intricate network of tracks and lines that connect the nation. Understanding its structure, key players, and benefits provides insights into the vital role railways play in transportation, commerce, and economic development. By utilizing the map and staying informed about the system, individuals and businesses can leverage the efficiency and sustainability of rail transportation, contributing to a more connected and prosperous nation.

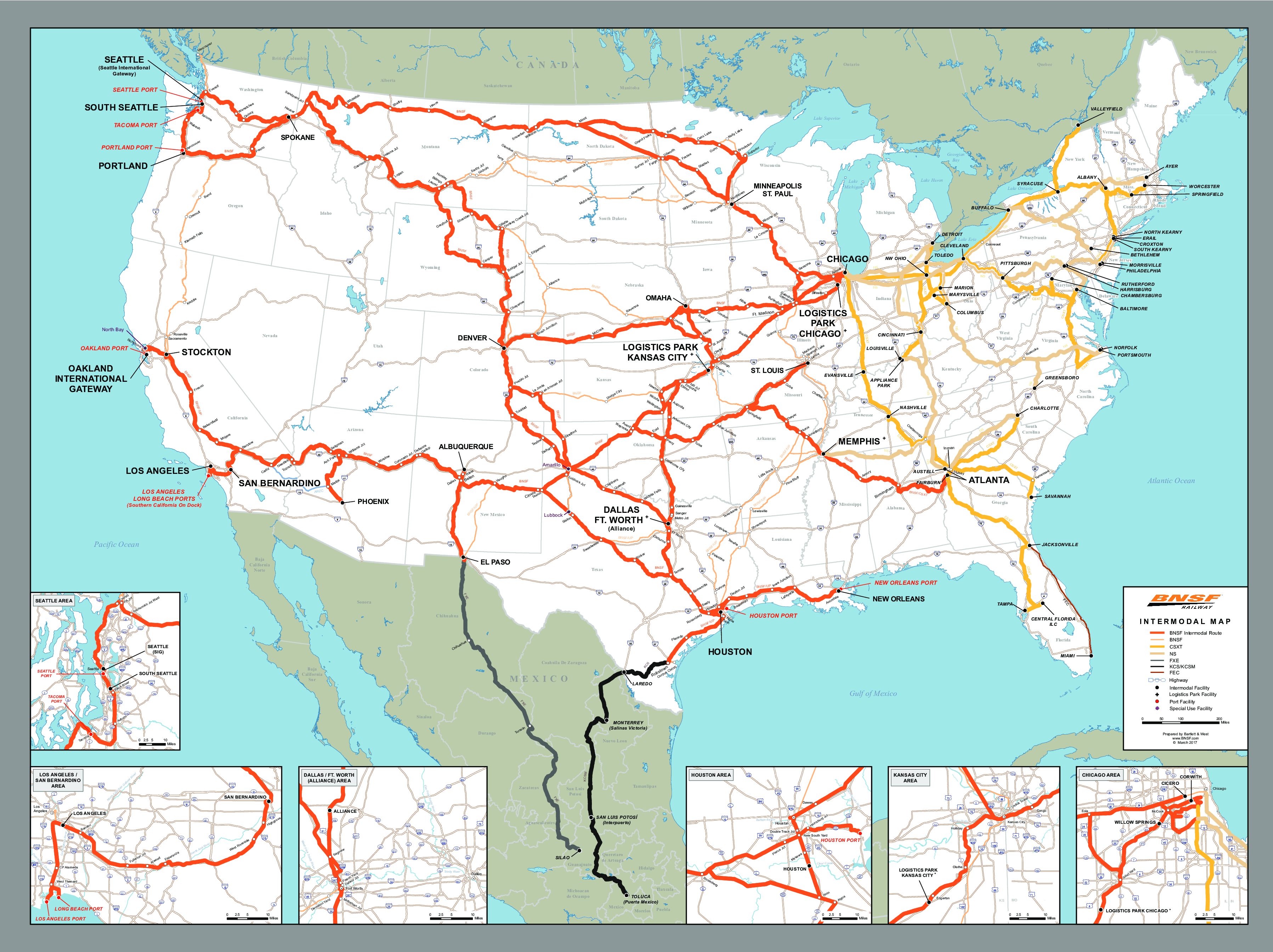
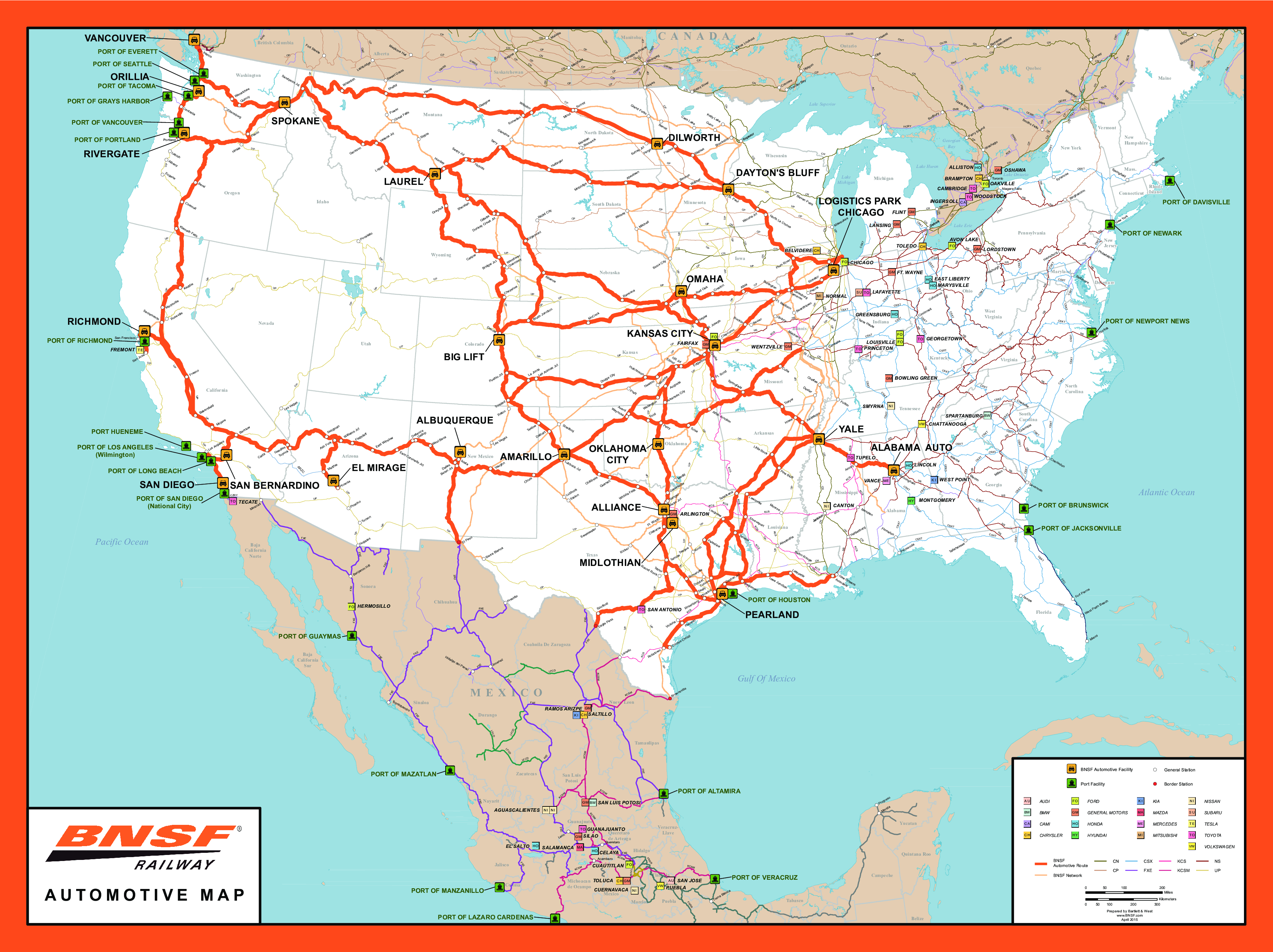
![[Map] Map of every passenger railway in the United States](https://external-preview.redd.it/KY77RSK1oOXoPbPV_K05eTgdlnivXVlWzT_OApYTvNA.jpg?auto=webpu0026s=ed29ec63fb7411f82790072439a6c6bdda79217e)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Vast Network: An In-Depth Look at the US Railway System Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!