Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude
- 3.1 The Grid of Latitude and Longitude
- 3.2 Understanding the Importance of Latitude and Longitude
- 3.3 The Evolution of Latitude and Longitude
- 3.4 Modern Applications of Latitude and Longitude
- 3.5 FAQs about Latitude and Longitude
- 3.6 Tips for Understanding Latitude and Longitude
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude

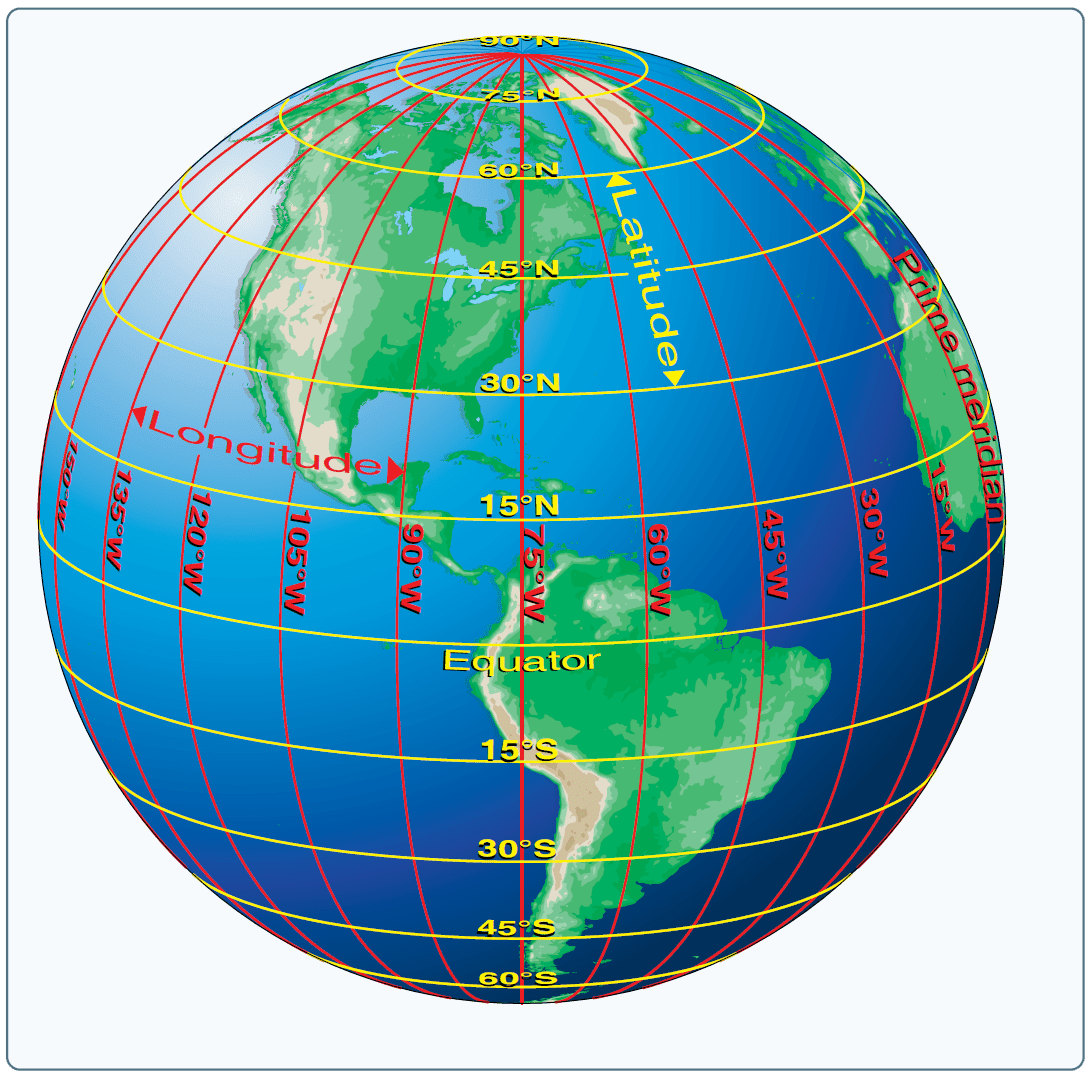
The Earth, a vast and complex sphere, has long been a subject of exploration and mapping. To effectively navigate its surface and pinpoint locations with precision, a system of coordinates was developed: latitude and longitude. This grid system, akin to a giant web woven across the globe, provides a universal language for describing any point on Earth, facilitating communication, exploration, and understanding of our planet.
The Grid of Latitude and Longitude
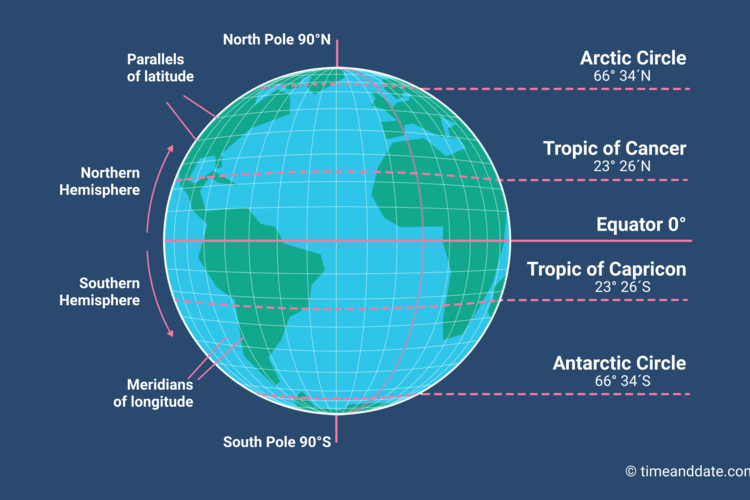
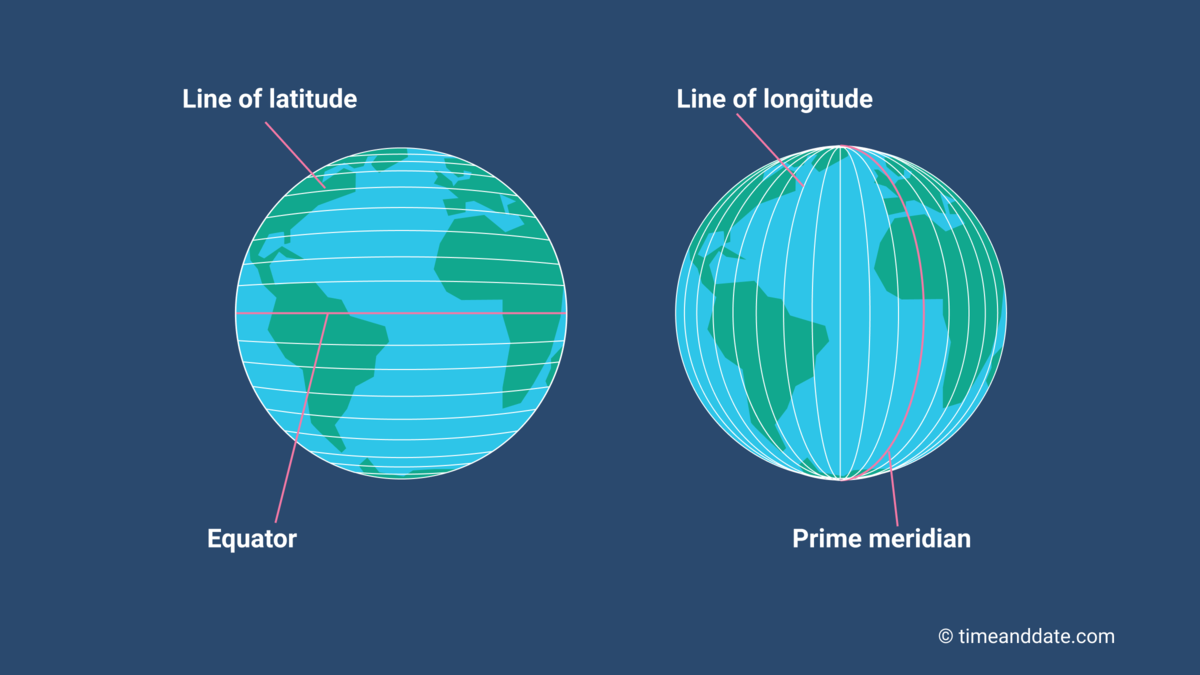
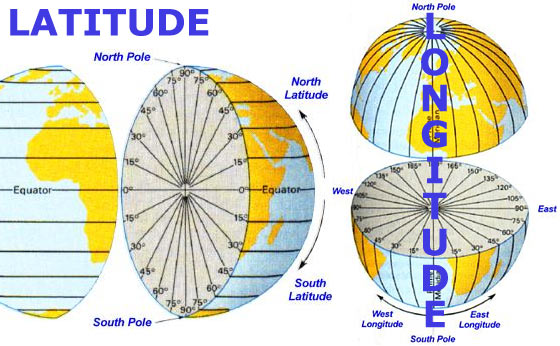
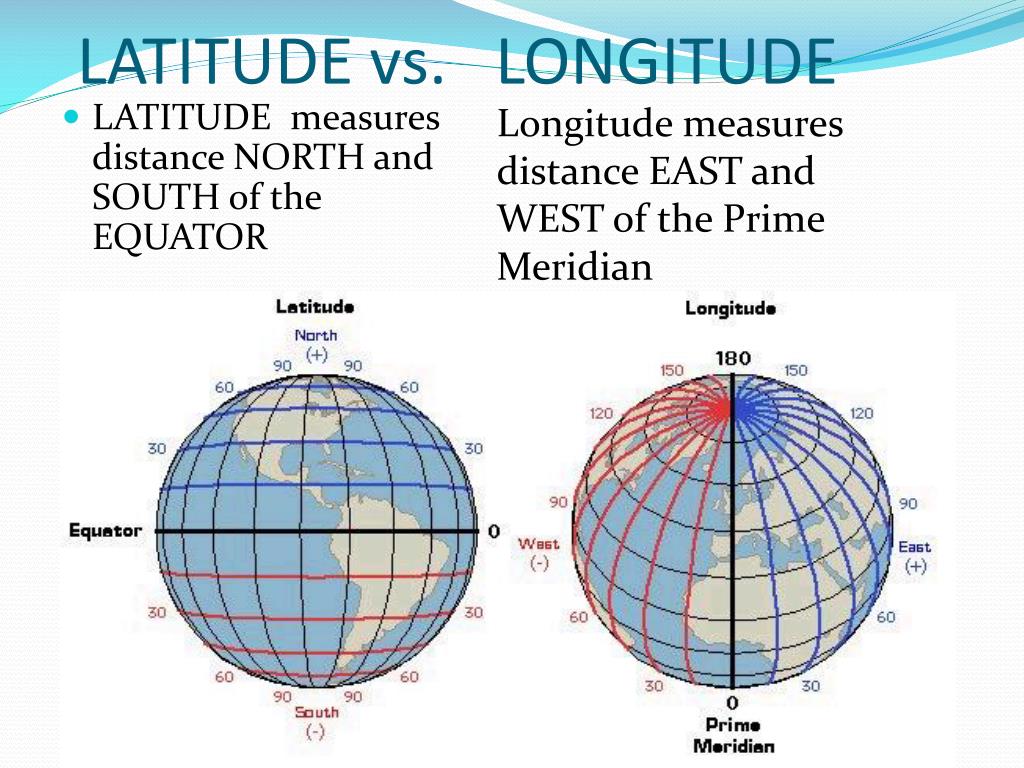
Latitude, often referred to as "parallels," are imaginary lines that run horizontally around the Earth, parallel to the equator. The equator, positioned at 0 degrees latitude, divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Latitude values range from 0 degrees at the equator to 90 degrees North at the North Pole and 90 degrees South at the South Pole.
Longitude, also known as "meridians," are imaginary lines that run vertically from the North Pole to the South Pole. The prime meridian, at 0 degrees longitude, passes through Greenwich, England. Longitude values range from 0 degrees at the prime meridian to 180 degrees East and 180 degrees West.
Together, latitude and longitude form a grid system that uniquely identifies every point on Earth. Each point is defined by its specific latitude and longitude coordinates, expressed in degrees, minutes, and seconds. For instance, the coordinates of the Eiffel Tower in Paris are 48°51′29″N 2°17′40″E.
Understanding the Importance of Latitude and Longitude
The global map with latitude and longitude serves as a fundamental tool for various applications, including:
- Navigation and Geolocation: Latitude and longitude are essential for navigation systems like GPS (Global Positioning System). They allow devices to pinpoint locations accurately, facilitating travel, mapping, and resource management.
- Mapping and Cartography: Geographers and cartographers rely heavily on latitude and longitude to create maps, charts, and atlases. These maps provide a visual representation of the Earth’s surface, aiding in understanding geographical features, population distribution, and resource allocation.
- Scientific Research: Latitude and longitude are crucial for scientific research, particularly in fields like meteorology, oceanography, and climate science. They enable scientists to track weather patterns, ocean currents, and climate changes, providing valuable data for analysis and prediction.
- International Communication and Collaboration: The universal language of latitude and longitude facilitates communication and collaboration across international borders. It allows researchers, explorers, and policymakers to share data and coordinate efforts effectively.
- Understanding Time Zones: Longitude plays a significant role in determining time zones. As the Earth rotates on its axis, different longitudes experience sunrise and sunset at different times. Time zones are established based on longitude, ensuring consistent timekeeping across the globe.
The Evolution of Latitude and Longitude
The concept of latitude and longitude dates back to ancient civilizations. The Greeks, particularly Eratosthenes, developed early methods for measuring the Earth’s circumference and establishing a grid system. However, it was the development of accurate clocks and astronomical observations in the 17th and 18th centuries that led to more precise measurements and the establishment of the prime meridian at Greenwich.
The invention of the sextant, a navigational instrument, further revolutionized the use of latitude and longitude. By measuring the angles of celestial bodies, sailors could determine their latitude and longitude at sea, enabling safer and more efficient voyages.
Modern Applications of Latitude and Longitude
Today, the global map with latitude and longitude is more integrated into our lives than ever before. From smartphones and navigation apps to satellite imagery and weather forecasts, latitude and longitude are the backbone of countless technologies and applications.
- GPS Navigation: GPS devices utilize latitude and longitude to pinpoint locations and provide directions. They work by receiving signals from satellites orbiting Earth, triangulating their position based on the time it takes for the signals to reach the device.
- Mapping and Geolocation Services: Online mapping services like Google Maps and Apple Maps rely on latitude and longitude to display locations, provide directions, and offer a wealth of information about specific places.
- Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists use latitude and longitude to track weather patterns, predict storms, and issue warnings. They analyze data from weather stations and satellites, which are positioned at specific latitude and longitude coordinates.
- Resource Management: Latitude and longitude are used to manage natural resources, track wildlife populations, and monitor environmental changes. They enable researchers to collect data from specific locations and analyze trends over time.
- Emergency Response: Latitude and longitude play a crucial role in emergency response, allowing first responders to locate incidents quickly and dispatch resources efficiently.
FAQs about Latitude and Longitude
1. What is the difference between latitude and longitude?
Latitude refers to the angular distance, measured in degrees, north or south of the equator. Longitude refers to the angular distance, measured in degrees, east or west of the prime meridian.
2. How are latitude and longitude used to locate a place?
Latitude and longitude form a grid system that uniquely identifies every point on Earth. Each point is defined by its specific latitude and longitude coordinates, expressed in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
3. What are the units of measurement for latitude and longitude?
Latitude and longitude are measured in degrees, minutes, and seconds. One degree is divided into 60 minutes, and one minute is divided into 60 seconds.
4. What is the significance of the equator and the prime meridian?
The equator is an imaginary line that circles the Earth at 0 degrees latitude, dividing it into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The prime meridian is an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole at 0 degrees longitude, passing through Greenwich, England.
5. How can I find the latitude and longitude of a specific location?
You can find the latitude and longitude of a specific location using online mapping services like Google Maps or Apple Maps. Simply enter the location name or address, and the service will display its coordinates.
6. What are some real-world applications of latitude and longitude?
Latitude and longitude are used in various applications, including navigation, mapping, scientific research, international communication, and emergency response.
7. How does latitude affect climate?
Latitude influences climate by affecting the amount of solar radiation received at different parts of the Earth. Locations closer to the equator receive more direct sunlight, resulting in warmer temperatures, while locations further away from the equator receive less direct sunlight, resulting in colder temperatures.
8. How does longitude affect time zones?
Longitude plays a significant role in determining time zones. As the Earth rotates on its axis, different longitudes experience sunrise and sunset at different times. Time zones are established based on longitude, ensuring consistent timekeeping across the globe.
9. What are some historical examples of the use of latitude and longitude?
The concept of latitude and longitude dates back to ancient civilizations. The Greeks, particularly Eratosthenes, developed early methods for measuring the Earth’s circumference and establishing a grid system. Sailors used sextants to determine their latitude and longitude at sea, enabling safer and more efficient voyages.
10. What are some future trends in the use of latitude and longitude?
With the advancements in technology, latitude and longitude are expected to play an even more crucial role in our lives. They will continue to be essential for navigation, mapping, resource management, and various other applications.
Tips for Understanding Latitude and Longitude
- Visualize the Earth as a sphere: Imagine a globe with lines drawn across it, representing latitude and longitude.
- Remember the equator and the prime meridian: These are the reference lines for latitude and longitude.
- Practice converting degrees, minutes, and seconds: This will help you understand how latitude and longitude are expressed.
- Use online mapping services: Explore the features of mapping services like Google Maps and Apple Maps to visualize how latitude and longitude are used.
- Explore the history of latitude and longitude: Understanding its evolution will enhance your appreciation for its significance.
Conclusion
The global map with latitude and longitude is a testament to human ingenuity and our desire to understand and navigate the world. This fundamental system of coordinates has revolutionized exploration, communication, and our understanding of the Earth. As technology continues to advance, latitude and longitude will remain an indispensable tool for navigating our planet and shaping our future.


![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the World: Understanding Latitude and Longitude. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!