The 1952 Presidential Election: A Map of Shifting Political Tides
Related Articles: The 1952 Presidential Election: A Map of Shifting Political Tides
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The 1952 Presidential Election: A Map of Shifting Political Tides. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The 1952 Presidential Election: A Map of Shifting Political Tides
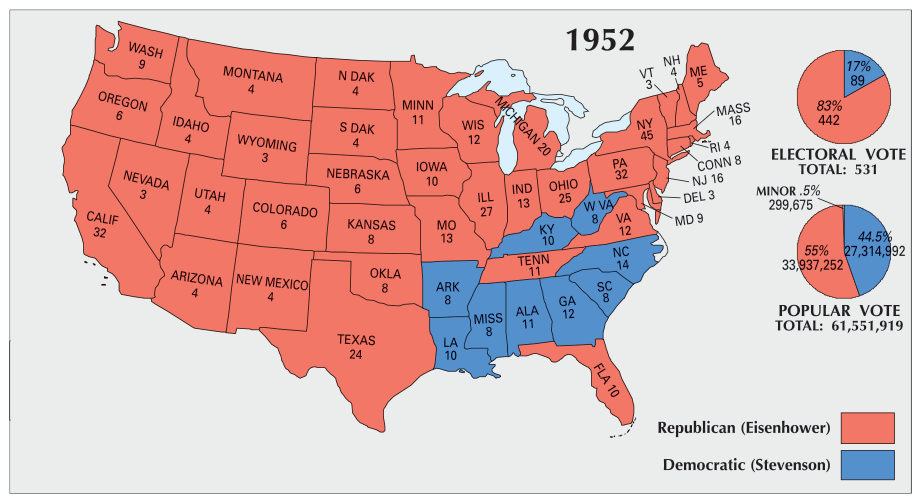
The 1952 presidential election marked a significant turning point in American politics. It witnessed the rise of a new political force, the Republican Party, under the leadership of Dwight D. Eisenhower, a war hero with immense popularity. This election, contested against the incumbent Democratic President Harry S. Truman, saw a dramatic shift in the electoral landscape, as evidenced by the 1952 presidential election map.
Understanding the 1952 Presidential Election Map
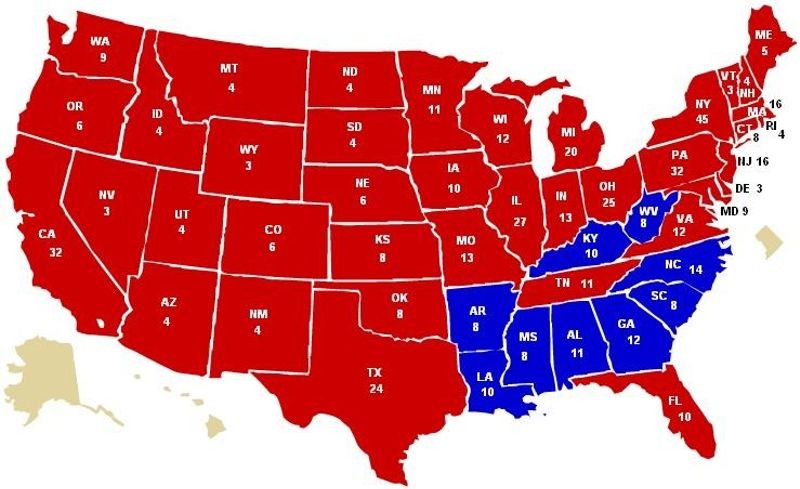
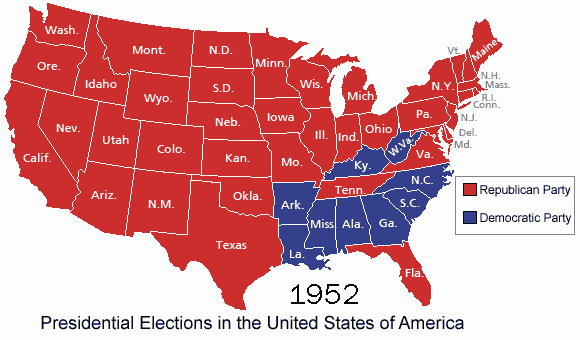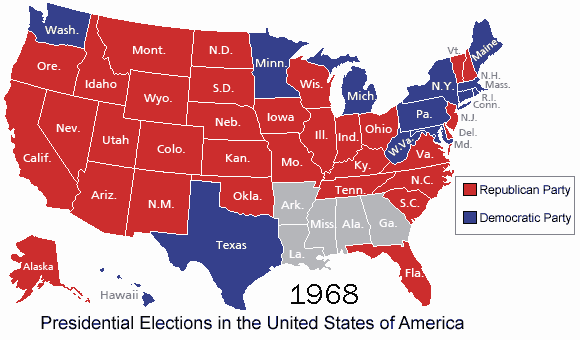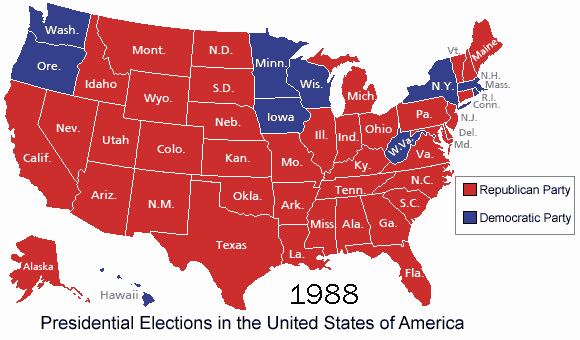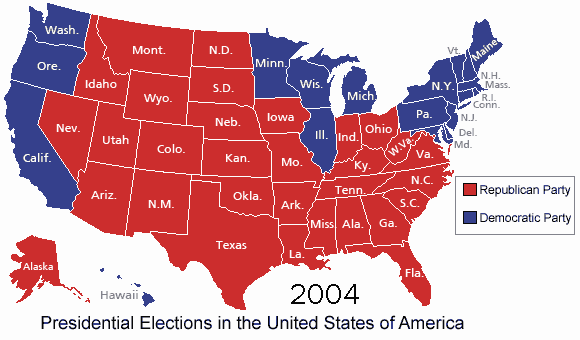
The 1952 presidential election map offers a visual representation of the electoral outcome, showcasing the distribution of electoral votes across the United States. Each state is colored based on the winning candidate, with red signifying a Republican victory and blue representing a Democratic win.
Key Features of the 1952 Election Map:
- Eisenhower’s Landslide Victory: The map clearly demonstrates Eisenhower’s decisive victory, capturing 442 electoral votes compared to Truman’s 89. This landslide win was driven by Eisenhower’s charisma, his promise of a "new deal" for the American people, and the public’s desire for a change after the tumultuous years of the Korean War and the Truman administration.
- Shifting Regional Support: The 1952 map also reveals a significant shift in regional support compared to previous elections. While the Democratic Party had traditionally dominated the South, Eisenhower secured victory in several Southern states, particularly in the Deep South, signifying a growing Republican presence in the region.
- The Rise of the "Solid South": The map also highlights the emergence of the "Solid South," a political phenomenon that would persist for several decades. This term referred to the consistent Republican dominance in the Southern states, a shift attributed to the changing demographics and racial tensions of the era.
Analyzing the 1952 Election Map: Insights and Implications
The 1952 presidential election map holds significant historical and political value. It provides valuable insights into the following:
- Electoral College Dynamics: The map illustrates the influence of the Electoral College system in shaping presidential elections. Eisenhower’s victory, despite losing the popular vote by a small margin, showcases the importance of winning key states with high electoral vote counts.
- Political Polarization: The map reflects the growing political polarization of the era, with the Republican and Democratic parties solidifying their positions on key issues like the Korean War, Communism, and domestic economic policies.
- Shifting Demographics: The map reveals the influence of changing demographics on voting patterns. Eisenhower’s victory in several Southern states suggests a growing Republican appeal among white voters in the region, driven by economic anxieties and concerns about racial integration.
Beyond the Map: Factors Shaping the 1952 Election
While the 1952 presidential election map provides a valuable visual representation of the electoral outcome, it is crucial to understand the broader context that shaped the election:
- The Korean War: The ongoing Korean War played a significant role in shaping the election. Eisenhower, a decorated war hero, campaigned on a promise to end the war, appealing to a war-weary nation.
- The Cold War: The Cold War and the threat of Communism loomed large over the 1952 election. Eisenhower’s strong anti-communist stance resonated with voters, particularly in the context of the "Red Scare" and the McCarthy era.
- Economic Concerns: The economic anxieties of the post-war era also influenced the election. Eisenhower promised to bring economic stability and prosperity, appealing to voters who were struggling with inflation and unemployment.
FAQs about the 1952 Presidential Election Map:
Q: Why did Eisenhower win so decisively?
A: Eisenhower’s victory was driven by a combination of factors, including his charisma, his promise of a "new deal" for the American people, and the public’s desire for a change after the tumultuous years of the Korean War and the Truman administration. His strong anti-communist stance and promises of economic stability also resonated with voters.
Q: What was the significance of the "Solid South"?
A: The emergence of the "Solid South" in the 1952 election marked a significant shift in Southern politics. This term referred to the consistent Republican dominance in the Southern states, driven by changing demographics, racial tensions, and the appeal of conservative policies.
Q: How did the Electoral College system influence the outcome?
A: The Electoral College system played a crucial role in Eisenhower’s victory. Despite losing the popular vote by a small margin, he secured a landslide victory in the Electoral College by winning key states with high electoral vote counts.
Q: How did the 1952 election map reflect the political climate of the time?
A: The 1952 election map reflects the growing political polarization of the era, with the Republican and Democratic parties solidifying their positions on key issues like the Korean War, Communism, and domestic economic policies. It also reflects the changing demographics and the influence of the Cold War and economic anxieties on voting patterns.
Tips for Understanding the 1952 Presidential Election Map:
- Consider the Historical Context: The map should be viewed within the broader historical context of the Korean War, the Cold War, and the economic anxieties of the post-war era.
- Analyze Regional Variations: Pay attention to the regional variations in voting patterns and consider the factors that might have contributed to these differences.
- Compare to Previous Elections: Compare the 1952 map to previous election maps to understand the historical shifts in voting patterns and the emergence of new political trends.
- Research the Candidates and Their Platforms: Learn about the candidates, their policies, and their campaigns to gain a deeper understanding of the factors that influenced the election outcome.
Conclusion
The 1952 presidential election map stands as a testament to the dynamic nature of American politics. It reflects the shifting political tides of the era, marked by the rise of a new political force in the Republican Party, the emergence of the "Solid South," and the growing influence of the Cold War and economic anxieties. By understanding the map’s historical context, its regional variations, and its implications for the future of American politics, we can gain valuable insights into the complex interplay of factors that shape presidential elections and the evolving landscape of American political discourse.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The 1952 Presidential Election: A Map of Shifting Political Tides. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!