The Caspian Sea Region: A Crossroads of Geography, History, and Geopolitics
Related Articles: The Caspian Sea Region: A Crossroads of Geography, History, and Geopolitics
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Caspian Sea Region: A Crossroads of Geography, History, and Geopolitics. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Caspian Sea Region: A Crossroads of Geography, History, and Geopolitics
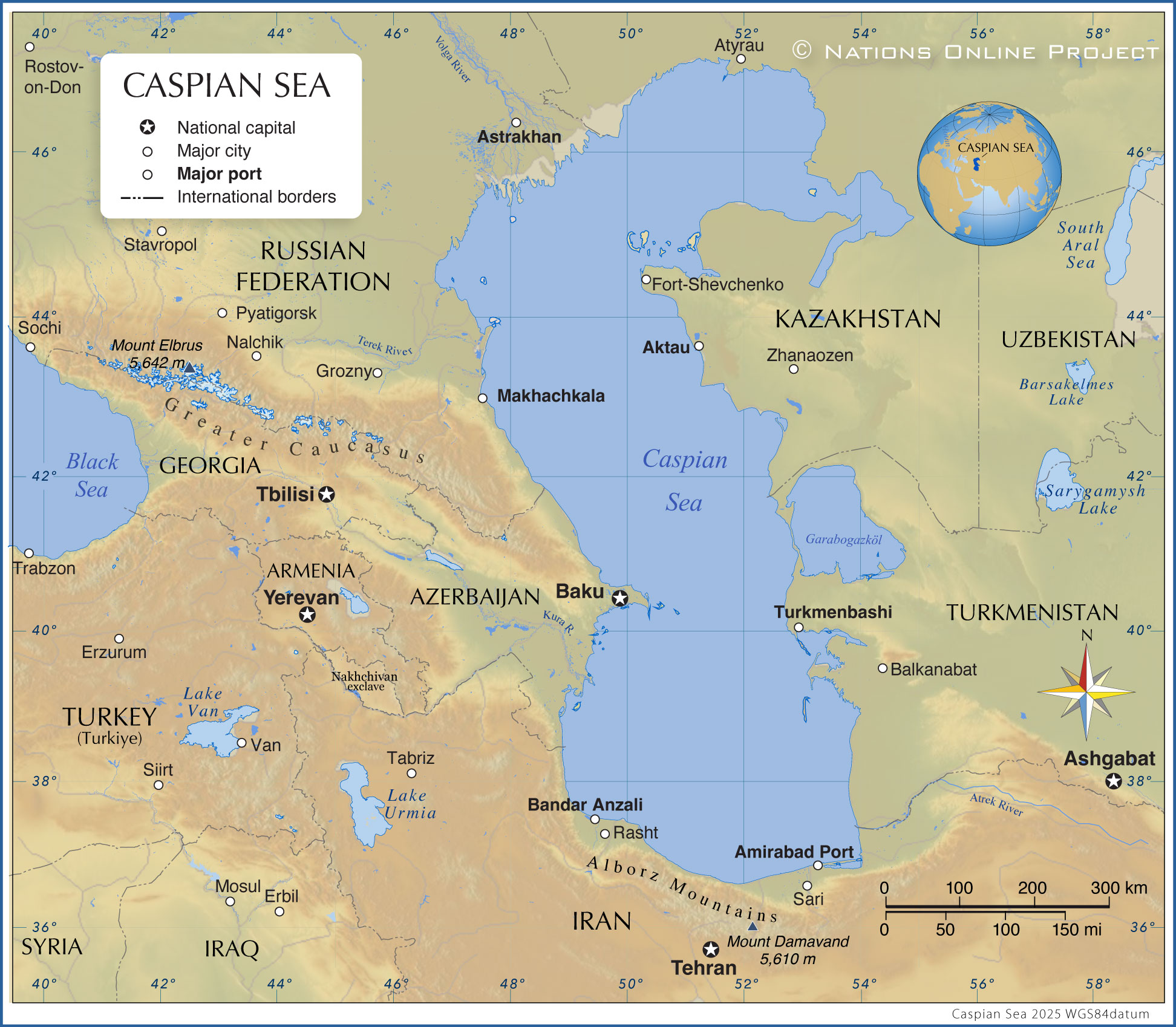
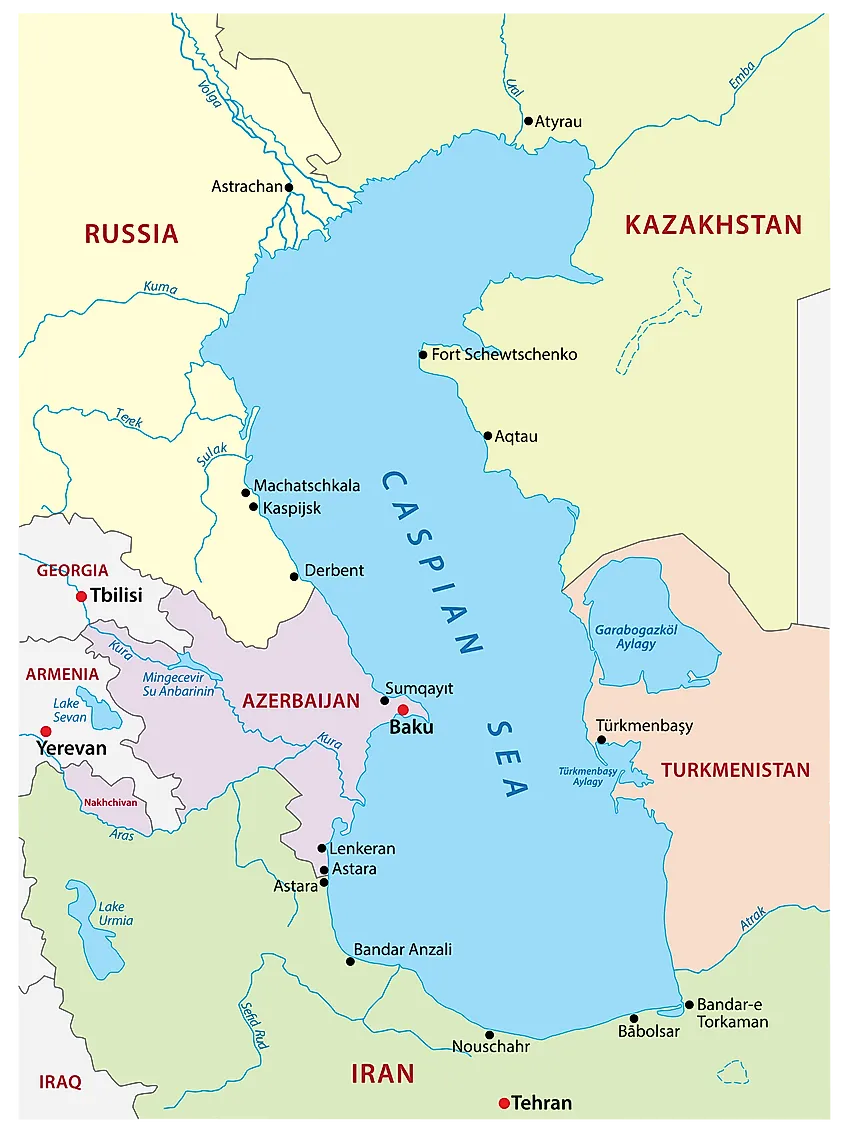
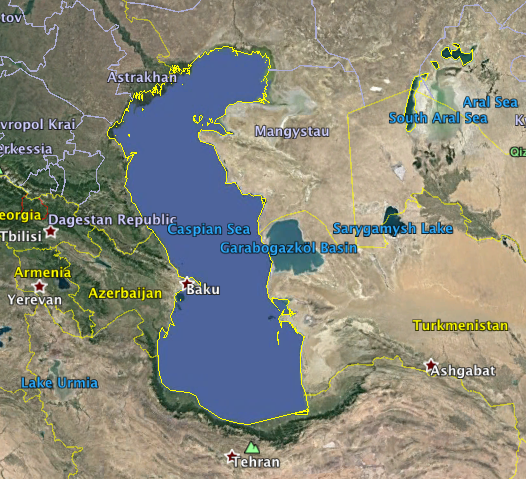
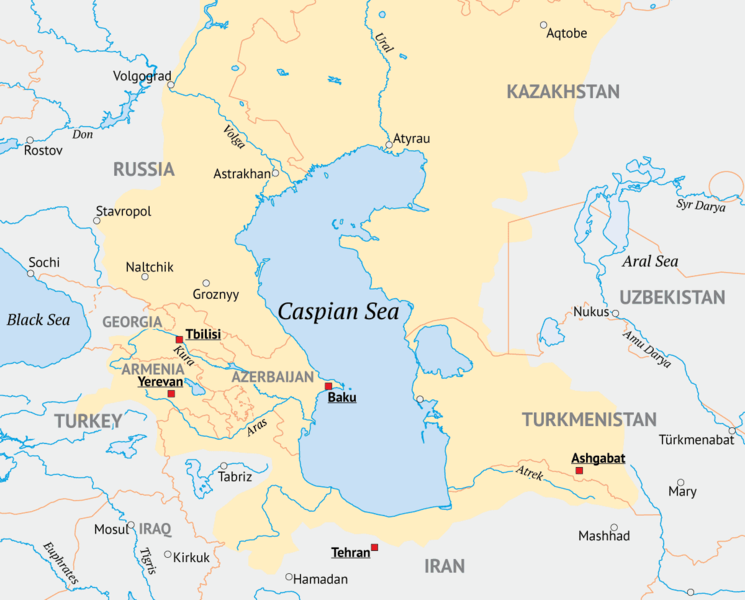
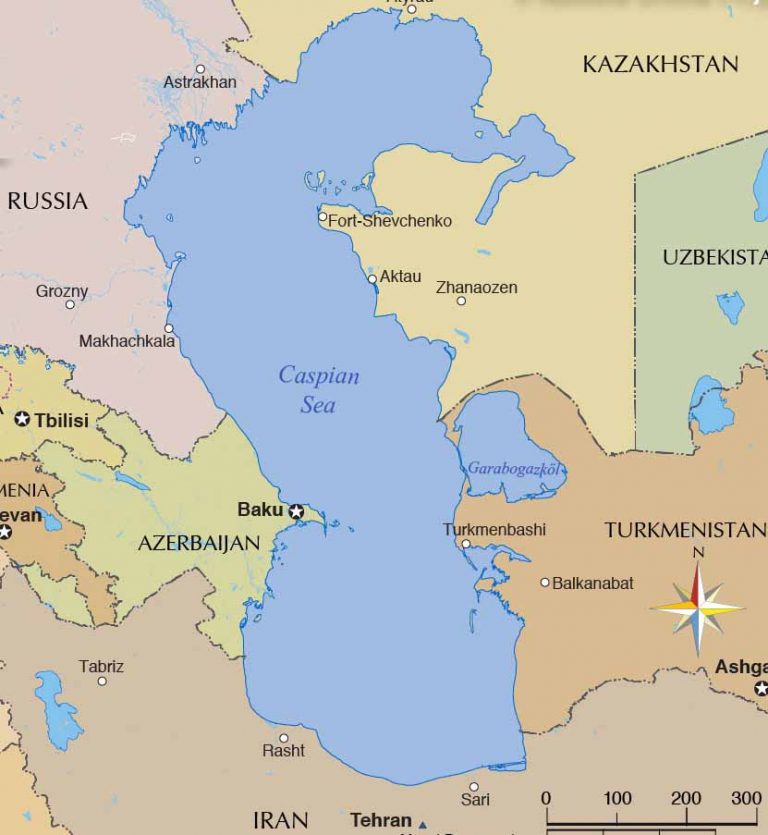
The Caspian Sea, the world’s largest inland body of water, is not a sea in the traditional sense. It is a large, endorheic (landlocked) basin that sits at the crossroads of Eastern Europe, Western Asia, and the Caucasus region. Its shores are shared by five countries: Azerbaijan, Iran, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Turkmenistan. This unique geographic location has shaped the region’s history, culture, and geopolitics, making the Caspian Sea a vital area of interest for researchers, policymakers, and businesses alike.
A Brief Overview of the Caspian Sea Region
The Caspian Sea is a vast expanse of water, covering an area of approximately 371,000 square kilometers. Its average depth is around 200 meters, with a maximum depth exceeding 1,000 meters. The sea is home to a diverse ecosystem, including numerous fish species, marine mammals, and migratory birds. Its rich resources, particularly oil and natural gas reserves, have attracted significant global attention.
The Caspian Sea Region: A Historical Perspective
The Caspian Sea region boasts a rich and complex history, spanning millennia. Ancient civilizations, including the Persians, Greeks, and Scythians, have left their mark on the region’s cultural landscape. The Silk Road, a historic trade route that connected the East and West, passed through the Caspian Sea region, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and cultures.
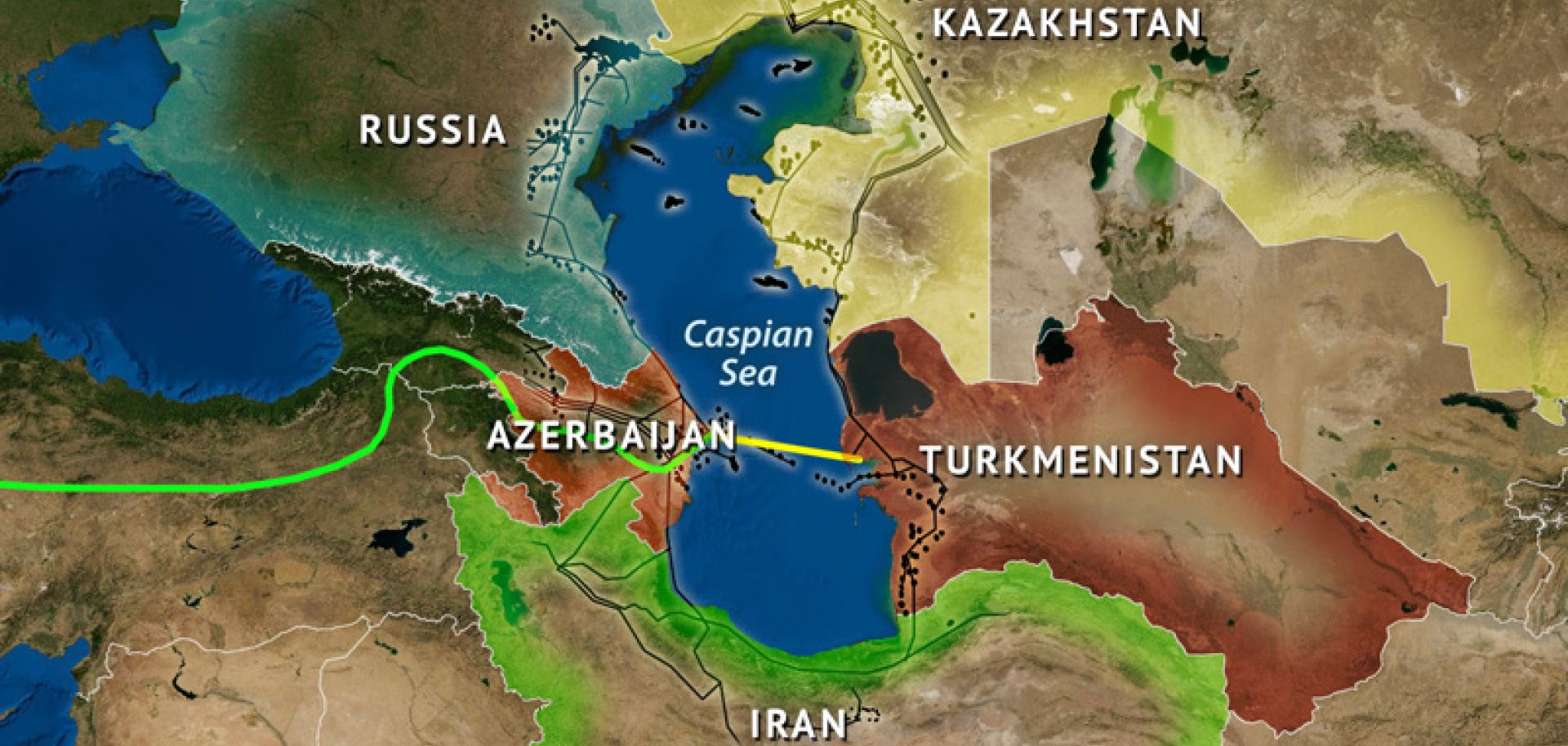
Geopolitical Significance of the Caspian Sea Region
The Caspian Sea region holds immense geopolitical significance due to its strategic location and vast natural resources. The region is a major transit route for oil and gas pipelines, connecting the Caspian Sea’s energy reserves to global markets. The Caspian Sea is also a focal point for international trade and cooperation.
The Caspian Sea Region’s Diverse Landscape
The Caspian Sea region is characterized by a diverse landscape, encompassing vast steppes, fertile plains, towering mountains, and arid deserts. The region’s diverse topography has influenced its economic activities, from agriculture and fishing to oil and gas production.
The Caspian Sea Region’s Cultural Tapestry
The Caspian Sea region is home to a rich cultural tapestry, influenced by centuries of interaction between different ethnicities and religions. The region’s cultural diversity is reflected in its art, music, literature, and cuisine.
Environmental Challenges in the Caspian Sea Region
The Caspian Sea region faces a number of environmental challenges, including pollution from industrial activities, overfishing, and climate change. These challenges threaten the region’s biodiversity and ecosystem, highlighting the need for sustainable development and environmental protection.
The Future of the Caspian Sea Region
The Caspian Sea region stands at a crossroads, facing challenges and opportunities. The region’s future will be shaped by its ability to manage its resources sustainably, foster regional cooperation, and address environmental concerns.
Exploring the Caspian Sea Region: A Detailed Look at Its Five Countries
1. Azerbaijan:
- Geography: Azerbaijan is located on the western shores of the Caspian Sea. The country is characterized by a diverse landscape, including the Greater Caucasus Mountains, the Kura-Araks Lowland, and the Absheron Peninsula.
- Economy: Azerbaijan’s economy is heavily reliant on oil and gas production, with the country being a major exporter of these resources. The country is also developing its tourism sector.
- Culture: Azerbaijan has a rich cultural heritage, with a unique blend of Persian, Turkic, and European influences. The country is known for its traditional music, dance, and cuisine.
2. Iran:
- Geography: Iran borders the Caspian Sea to the north, with a coastline stretching for over 700 kilometers. The country’s Caspian Sea region is characterized by fertile plains, mountains, and forests.
- Economy: Iran’s economy is diversified, with a focus on oil and gas production, agriculture, and manufacturing. The country has significant potential for tourism development.
- Culture: Iran has a rich cultural heritage, with a long history of art, literature, and philosophy. The country is known for its Persian carpets, calligraphy, and traditional cuisine.
3. Kazakhstan:
- Geography: Kazakhstan shares the longest coastline with the Caspian Sea, stretching for over 2,300 kilometers. The country’s Caspian Sea region is characterized by vast steppes, deserts, and oil-rich fields.
- Economy: Kazakhstan’s economy is dominated by oil and gas production, with the country being a major exporter of these resources. The country is also developing its mining, agricultural, and manufacturing sectors.
- Culture: Kazakhstan has a diverse cultural heritage, influenced by Turkic, Russian, and Central Asian traditions. The country is known for its nomadic culture, traditional music, and folklore.
4. Russia:
- Geography: Russia’s Caspian Sea coastline stretches for over 690 kilometers. The country’s Caspian Sea region is characterized by the Caucasus Mountains, the Volga River delta, and the Dagestan Republic.
- Economy: Russia’s Caspian Sea region is a major center for oil and gas production, with the country being a major exporter of these resources. The region also has a significant fishing industry.
- Culture: Russia’s Caspian Sea region has a rich cultural heritage, influenced by Russian, Caucasian, and Turkic traditions. The region is known for its traditional music, dance, and folklore.
5. Turkmenistan:
- Geography: Turkmenistan’s Caspian Sea coastline stretches for over 530 kilometers. The country’s Caspian Sea region is characterized by deserts, the Karakum Desert, and the Kopet Dag Mountains.
- Economy: Turkmenistan’s economy is heavily reliant on oil and gas production, with the country being a major exporter of these resources. The country is also developing its agricultural sector.
- Culture: Turkmenistan has a unique cultural heritage, influenced by Turkic, Persian, and Central Asian traditions. The country is known for its traditional carpets, music, and folklore.
FAQs about the Caspian Sea Region
1. What are the major economic activities in the Caspian Sea region?
The Caspian Sea region is rich in natural resources, particularly oil and natural gas. Oil and gas production are major economic activities in all five countries bordering the Caspian Sea. Other important economic activities include fishing, agriculture, tourism, and transportation.
2. What are the main environmental challenges facing the Caspian Sea region?
The Caspian Sea region faces a number of environmental challenges, including pollution from industrial activities, overfishing, and climate change. These challenges threaten the region’s biodiversity and ecosystem, highlighting the need for sustainable development and environmental protection.
3. What are the key geopolitical issues surrounding the Caspian Sea?
The Caspian Sea region is a focal point for geopolitical tensions, particularly regarding the division of the sea’s resources and the status of its waters. The five Caspian Sea countries have been engaged in protracted negotiations to establish a legal framework for the sea’s management.
4. What is the future of the Caspian Sea region?
The Caspian Sea region stands at a crossroads, facing challenges and opportunities. The region’s future will be shaped by its ability to manage its resources sustainably, foster regional cooperation, and address environmental concerns.
Tips for Understanding the Caspian Sea Region
- Study the region’s geography: Understanding the region’s diverse landscape and geography is crucial for comprehending its history, culture, and geopolitics.
- Learn about the region’s history: The Caspian Sea region has a long and complex history, which has shaped its present-day situation.
- Explore the region’s cultural diversity: The Caspian Sea region is home to a rich cultural tapestry, influenced by centuries of interaction between different ethnicities and religions.
- Stay informed about current events: The Caspian Sea region is a dynamic area, with ongoing geopolitical developments and environmental challenges.
Conclusion
The Caspian Sea region is a vital area of interest for researchers, policymakers, and businesses alike. Its strategic location, diverse resources, and rich cultural heritage make it a fascinating and complex region. Understanding the Caspian Sea region’s geography, history, culture, and geopolitics is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. By fostering regional cooperation, promoting sustainable development, and addressing environmental concerns, the Caspian Sea region can unlock its full potential and contribute to a more peaceful and prosperous future.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Caspian Sea Region: A Crossroads of Geography, History, and Geopolitics. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!