The Cave Creek Fire: A Legacy of Destruction and Resilience
Related Articles: The Cave Creek Fire: A Legacy of Destruction and Resilience
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Cave Creek Fire: A Legacy of Destruction and Resilience. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Cave Creek Fire: A Legacy of Destruction and Resilience

The Cave Creek Fire, a devastating wildfire that scorched the landscape of Arizona in 2000, remains a poignant reminder of the destructive power of nature and the importance of wildfire preparedness. This article examines the fire’s impact, its lasting legacy, and the lessons learned from this catastrophic event.
The Fire’s Origins and Spread
The Cave Creek Fire ignited on May 20, 2000, in the rugged terrain of the Tonto National Forest, north of Phoenix, Arizona. The exact cause remains unknown, but it is believed to have been human-caused, possibly through a discarded cigarette or campfire.
Fueled by dry brush, scorching temperatures, and strong winds, the fire quickly spread, engulfing thousands of acres of chaparral, grasslands, and pine forests. It became a raging inferno, jumping fire lines and defying containment efforts.
The Impact of the Fire
The Cave Creek Fire consumed over 211,000 acres, leaving behind a scarred landscape. It destroyed over 500 homes, businesses, and other structures, displacing hundreds of residents. The fire’s impact extended beyond the immediate area, causing significant air quality problems throughout the Phoenix metropolitan area.
Lessons Learned and Legacy
The Cave Creek Fire served as a stark reminder of the importance of wildfire prevention and preparedness. It highlighted the need for:
- Improved fire management: The fire’s rapid spread emphasized the need for better forest management practices, including controlled burns and thinning of vegetation to reduce fuel loads.
- Enhanced public awareness: The fire underscored the importance of educating the public about wildfire risks, safe fire practices, and evacuation procedures.
- Strengthened emergency response: The fire highlighted the need for improved coordination and communication between fire agencies, local governments, and communities.
The fire’s legacy also extends to the long-term impact on the ecosystem. The burned area is now undergoing ecological recovery, with new plant growth and wildlife returning. However, the fire also left behind significant erosion and sedimentation issues, requiring ongoing restoration efforts.
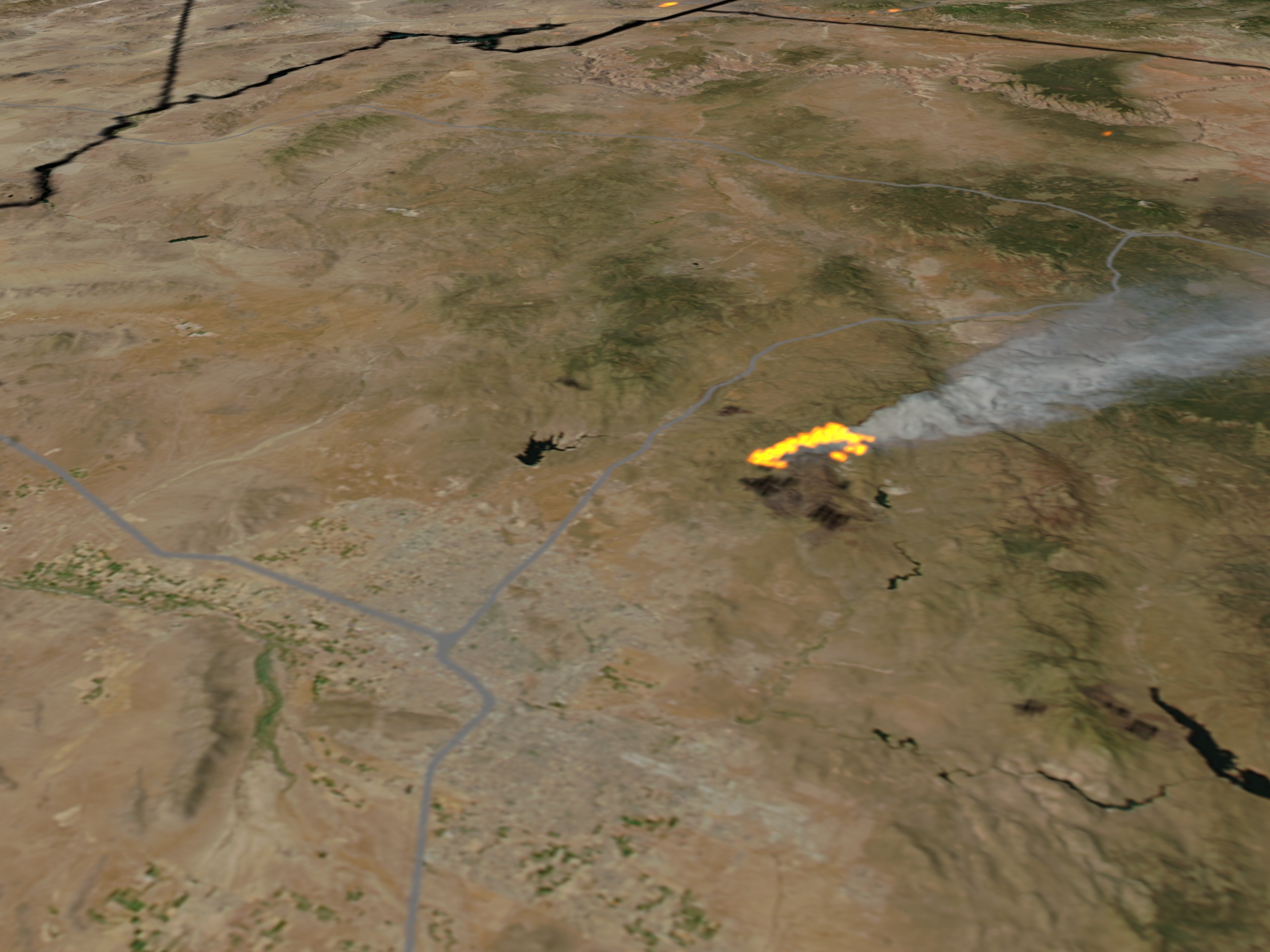
The Map as a Tool for Understanding
A map of the Cave Creek Fire provides a crucial visual representation of the fire’s extent, impact, and evolution. It allows for a comprehensive understanding of the fire’s trajectory, the areas affected, and the locations of critical infrastructure and communities. The map is an invaluable tool for:
- Assessing the fire’s impact: It helps visualize the scope of the fire’s destruction and its effects on different landscapes and communities.
- Planning for future fires: It provides valuable data for developing fire prevention and suppression strategies, identifying areas at high risk, and planning evacuation routes.
- Understanding ecological recovery: It allows researchers and ecologists to track the fire’s long-term impact on the ecosystem and monitor the recovery process.
FAQs
Q: How long did the Cave Creek Fire burn?
A: The fire raged for over a month, from May 20, 2000, to June 26, 2000.
Q: What was the estimated cost of the Cave Creek Fire?
A: The estimated cost of the fire, including damage and suppression efforts, exceeded $100 million.
Q: What were the primary causes of the fire’s rapid spread?
A: The fire’s rapid spread was attributed to a combination of factors, including dry brush, high temperatures, strong winds, and rugged terrain.
Q: What measures were taken to prevent future fires?
A: After the fire, the Tonto National Forest implemented a number of measures, including controlled burns, thinning of vegetation, and public education campaigns.
Q: What are the long-term effects of the fire on the ecosystem?
A: The fire has had a significant impact on the ecosystem, including soil erosion, altered plant communities, and changes in wildlife populations. However, the area is now undergoing ecological recovery, with new plant growth and wildlife returning.
Tips for Fire Safety
- Be aware of fire danger: Stay informed about current fire danger levels and follow local fire restrictions.
- Practice fire safety: Exercise caution when using fire, ensuring that campfires are properly extinguished and that machinery is equipped with working spark arrestors.
- Create defensible space: Clear vegetation around your home to create a buffer zone that can help prevent fire spread.
- Develop a fire evacuation plan: Have a plan in place for evacuating your home in the event of a wildfire, including designated meeting points and emergency contacts.
Conclusion
The Cave Creek Fire serves as a stark reminder of the destructive power of wildfires and the importance of preparedness. Through lessons learned and ongoing efforts in fire management, public education, and emergency response, we can strive to mitigate the risks associated with wildfire and protect our communities and ecosystems. The map of the Cave Creek Fire remains a powerful tool for understanding the fire’s impact and guiding future efforts in wildfire prevention and preparedness.




![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Cave Creek Fire: A Legacy of Destruction and Resilience. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!