The Nile River Basin: A Lifeline Across Africa
Related Articles: The Nile River Basin: A Lifeline Across Africa
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Nile River Basin: A Lifeline Across Africa. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Nile River Basin: A Lifeline Across Africa
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Nile River Basin: A Lifeline Across Africa
- 3.1 A Geographic Overview
- 3.2 The Importance of the Nile River Basin
- 3.3 Challenges Facing the Nile River Basin
- 3.4 Addressing the Challenges
- 3.5 FAQs
- 3.6 Tips
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Nile River Basin: A Lifeline Across Africa

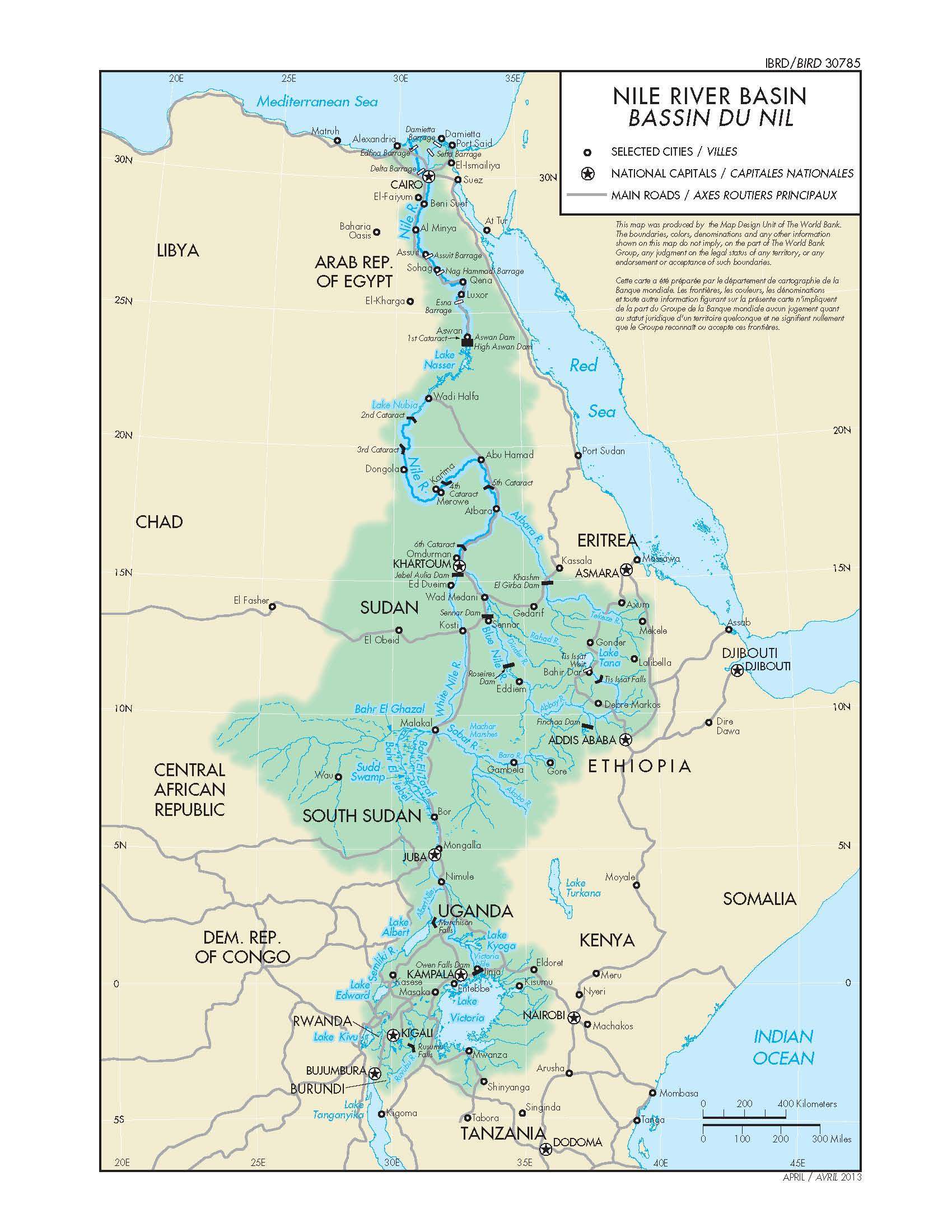
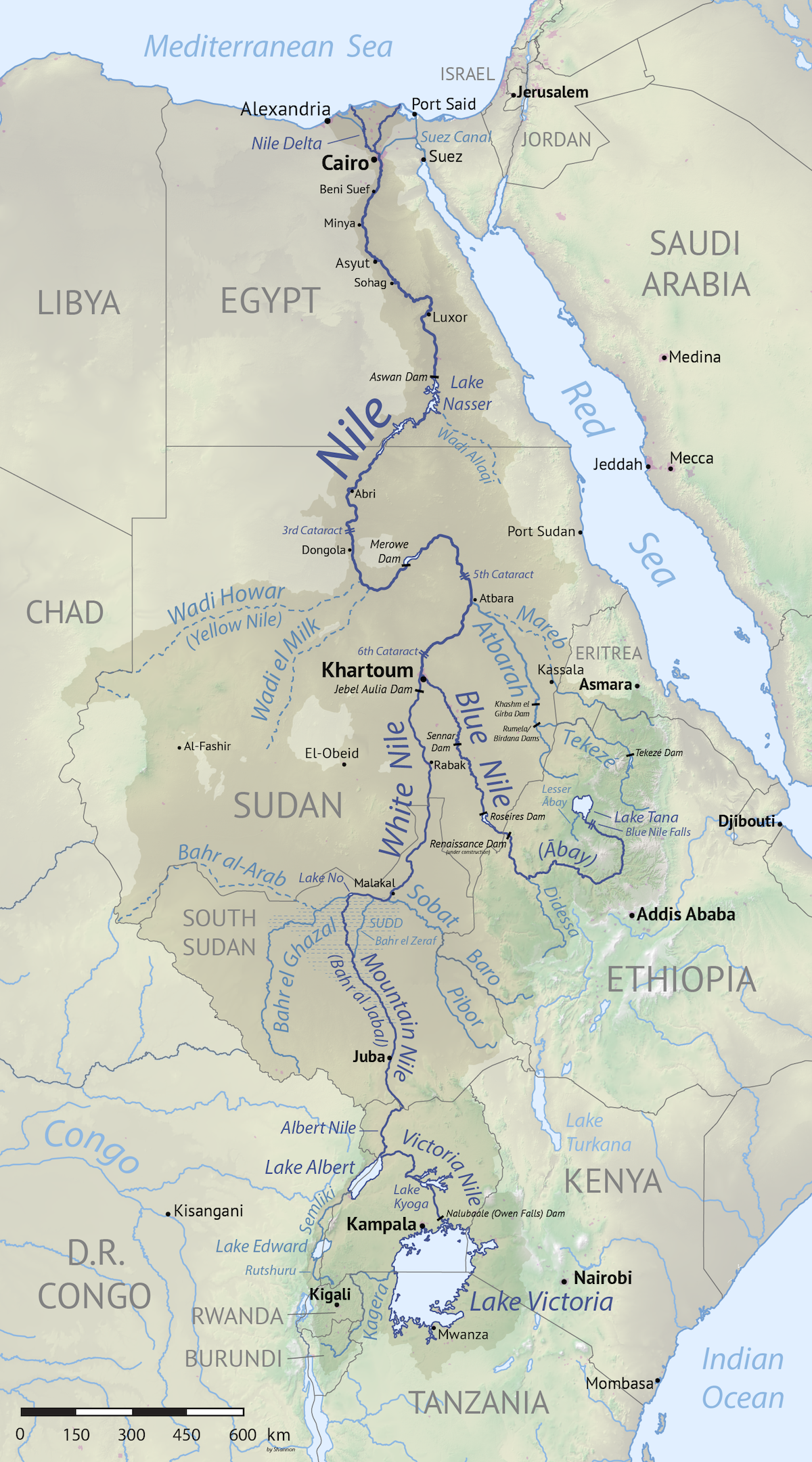
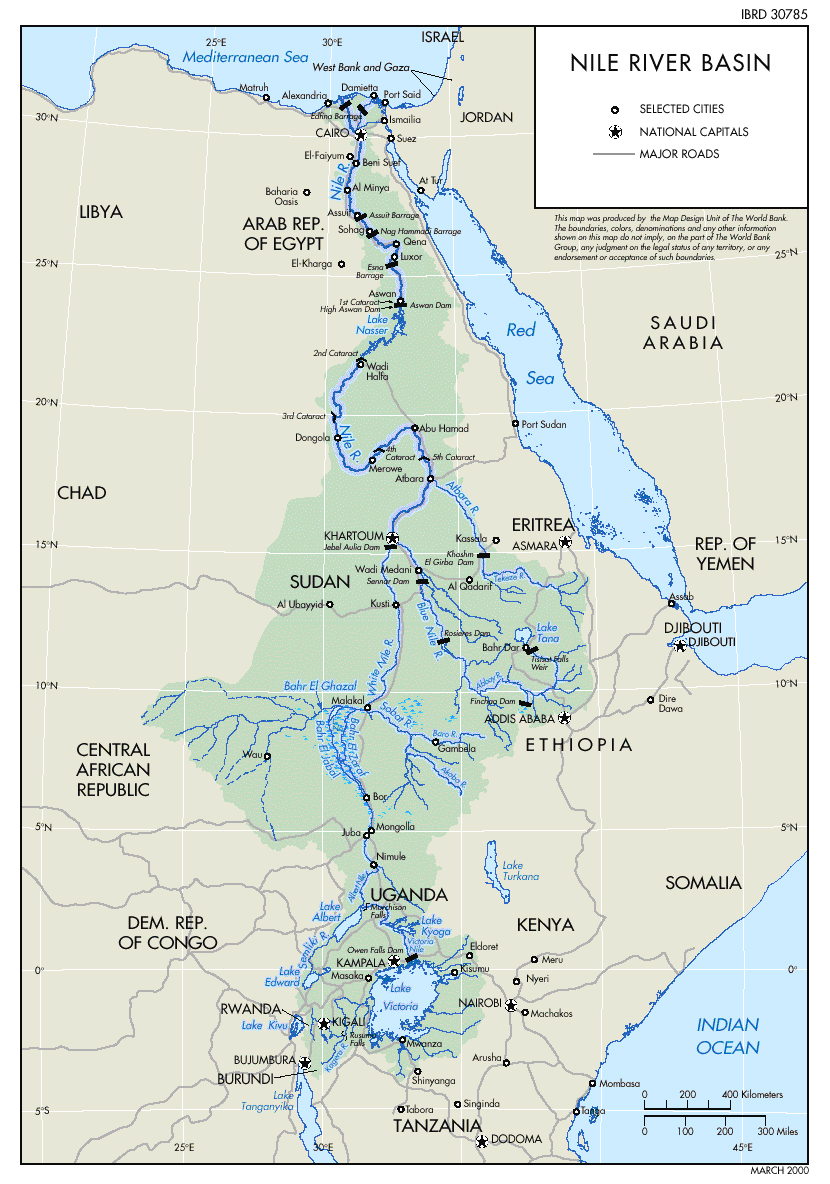
The Nile River, the longest river in the world, flows through eleven countries in northeastern Africa, forming the Nile River Basin. This vast and intricate system, encompassing over 3,349,000 square kilometers, is a vital lifeline for the region, supporting a population of over 300 million people.
A Geographic Overview
The Nile River Basin, shaped by the confluence of numerous tributaries, stretches from the highlands of Ethiopia in the south to the Mediterranean Sea in the north. It can be broadly divided into two main branches:
- The Blue Nile: Originating in the Ethiopian Highlands, this branch is known for its sediment-rich waters, contributing significantly to the Nile’s fertile floodplain.
- The White Nile: Flowing from the Great Lakes region of Central Africa, this branch carries a higher volume of water, contributing to the Nile’s overall flow.
Mapping the Lifeline:
The map of the Nile River Basin offers a visual representation of this complex ecosystem. It reveals the intricate network of tributaries, lakes, and wetlands that contribute to the Nile’s flow. The map highlights the geographical diversity of the basin, encompassing various landscapes, including:
- Highlands: The Ethiopian Highlands and the Ruwenzori Mountains are the source of the Nile’s water, contributing to the river’s flow through rainfall and snowmelt.
- Lakes: The Great Lakes region, including Lake Victoria, Lake Albert, and Lake Kyoga, act as reservoirs, regulating the Nile’s flow and providing a vital source of water for surrounding communities.
- Wetlands: The Sudd, a vast wetland in South Sudan, serves as a natural filter, slowing down the Nile’s flow and contributing to its biodiversity.
- Floodplains: The Nile’s fertile floodplains have supported agriculture for millennia, fostering the development of civilizations along its banks.
A Tapestry of Life:
The Nile River Basin is home to a rich biodiversity, with diverse flora and fauna adapted to the unique conditions of the region. It is a vital habitat for numerous species, including:
- Fish: The Nile River is home to a vast array of fish species, including Nile perch, tilapia, and catfish, providing a crucial source of protein for local communities.
- Birds: The basin attracts a wide variety of birds, including migratory species, making it a popular destination for birdwatchers.
- Mammals: The basin supports a range of mammals, including elephants, hippopotamuses, crocodiles, and various antelope species.
The Importance of the Nile River Basin
The Nile River Basin plays a critical role in the socio-economic development of the region, providing:
- Water for Irrigation: The Nile River is a vital source of irrigation for agriculture, supporting a significant portion of the region’s food production.
- Hydropower: The basin’s numerous dams provide electricity to millions of people, contributing to economic growth and development.
- Transportation: The Nile River serves as a major transportation route, facilitating trade and communication between communities along its banks.
- Tourism: The basin’s natural beauty and cultural heritage attract tourists from around the world, contributing to local economies.
Challenges Facing the Nile River Basin
Despite its immense importance, the Nile River Basin faces significant challenges, including:
- Water Scarcity: The increasing demand for water resources, driven by population growth and development, is putting pressure on the Nile’s water supply.
- Climate Change: Climate change is altering rainfall patterns and increasing the frequency and intensity of droughts, impacting the Nile’s flow and exacerbating water scarcity.
- Pollution: Industrial and agricultural activities contribute to pollution, impacting the Nile’s water quality and threatening human health and aquatic ecosystems.
- Dam Construction: The construction of dams along the Nile River can disrupt the natural flow of water, impacting downstream communities and ecosystems.
Addressing the Challenges
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from all countries in the Nile River Basin. Strategies include:
- Water Management: Implementing sustainable water management practices to ensure equitable distribution and efficient use of water resources.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Investing in climate change adaptation measures to mitigate the impacts of climate change on the Nile River Basin.
- Pollution Control: Strengthening regulations and enforcing measures to control pollution and protect the Nile’s water quality.
- Transboundary Cooperation: Fostering cooperation between Nile Basin countries to address shared challenges and promote sustainable development.
FAQs
1. What are the main tributaries of the Nile River?
The main tributaries of the Nile River include the Blue Nile, the White Nile, the Atbara River, and the Sobat River.
2. How does the Nile River contribute to the economy of the region?
The Nile River contributes to the economy of the region through agriculture, hydropower generation, transportation, and tourism.
3. What are the main environmental challenges facing the Nile River Basin?
The main environmental challenges facing the Nile River Basin include water scarcity, climate change, pollution, and dam construction.
4. What is the role of the Nile Basin Initiative?
The Nile Basin Initiative is a collaborative effort between the Nile Basin countries to promote sustainable development and manage shared water resources.
5. What are some examples of sustainable water management practices?
Sustainable water management practices include water conservation, efficient irrigation systems, and rainwater harvesting.
Tips
- Learn about the Nile River Basin: Educate yourself about the importance of the Nile River Basin and the challenges it faces.
- Support sustainable water management: Choose products and services that promote sustainable water use.
- Reduce your water consumption: Take steps to conserve water in your daily life.
- Advocate for environmental protection: Support organizations working to protect the Nile River Basin.
Conclusion
The Nile River Basin is a complex and dynamic ecosystem that plays a vital role in the lives of millions of people. Understanding the basin’s geography, biodiversity, and challenges is essential for promoting sustainable development and ensuring the long-term health of this vital resource. Through collaboration and responsible stewardship, we can safeguard the future of the Nile River Basin for generations to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Nile River Basin: A Lifeline Across Africa. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!