topographic map of mt st helens
Related Articles: topographic map of mt st helens
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to topographic map of mt st helens. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape of Mount St. Helens: A Topographic Journey
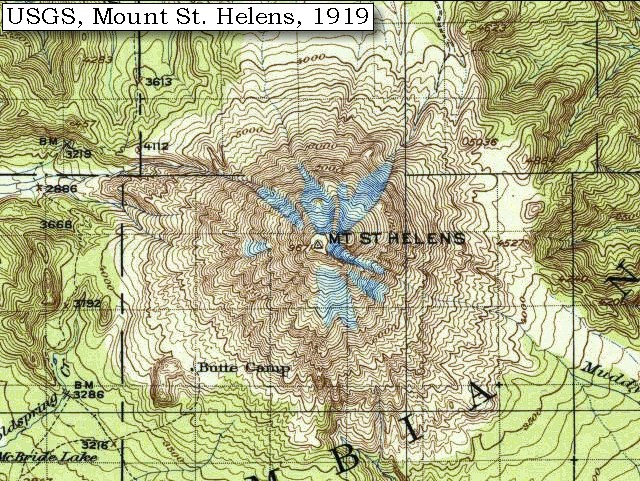
Mount St. Helens, a stratovolcano in the Cascade Range of Washington State, is renowned for its dramatic eruption in 1980. This catastrophic event reshaped the landscape, leaving behind a stark and powerful testament to the forces of nature. Understanding the topographic map of Mount St. Helens is crucial for comprehending the volcano’s history, its current state, and the ongoing geological processes that continue to mold the region.
A Visual Representation of the Mountain’s Anatomy
Topographic maps, using contour lines to depict elevation changes, provide a comprehensive visual representation of Mount St. Helens’ complex topography. These lines connect points of equal elevation, allowing us to visualize the mountain’s slopes, valleys, and craters. By examining these lines, we can glean insights into the following:
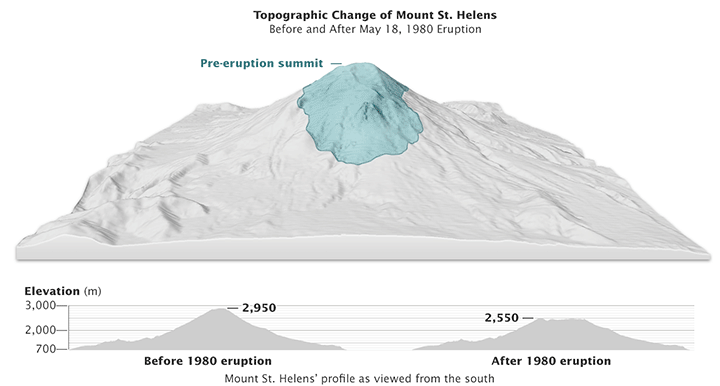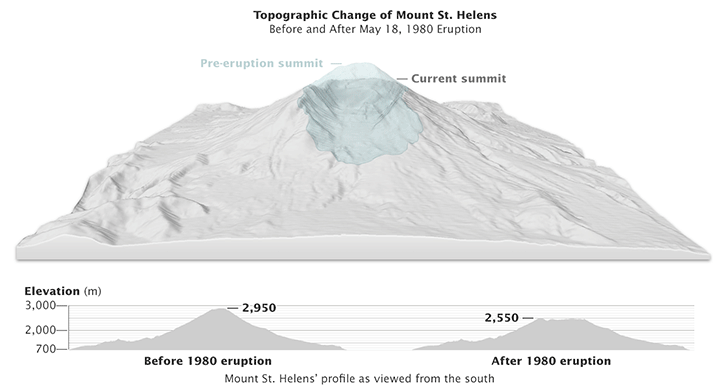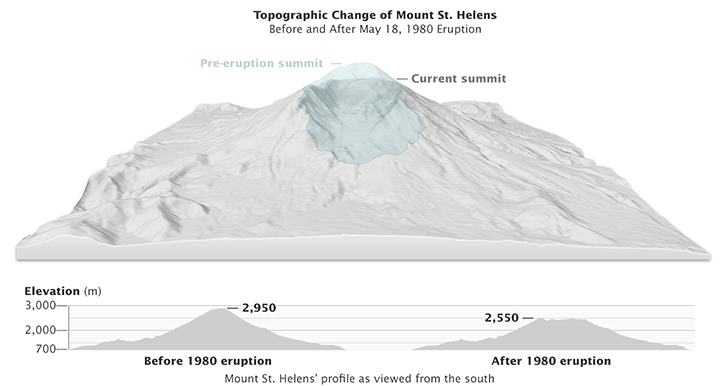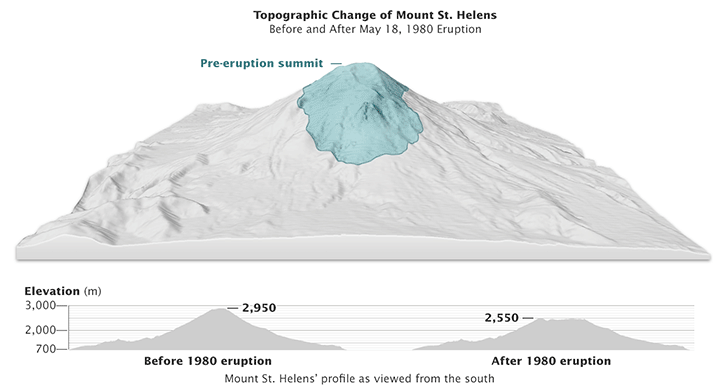
- The Pre-Eruption Landscape: The pre-1980 topographic map reveals the symmetrical cone shape of the volcano before the eruption. This map highlights the presence of a prominent summit crater, a network of radial valleys, and the gentle slopes leading up to the summit.
- The Impact of the 1980 Eruption: The post-eruption topographic map vividly illustrates the dramatic changes wrought by the event. The northern flank of the mountain was obliterated, leaving behind a vast horseshoe-shaped crater. This crater, now filled with a lake, is a poignant reminder of the eruption’s destructive power.
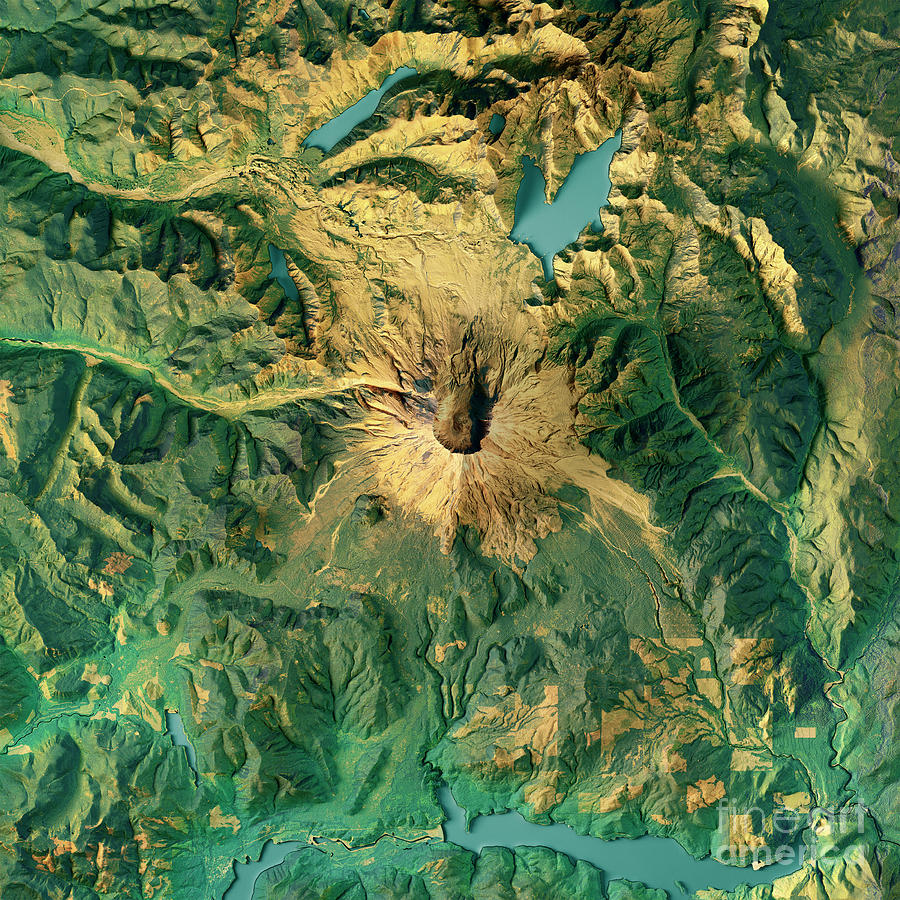
- The Evolving Landscape: The topographic map also reveals the ongoing evolution of the landscape. The crater floor is steadily being filled by sediment, and new volcanic features, such as lava domes, are emerging within the crater. These changes highlight the dynamic nature of the volcano and the ongoing geological processes shaping the area.
Applications of the Topographic Map
The topographic map of Mount St. Helens serves as an invaluable tool for a range of purposes, including:
- Scientific Research: Geologists, volcanologists, and other researchers utilize topographic maps to study the volcano’s structure, its eruptive history, and the ongoing processes shaping the landscape. The maps provide critical data for understanding the dynamics of volcanic eruptions and predicting future activity.
- Hazard Assessment: Topographic maps are crucial for assessing the risks associated with volcanic eruptions. By analyzing the topography, experts can identify areas vulnerable to lava flows, mudslides, and ashfall, aiding in the development of evacuation plans and mitigation strategies.
- Land Management: The topographic map informs land management decisions in the area. It assists in identifying areas suitable for recreation, resource extraction, and conservation, while also highlighting areas at risk from volcanic hazards.
- Education and Public Awareness: Topographic maps serve as powerful educational tools, allowing individuals to visualize the complexities of the landscape and understand the impact of volcanic activity. They contribute to public awareness about the potential risks and the importance of preparedness.
Exploring the Topographic Map: A Detailed Look
Let’s delve deeper into the topographic map of Mount St. Helens, focusing on key features and their significance:
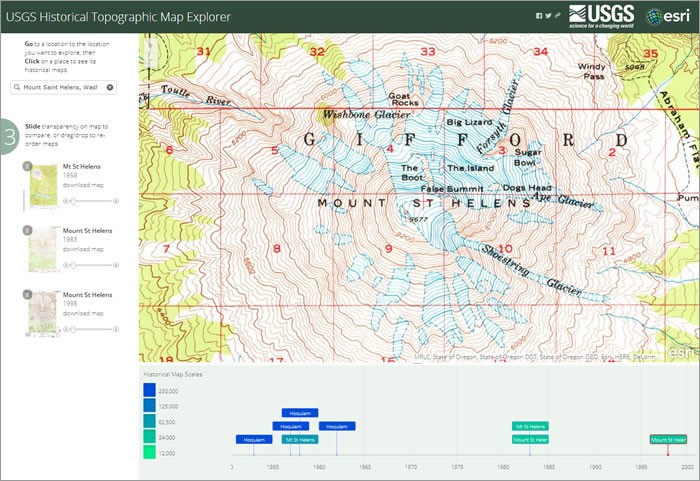
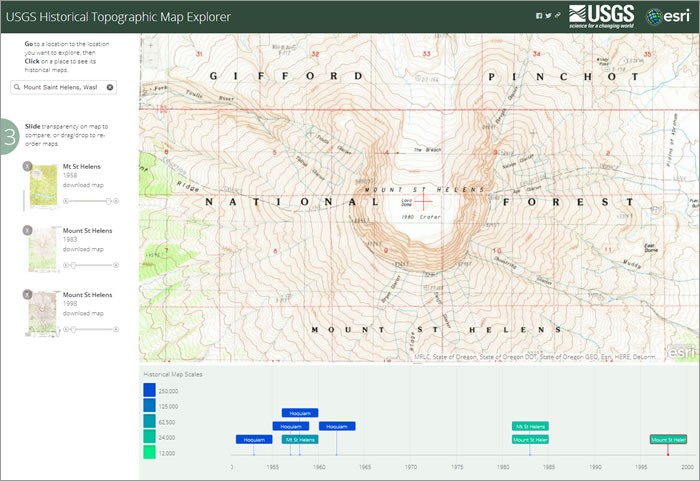
- Summit Crater: The most prominent feature on the map is the horseshoe-shaped crater formed during the 1980 eruption. This crater, approximately 2 miles wide and 1,500 feet deep, is now filled with a lake known as Spirit Lake. The crater rim, marked by sharp cliffs, offers breathtaking views of the surrounding landscape.
- Lava Domes: Within the crater, several lava domes have emerged since the 1980 eruption. These domes, formed by the slow extrusion of viscous lava, are evidence of the volcano’s ongoing activity. The largest dome, known as the "Dome," is a prominent feature on the map, rising approximately 800 feet above the crater floor.
- Spirit Lake: The lake within the crater is a unique feature, formed by the damming of the Toutle River by the 1980 eruption. The lake is characterized by its deep blue color and the presence of floating logs, remnants of the forests that were destroyed by the eruption.
- Radial Valleys: The topographic map reveals a network of radial valleys radiating outward from the summit. These valleys were formed by erosion and glacial activity, and they provide access to the mountain’s flanks.
- The Pumice Plain: The area surrounding the crater is covered by a vast pumice plain, formed by the deposition of volcanic ash during the 1980 eruption. The pumice plain is characterized by its light color and porous texture, and it serves as a reminder of the eruption’s immense power.
- The Toutle River: This river, which flows through the area, was heavily impacted by the 1980 eruption. The eruption triggered a massive landslide, which dammed the river and created Spirit Lake. The river continues to play a significant role in shaping the landscape, transporting sediment and eroding the surrounding hillsides.
Understanding the Scale and Elevation
Topographic maps utilize a scale to represent the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground. The scale of a map is typically expressed as a ratio, such as 1:24,000, which means that one unit on the map represents 24,000 units on the ground. Elevation is depicted using contour lines, which connect points of equal elevation. The closer the contour lines are to each other, the steeper the slope.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How often are topographic maps of Mount St. Helens updated?
A: Topographic maps of Mount St. Helens are updated periodically to reflect changes in the landscape, particularly after major eruptions or other significant events. The frequency of updates depends on the level of volcanic activity and the availability of resources.
Q: What are the best resources for obtaining topographic maps of Mount St. Helens?
A: Several resources provide access to topographic maps of Mount St. Helens, including:
- United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS is a primary source for topographic maps, providing both paper and digital versions.
- National Map: This online platform, maintained by the USGS, provides access to a wide range of geospatial data, including topographic maps.
- Mount St. Helens National Volcanic Monument: The park service provides topographic maps specific to the volcano and its surrounding area.
Q: Can topographic maps be used to predict future volcanic activity?
A: While topographic maps can provide valuable insights into the structure and history of a volcano, they cannot be used to predict future eruptions with certainty. However, by studying the topographic features and their relationship to past eruptive activity, scientists can identify areas at risk and develop models to assess the likelihood of future eruptions.
Tips for Using Topographic Maps of Mount St. Helens
- Familiarize yourself with the map’s scale and legend: Understanding the map’s scale and the symbols used to represent different features is essential for accurate interpretation.
- Use a compass and altimeter: These tools can assist in navigating the terrain and determining your location and elevation.
- Be aware of hazards: Topographic maps can highlight areas at risk from volcanic hazards, such as lava flows, mudslides, and ashfall.
- Consult with park rangers: Rangers at Mount St. Helens National Volcanic Monument can provide valuable information about the area, including hiking trails, safety precautions, and current conditions.
Conclusion
The topographic map of Mount St. Helens is a powerful tool for understanding the volcano’s history, its current state, and the ongoing geological processes that continue to shape the landscape. By examining the contour lines and interpreting the features they represent, we gain a deeper appreciation for the dynamic nature of this iconic volcano and the forces that have shaped its dramatic landscape. The map serves as a reminder of the immense power of nature and the importance of scientific understanding in mitigating the risks associated with volcanic activity.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into topographic map of mt st helens. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!