Uncovering Montana’s Mineral Riches: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geological Landscape
Related Articles: Uncovering Montana’s Mineral Riches: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geological Landscape
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Uncovering Montana’s Mineral Riches: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geological Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Uncovering Montana’s Mineral Riches: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geological Landscape
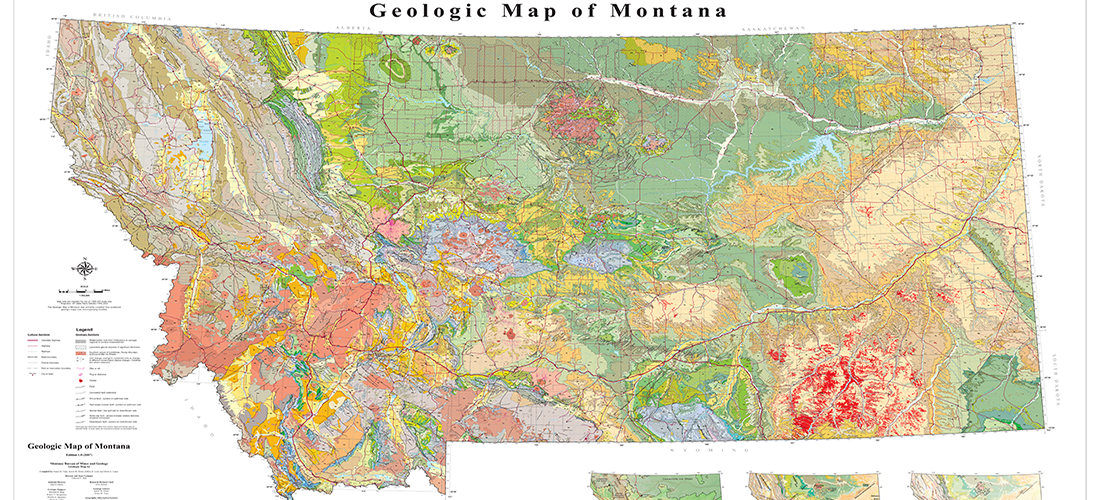
Montana, known for its breathtaking landscapes and diverse ecosystems, also boasts a wealth of mineral resources that have played a pivotal role in its history and continue to shape its economy. Understanding the distribution and significance of these minerals requires a deep dive into the state’s geological map, a valuable tool for researchers, industry professionals, and anyone interested in the natural world.
A Glimpse into Montana’s Geological Past:
Montana’s mineral wealth is a direct consequence of its complex geological history. The state’s bedrock, primarily composed of Precambrian metamorphic and igneous rocks, was formed over billions of years through volcanic eruptions, mountain building, and tectonic activity. These ancient processes left behind vast deposits of various minerals, including precious metals, industrial minerals, and energy resources.
The Montana Minerals Map: A Key to Understanding the State’s Geological Landscape
The Montana Minerals Map, available through the Montana Bureau of Mines and Geology (MBMG), provides a detailed and comprehensive overview of the state’s mineral resources. This map, a visual representation of geological data, is instrumental in understanding the distribution, abundance, and potential economic value of different minerals across Montana.
Key Features of the Montana Minerals Map:
- Mineral Deposits: The map clearly identifies the locations of known mineral deposits, ranging from gold and silver to copper, zinc, and coal.
- Geological Formations: It delineates different geological formations, providing insights into the age, composition, and origin of rocks.
- Mineral Potential Zones: The map highlights areas with high potential for undiscovered mineral deposits, guiding exploration efforts.
- Land Ownership and Access: It indicates land ownership, including public and private lands, facilitating responsible mineral development.
- Environmental Considerations: The map considers environmental factors, such as sensitive ecosystems and water resources, promoting sustainable mining practices.
The Importance of the Montana Minerals Map:
The Montana Minerals Map serves multiple purposes, making it an invaluable resource for various stakeholders:
1. Economic Development:
- Investment Opportunities: The map helps identify potential mineral resources, attracting investors to explore and develop new mines.
- Job Creation: Mining operations generate employment opportunities in various sectors, contributing to economic growth.
- Tax Revenue: Mineral extraction generates tax revenue for the state, funding essential services and infrastructure.
2. Environmental Management:
- Resource Sustainability: The map facilitates responsible resource management, ensuring the long-term availability of minerals.
- Environmental Protection: By identifying sensitive areas, the map helps minimize environmental impacts associated with mining.
- Land Use Planning: It provides valuable information for land use planning, balancing mineral development with other land uses.
3. Education and Research:
- Geological Insights: The map serves as a valuable tool for researchers studying the state’s geology, mineral deposits, and environmental impacts.
- Public Education: It raises awareness about Montana’s mineral resources, fostering public understanding of the mining industry.
4. Historical Context:
- Mining Heritage: The map provides a historical perspective on Montana’s mining history, showcasing the legacy of mineral extraction in the state.
- Cultural Significance: It connects mineral resources to cultural heritage, highlighting the role of mining in shaping Montana’s identity.
Exploring the Map: A Deeper Dive into Montana’s Mineral Riches
The Montana Minerals Map reveals a diverse array of mineral resources, each with its own unique story and economic significance. Here’s a closer look at some key mineral deposits found across the state:
1. Precious Metals:
- Gold: Montana is renowned for its gold deposits, with significant production in the past and ongoing exploration efforts. The state’s gold mines are primarily located in the southwestern and central regions, including the famous gold rush towns of Virginia City and Helena.
- Silver: Montana also holds substantial silver deposits, often found in association with gold. The state’s silver mines are concentrated in the southwestern and central regions, contributing to the state’s mining heritage.
2. Base Metals:
- Copper: Copper deposits are found throughout Montana, with significant mines located in the southwestern and central regions. The state’s copper production plays a crucial role in the national economy, supplying materials for various industries.
- Zinc: Montana also produces zinc, a vital metal used in various applications, including galvanizing steel and manufacturing batteries. Zinc deposits are found in association with copper and other base metals.
3. Industrial Minerals:
- Sand and Gravel: Montana is a significant producer of sand and gravel, essential materials used in construction, road building, and other industries. These resources are widely distributed across the state, contributing to its economic development.
- Limestone: Limestone, a versatile industrial mineral, is used in cement production, agriculture, and water treatment. Montana’s limestone deposits are found in various regions, supporting local industries.
4. Energy Resources:
- Coal: Montana is a major coal producer, with significant reserves located in the eastern and southeastern regions. Coal remains a vital energy source, providing electricity and fuel for various industries.
- Natural Gas: Montana also holds natural gas reserves, which are increasingly being developed to meet growing energy demands. These reserves are found in various regions, contributing to the state’s energy portfolio.
FAQs about the Montana Minerals Map:
1. How can I access the Montana Minerals Map?
The Montana Minerals Map is available online through the Montana Bureau of Mines and Geology (MBMG) website. You can access it through their website or request printed copies.
2. What types of information are included on the map?
The Montana Minerals Map includes information on mineral deposits, geological formations, mineral potential zones, land ownership, and environmental considerations.
3. How can I use the Montana Minerals Map for research purposes?
The map can be used to identify potential mineral deposits, analyze geological formations, and understand the environmental impacts of mining. It can also be used to develop research projects related to mineral resources and their implications.
4. Is the Montana Minerals Map updated regularly?
Yes, the map is updated regularly as new data becomes available. The MBMG continuously monitors mineral exploration and development activities, ensuring the map remains accurate and relevant.
5. How can I contribute to the Montana Minerals Map?
You can contribute to the map by providing information on mineral occurrences, geological formations, or environmental conditions. The MBMG welcomes contributions from individuals, businesses, and research institutions.
Tips for Using the Montana Minerals Map:
- Understand the map’s scale and legend: Familiarize yourself with the map’s scale and legend to interpret the information accurately.
- Use the map in conjunction with other resources: Combine the map with other geological data, such as aerial photographs and satellite imagery, for a more comprehensive understanding.
- Contact the MBMG for assistance: If you have questions or need further clarification, contact the Montana Bureau of Mines and Geology for assistance.
Conclusion:
The Montana Minerals Map serves as a vital tool for understanding the state’s geological landscape and its vast mineral resources. It provides crucial information for economic development, environmental management, education, and research, highlighting the interconnectedness of mineral resources, the environment, and human activities. By leveraging this valuable resource, Montana can continue to develop its mineral wealth while ensuring sustainable practices and protecting its natural heritage.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Uncovering Montana’s Mineral Riches: A Comprehensive Guide to the State’s Geological Landscape. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!