Understanding Georgia’s Growing Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening
Related Articles: Understanding Georgia’s Growing Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Georgia’s Growing Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Georgia’s Growing Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening

Georgia, with its diverse topography and climate, offers a wide range of growing conditions, making it a haven for both seasoned gardeners and enthusiastic beginners. However, navigating the complexities of planting and cultivating in such a varied landscape can be challenging. This is where the Georgia Growing Zone Map comes into play, providing invaluable insights into the specific microclimates across the state and offering essential guidance for successful gardening.
The Significance of Growing Zones
The Georgia Growing Zone Map, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), divides the state into distinct zones based on average annual minimum winter temperatures. This information is crucial for gardeners as it helps them determine which plants are likely to thrive in their specific location. Plants with varying cold hardiness levels, the ability to withstand freezing temperatures, are categorized according to their suitability for each zone.
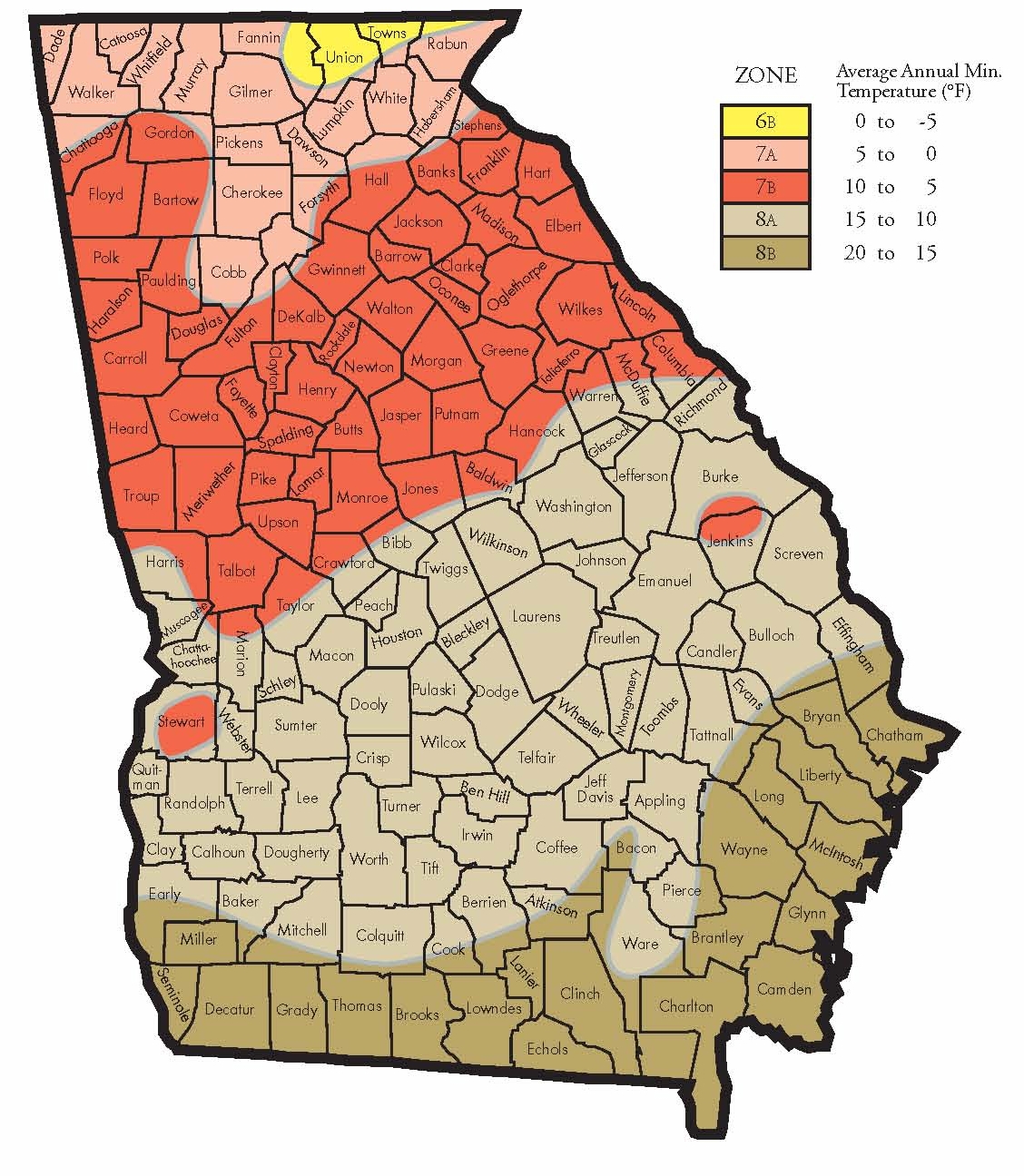
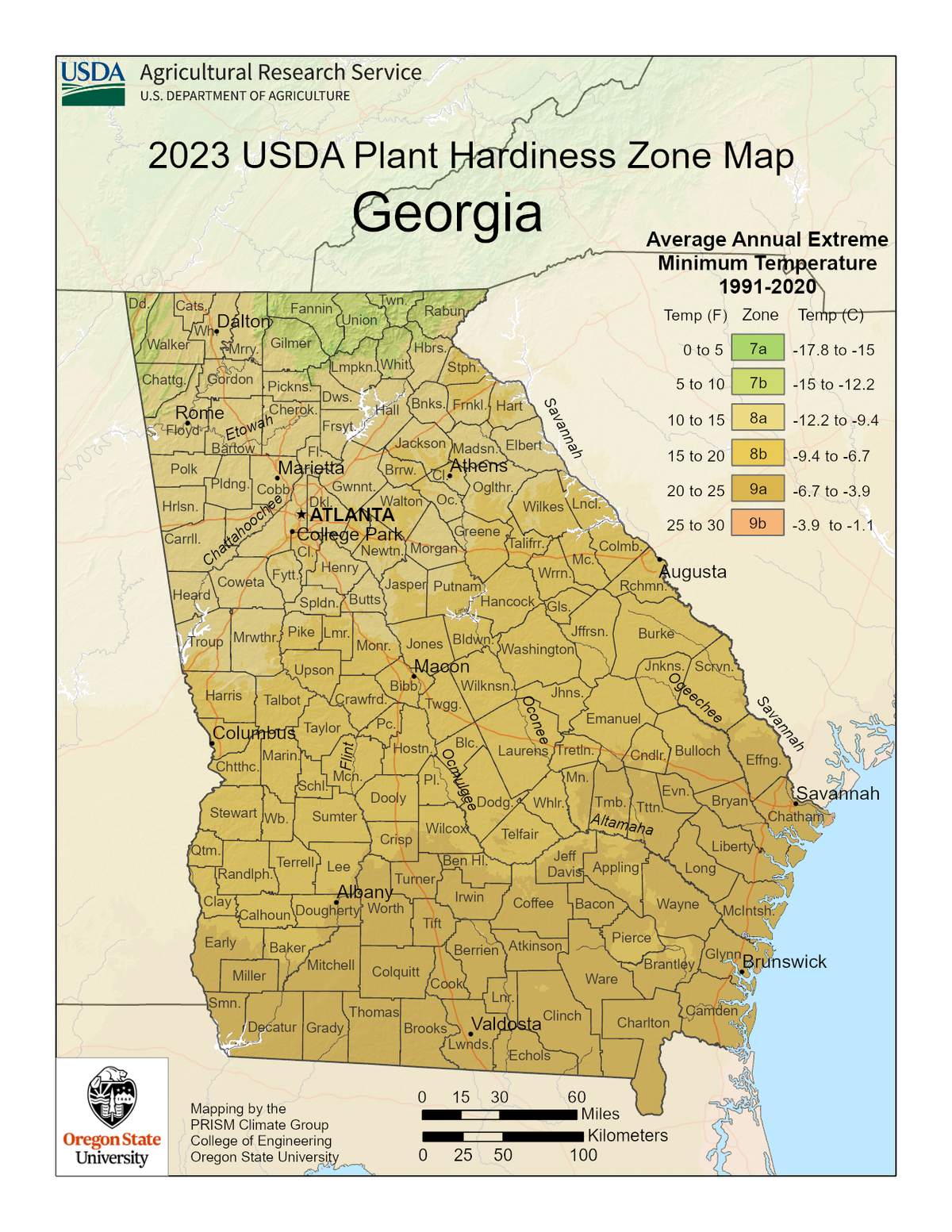
Decoding the Georgia Growing Zone Map
The map features ten distinct zones, ranging from Zone 7a in the northernmost parts of Georgia to Zone 8b in the southernmost regions. Each zone represents a temperature range that plants can tolerate. For example, Zone 7a indicates an average annual minimum winter temperature of 0 to 10 degrees Fahrenheit, while Zone 8b signifies a range of 25 to 30 degrees Fahrenheit.
Navigating the Zones: A Practical Approach
Understanding your specific zone is the first step towards successful gardening. The Georgia Growing Zone Map provides a valuable starting point, but it’s crucial to consider other factors that influence plant growth, such as:
- Microclimates: Even within a single zone, local conditions can vary significantly. Factors like elevation, proximity to bodies of water, and urban heat islands can influence temperatures and create unique microclimates.
- Soil Type: The composition of your soil impacts drainage, nutrient availability, and overall plant health. Understanding your soil type is essential for choosing plants that thrive in your specific conditions.
- Sunlight Exposure: Different plants require varying amounts of sunlight. Consider the amount of direct sunlight your garden receives throughout the day when selecting plants.
Benefits of Utilizing the Georgia Growing Zone Map
The Georgia Growing Zone Map offers numerous benefits for gardeners of all levels:
- Increased Success Rates: By choosing plants suited to your specific zone, you significantly increase their chances of survival and flourishing.
- Reduced Waste and Frustration: Selecting plants that are unlikely to thrive in your climate can lead to wasted resources and disappointment. The map helps you avoid these pitfalls.
- Enhanced Garden Diversity: Understanding the nuances of your zone allows you to explore a wider range of plant options, fostering a diverse and vibrant garden.
- Conservation of Resources: Selecting appropriate plants reduces the need for excessive watering, fertilizers, and other resources, promoting sustainable gardening practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Georgia Growing Zone Map
Q: How can I find my specific growing zone?
A: The Georgia Growing Zone Map is readily available online through various sources, including the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map website. You can also find interactive maps that allow you to pinpoint your location and determine your zone.
Q: What if my garden is located in a transitional zone?
A: Transitional zones occur where two zones meet. In such cases, consider the characteristics of both zones and choose plants that are tolerant of the temperature fluctuations within that range.
Q: Can I grow plants outside of my designated zone?
A: It’s possible, but it’s crucial to select plants with exceptional cold hardiness or provide them with extra protection, such as winterizing measures.
Q: How often is the Georgia Growing Zone Map updated?
A: The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is updated every few years to reflect long-term temperature trends and changes in climate.
Tips for Utilizing the Georgia Growing Zone Map
- Consult with Local Garden Centers: Garden centers in your area have expertise on local growing conditions and can offer specific recommendations for plants suitable for your zone.
- Consider Microclimates: Observe your garden’s microclimates, such as shaded areas or wind-protected spots, to identify potential variations within your zone.
- Experiment with Different Plants: Once you’ve established your zone, don’t be afraid to experiment with a few plants outside of your designated range. You might discover surprising successes!
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of any updates to the Georgia Growing Zone Map and adapt your gardening practices accordingly.
Conclusion
The Georgia Growing Zone Map is an invaluable tool for gardeners seeking to cultivate vibrant and thriving gardens. By understanding the nuances of your specific zone and considering the factors that influence plant growth, you can make informed decisions that lead to successful gardening outcomes. Whether you’re a seasoned horticulturalist or a novice green thumb, the map serves as a valuable resource to guide your gardening journey in Georgia’s diverse landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Georgia’s Growing Zones: A Guide to Successful Gardening. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!