Understanding the Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to Liquefaction Zone Maps
Related Articles: Understanding the Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to Liquefaction Zone Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to Liquefaction Zone Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to Liquefaction Zone Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to Liquefaction Zone Maps
- 3.1 Demystifying Liquefaction Zone Maps
- 3.2 The Importance of Liquefaction Zone Maps
- 3.3 Understanding the Limitations of Liquefaction Zone Maps
- 3.4 FAQs about Liquefaction Zone Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Using Liquefaction Zone Maps Effectively
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to Liquefaction Zone Maps

Earthquakes are powerful forces of nature capable of causing widespread devastation. While seismic waves are the primary cause of damage, a lesser-known phenomenon, soil liquefaction, can amplify the destruction, leading to catastrophic consequences. Liquefaction occurs when saturated, loose soil, under the stress of an earthquake, loses its strength and behaves like a liquid. This sudden change in soil behavior can result in severe damage to buildings, infrastructure, and even loss of life.
To mitigate the risks posed by liquefaction, scientists and engineers have developed liquefaction hazard maps. These maps serve as crucial tools for understanding and managing the potential for soil liquefaction in a specific region. They are essential for urban planning, infrastructure development, and emergency preparedness, providing valuable information for policymakers, engineers, and the general public.
Demystifying Liquefaction Zone Maps
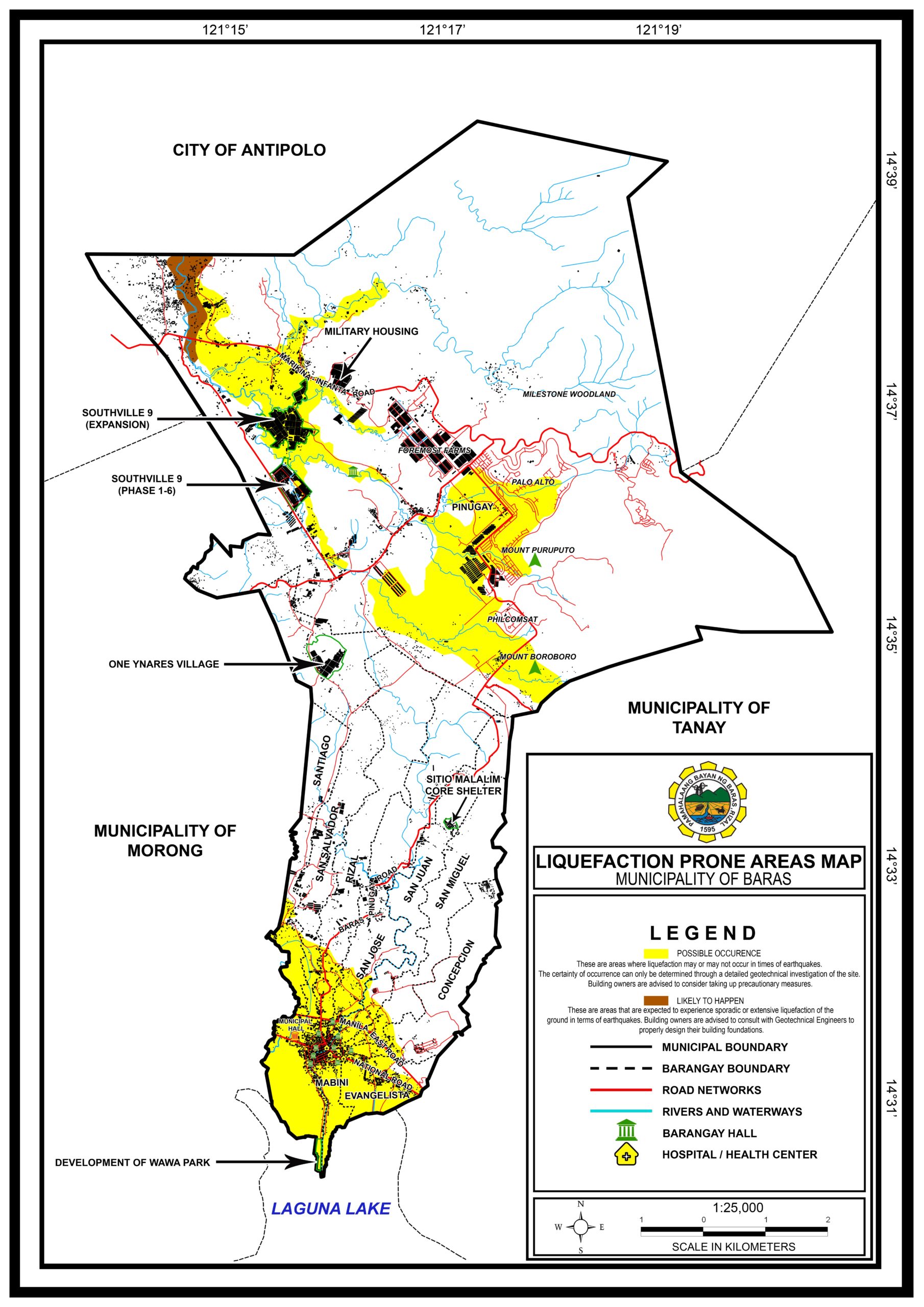
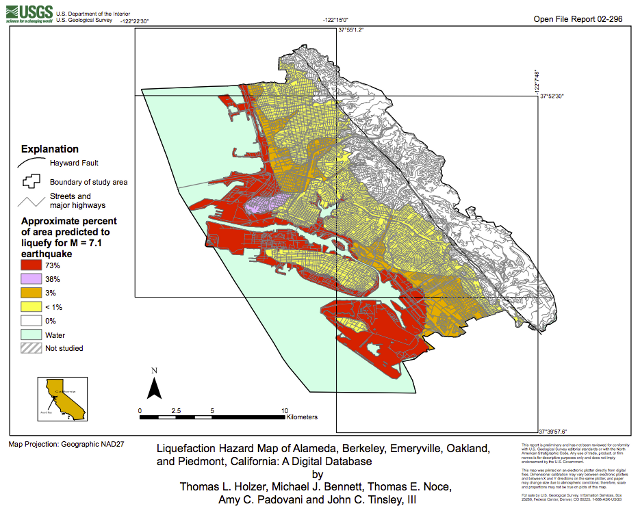
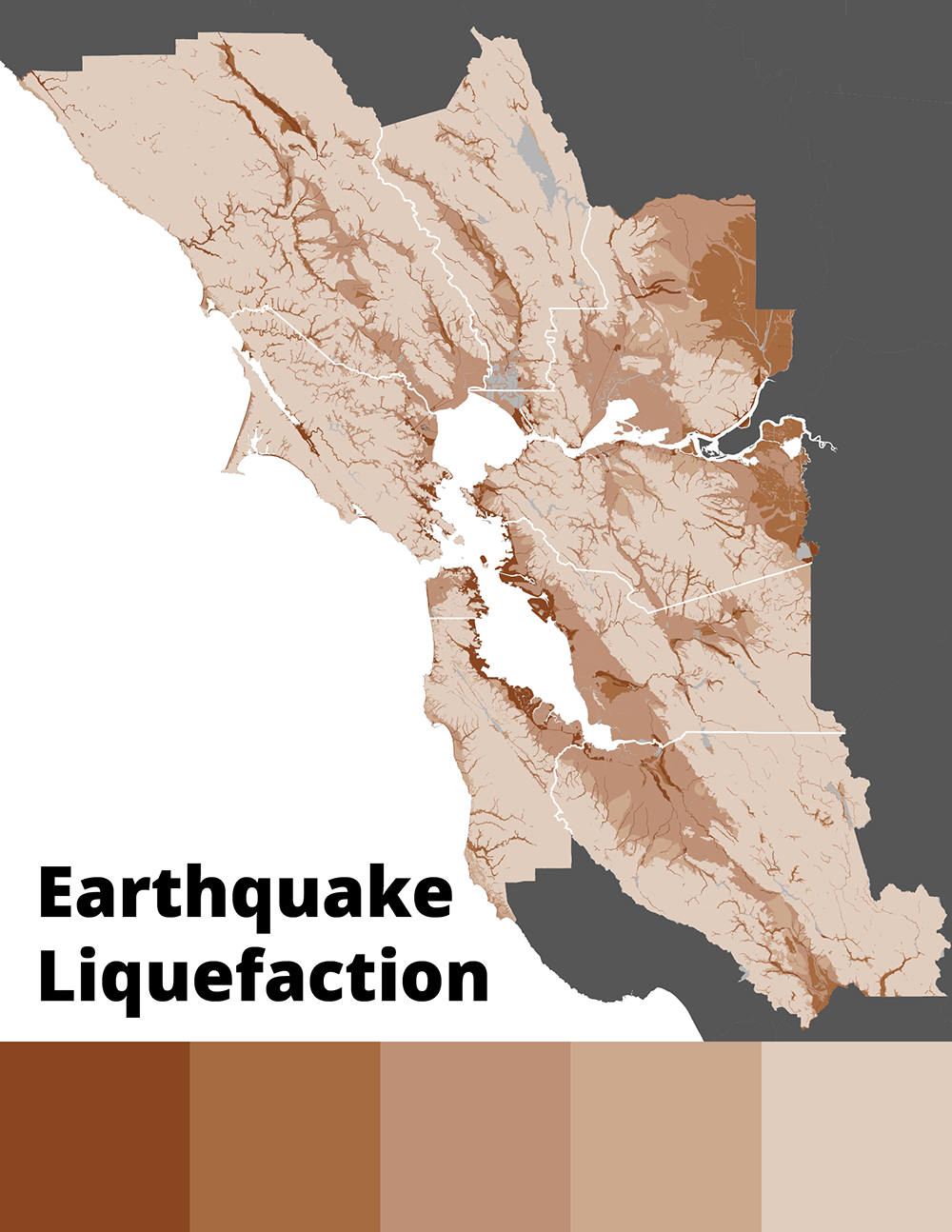
Liquefaction zone maps are spatial representations of the likelihood of soil liquefaction occurring in a specific area. They are typically created using a combination of geological data, soil investigations, and historical earthquake records. The maps are often color-coded, with different colors representing varying levels of liquefaction susceptibility, ranging from low to high.
Key Components of Liquefaction Zone Maps:
- Soil Type and Characteristics: The type of soil and its physical properties, such as grain size, density, and water content, are critical factors influencing liquefaction susceptibility.
- Ground Water Table Depth: The depth of the water table plays a significant role in determining the saturation level of the soil, which directly impacts its liquefaction potential.
- Magnitude and Proximity of Earthquakes: Historical earthquake data, including magnitude and epicenter location, provide valuable insights into the potential for seismic shaking and its impact on soil stability.
- Site-Specific Conditions: Local factors, such as topography, ground slope, and the presence of buried infrastructure, can influence the likelihood of liquefaction.
The Importance of Liquefaction Zone Maps
Liquefaction zone maps play a vital role in mitigating earthquake risks by providing valuable information for various stakeholders:
1. Urban Planning and Development:
- Land Use Planning: Identifying areas prone to liquefaction allows for informed land use planning, minimizing the development of critical infrastructure in high-risk zones.
- Building Codes and Regulations: Liquefaction zone maps inform the development of building codes and regulations, ensuring structures are designed to withstand potential liquefaction hazards.
- Infrastructure Design: Engineering projects, including roads, bridges, and pipelines, can be designed with appropriate mitigation measures to prevent liquefaction-related failures.
2. Emergency Preparedness and Response:
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation: Liquefaction zone maps help communities assess their vulnerability to liquefaction and develop effective mitigation strategies.
- Evacuation Planning: Knowing the potential for liquefaction allows for the development of targeted evacuation plans for high-risk areas, ensuring the safety of residents during earthquakes.
- Emergency Response: Liquefaction zone maps assist emergency responders in identifying areas most likely to be affected by liquefaction, enabling efficient resource allocation and response efforts.
3. Public Awareness and Education:
- Community Engagement: Liquefaction zone maps can be used to educate the public about the potential risks associated with soil liquefaction.
- Building Resilience: Public awareness can encourage individuals to take proactive measures to strengthen their homes and businesses against liquefaction hazards.
- Informed Decision-Making: Knowledge of liquefaction risks empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their property and safety during earthquakes.
Understanding the Limitations of Liquefaction Zone Maps
While liquefaction zone maps are valuable tools for managing earthquake risks, it is crucial to acknowledge their limitations:
- Simplified Representation: Liquefaction zone maps provide a simplified representation of complex geological and seismic conditions. They do not capture the full spectrum of site-specific variations.
- Uncertainty in Data: The accuracy of liquefaction zone maps depends on the quality and availability of data. Uncertainties in geological data, earthquake records, and soil investigations can influence the map’s reliability.
- Dynamic Nature of Ground Conditions: Soil properties can change over time due to factors such as groundwater fluctuations, land development, and natural processes. These changes can alter the liquefaction potential of an area.
FAQs about Liquefaction Zone Maps
1. How are liquefaction zone maps created?
Liquefaction zone maps are developed through a multi-step process involving geological investigations, soil testing, and analysis of historical earthquake data. Geotechnical engineers and seismologists collaborate to assess the liquefaction potential of different areas, considering factors such as soil type, ground water table depth, and seismic shaking intensity.
2. What are the different levels of liquefaction susceptibility shown on the map?
Liquefaction zone maps typically use color coding to represent different levels of liquefaction susceptibility. Common classifications include:
- Low Susceptibility: Areas with minimal potential for liquefaction.
- Moderate Susceptibility: Areas with moderate potential for liquefaction, requiring further investigation.
- High Susceptibility: Areas with a high likelihood of liquefaction, requiring significant mitigation measures.
3. Can I find a liquefaction zone map for my area?
Liquefaction zone maps are often developed and maintained by local, regional, or national authorities. You can contact your local building department, geological survey, or emergency management agency to inquire about the availability of liquefaction zone maps for your area.
4. What can I do if my property is located in a high liquefaction zone?
If your property is located in a high liquefaction zone, it is crucial to consult with a qualified geotechnical engineer to assess the specific risks and develop appropriate mitigation strategies. These strategies may include:
- Ground Improvement Techniques: Techniques such as soil compaction, drainage, and ground reinforcement can improve soil stability and reduce liquefaction potential.
- Building Design Modifications: Structures can be designed with features that enhance their resistance to liquefaction, such as deeper foundations and flexible connections.
- Retrofitting Existing Structures: Existing buildings can be retrofitted with structural improvements to enhance their resistance to liquefaction.
5. Are liquefaction zone maps updated regularly?
Liquefaction zone maps are typically updated periodically to reflect new data, advancements in scientific understanding, and changes in land use patterns. The frequency of updates varies depending on the specific area and the availability of resources.
Tips for Using Liquefaction Zone Maps Effectively
- Consult with Experts: Always consult with qualified geotechnical engineers and seismologists for accurate interpretation of liquefaction zone maps.
- Consider Site-Specific Factors: Remember that liquefaction zone maps provide a general overview of the risk. Site-specific factors can significantly influence the actual liquefaction potential of your property.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date on the latest information and updates regarding liquefaction zone maps and earthquake preparedness.
- Incorporate Mitigation Measures: Implement appropriate mitigation strategies based on the liquefaction risk assessment for your property.
Conclusion
Liquefaction zone maps are essential tools for managing earthquake risks, providing valuable information for planning, development, and emergency preparedness. By understanding the potential for soil liquefaction and implementing appropriate mitigation measures, we can build more resilient communities and protect lives and property.
It is crucial to remember that liquefaction zone maps are not static representations of risk but rather dynamic tools that require ongoing updates and interpretation. By staying informed and proactive, we can effectively manage the risks posed by soil liquefaction and create safer and more resilient environments.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Risks: A Comprehensive Guide to Liquefaction Zone Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!