Understanding the Shifting Political Landscape: An Examination of Lindsey Graham’s District Map Evolution
Related Articles: Understanding the Shifting Political Landscape: An Examination of Lindsey Graham’s District Map Evolution
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Shifting Political Landscape: An Examination of Lindsey Graham’s District Map Evolution. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Shifting Political Landscape: An Examination of Lindsey Graham’s District Map Evolution

Senator Lindsey Graham, a prominent figure in American politics, has represented South Carolina in the United States Senate since 2003. His electoral success is intricately tied to the evolution of his district’s boundaries, a dynamic process influenced by demographic shifts, political realignment, and the intricate dance of redistricting. Examining the historical and current configurations of Graham’s district offers a compelling glimpse into the complex interplay of electoral geography and political power.
A Historical Overview: The Shifting Boundaries of Representation
To grasp the significance of Lindsey Graham’s district map, it is essential to understand the historical context of redistricting in South Carolina. The state’s political landscape has undergone considerable transformation over the past decades, driven by factors such as population growth, urban sprawl, and the changing demographics of its citizenry.
The Pre-2010 Era: A Legacy of Rural Dominance
Prior to the 2010 Census, South Carolina’s congressional districts reflected the state’s predominantly rural character. Graham’s district, encompassing the Upstate region, largely consisted of rural counties with a strong conservative base. This configuration, a product of historical political alignments, favored Republican candidates, providing Graham with a solid electoral advantage.
The Impact of the 2010 Census: A New Era of Redistricting
The 2010 Census revealed a significant shift in South Carolina’s population distribution. The state’s urban areas experienced substantial growth, particularly in the Charleston and Greenville metropolitan areas. This demographic shift triggered a wave of redistricting, aiming to ensure equal representation based on population changes.
The 2011 Redistricting: Reshaping the Political Landscape
The 2011 redistricting process in South Carolina resulted in significant alterations to Graham’s district. The new boundaries incorporated portions of the rapidly growing Greenville metropolitan area, while simultaneously shedding some rural counties. This strategic move aimed to balance the district’s rural and urban constituencies, reflecting the state’s evolving demographics.
The 2020 Census and the Current District Map: A Continued Evolution
The 2020 Census once again highlighted the ongoing population shifts in South Carolina. The Greenville metropolitan area continued to experience substantial growth, while other parts of the state saw more modest gains. This demographic trend led to another round of redistricting, further shaping the contours of Graham’s district.
The Current District Map: A Reflection of a Changing South Carolina
The current district map, reflecting the 2020 redistricting, reflects the continued urban growth in South Carolina. Graham’s district now encompasses a significant portion of the Greenville metropolitan area, including its rapidly expanding suburbs. This shift in boundaries reflects the state’s evolving demographics and the growing influence of urban voters in the state’s political landscape.
Understanding the Importance of District Maps: A Window into Political Power
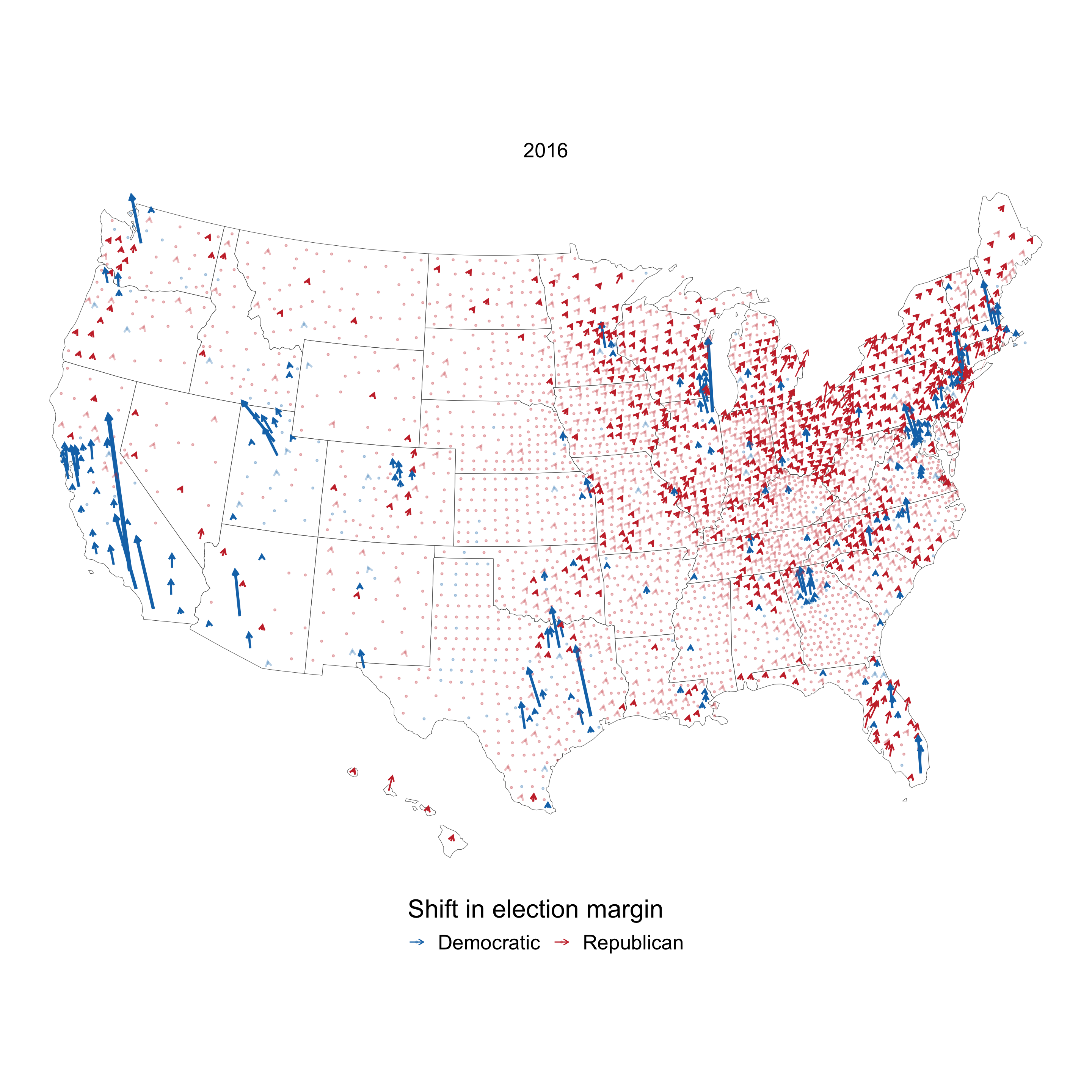
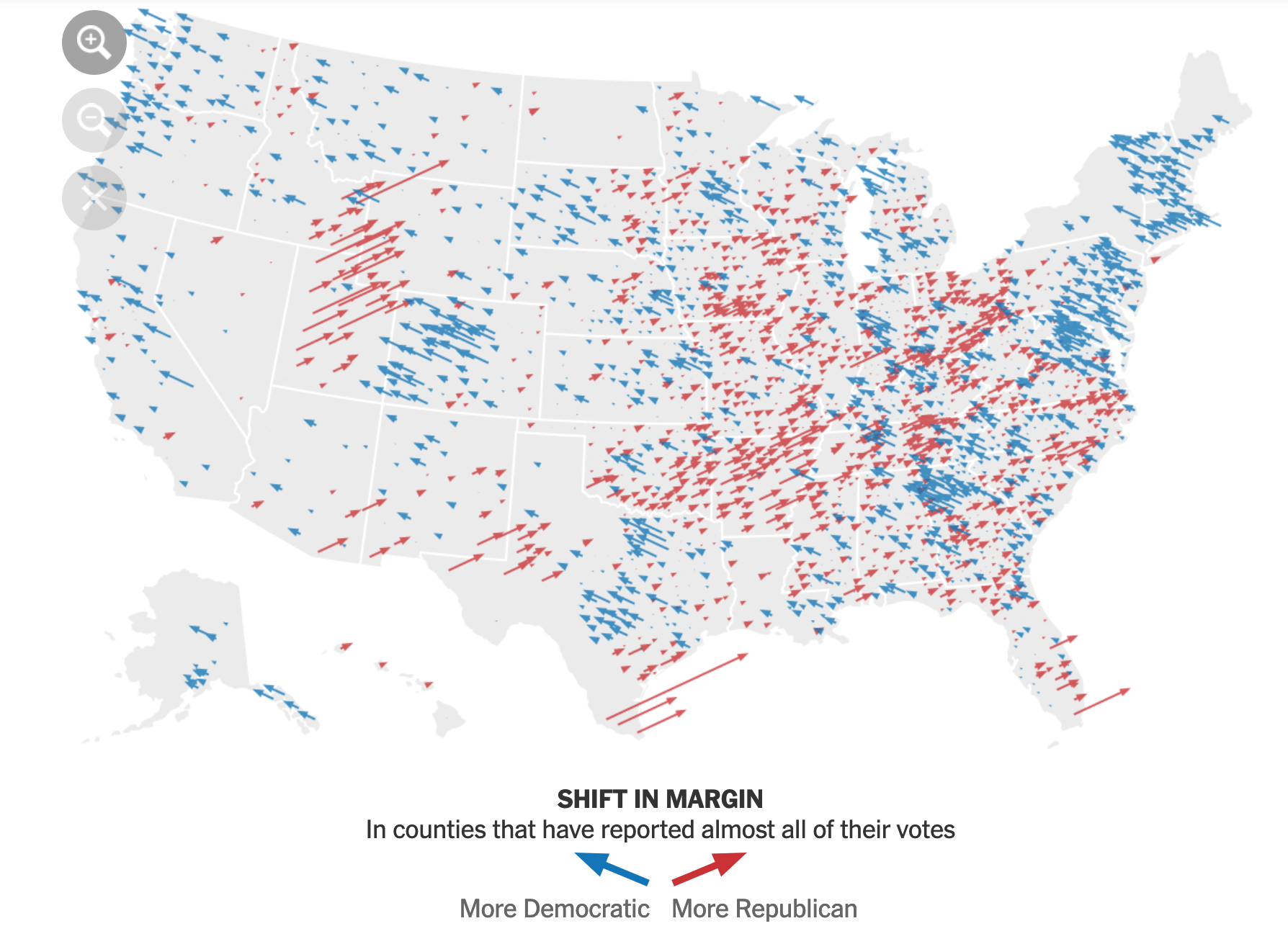
The evolution of Lindsey Graham’s district map underscores the crucial role that redistricting plays in shaping the political landscape. District maps, through their power to define the boundaries of representation, can influence electoral outcomes, the balance of power, and the priorities of elected officials.
The Impact of Gerrymandering: A Controversial Practice with Far-Reaching Consequences
The process of redistricting, while necessary to ensure fair and equal representation, has often been marred by the controversial practice of gerrymandering. Gerrymandering involves manipulating district boundaries to favor a particular party or candidate, often at the expense of fair representation. This practice can have significant consequences for the political process, leading to partisan polarization, reduced voter choice, and a weakening of democratic norms.
The Fight for Fair Representation: A Call for Reform
The potential for gerrymandering has led to widespread calls for reform in redistricting practices. Advocates for fair representation argue for independent commissions, rather than partisan legislatures, to oversee the process, ensuring that district boundaries are drawn based on neutral criteria, such as population equality and geographic contiguity.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Lindsey Graham’s District Map
Q: How has Lindsey Graham’s district map changed over time?
A: Graham’s district map has undergone significant changes since his initial election in 2003. The 2011 redistricting incorporated portions of the growing Greenville metropolitan area, while the 2020 redistricting further expanded the district’s urban footprint.
Q: What are the implications of these changes for Graham’s political prospects?
A: The shifting boundaries of Graham’s district have both advantages and disadvantages. The inclusion of urban voters could potentially increase competition, while the continued presence of a strong conservative base in the Upstate region provides him with a solid electoral foundation.
Q: How does gerrymandering affect the political process?
A: Gerrymandering can distort electoral outcomes, reduce voter choice, and exacerbate partisan polarization. It undermines the principles of fair representation and can lead to a weakening of democratic norms.
Q: What are the arguments for and against independent redistricting commissions?
A: Advocates for independent commissions argue that they provide a more neutral and less partisan approach to redistricting, fostering fair representation and reducing the potential for gerrymandering. Critics argue that such commissions lack accountability and may be susceptible to undue influence.
Tips: Navigating the Complexities of District Maps
Tip 1: Understand the Historical Context: To grasp the significance of a district map, it is essential to understand its historical evolution, including the demographic shifts, political realignments, and redistricting processes that have shaped its boundaries.
Tip 2: Examine the Demographics: Pay attention to the demographic characteristics of a district, including population density, racial composition, and socioeconomic indicators. These factors can provide insights into the electoral dynamics and the potential for political change.
Tip 3: Analyze the Political Landscape: Consider the partisan leanings of a district, the presence of incumbent politicians, and the potential for competitive elections. These factors can help to understand the political climate and the influence of district boundaries on electoral outcomes.
Tip 4: Stay Informed about Redistricting: Keep abreast of the latest developments in redistricting, including legal challenges, public hearings, and the proposed changes to district boundaries. This information can help to understand the ongoing evolution of political representation.
Conclusion: A Continuous Process of Adaptation and Change
The evolution of Lindsey Graham’s district map serves as a compelling case study of the dynamic nature of political representation. The shifting boundaries reflect the ongoing demographic transformations in South Carolina, the complex interplay of electoral geography and political power, and the ongoing debate over fair representation. As the state continues to evolve, so too will the contours of its political districts, shaping the future of South Carolina’s political landscape.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Shifting Political Landscape: An Examination of Lindsey Graham’s District Map Evolution. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!