Unraveling the Network: A Comprehensive Look at Illinois’ Pipeline Infrastructure
Related Articles: Unraveling the Network: A Comprehensive Look at Illinois’ Pipeline Infrastructure
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Network: A Comprehensive Look at Illinois’ Pipeline Infrastructure. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Network: A Comprehensive Look at Illinois’ Pipeline Infrastructure

Illinois, a state strategically positioned at the heartland of the United States, boasts a vast and intricate network of pipelines that play a crucial role in the nation’s energy landscape. These pipelines, transporting a variety of resources including oil, natural gas, and refined products, are essential for powering homes, businesses, and industries across the state and beyond. Understanding the intricacies of this network is crucial for informed decision-making regarding energy policy, environmental considerations, and public safety.
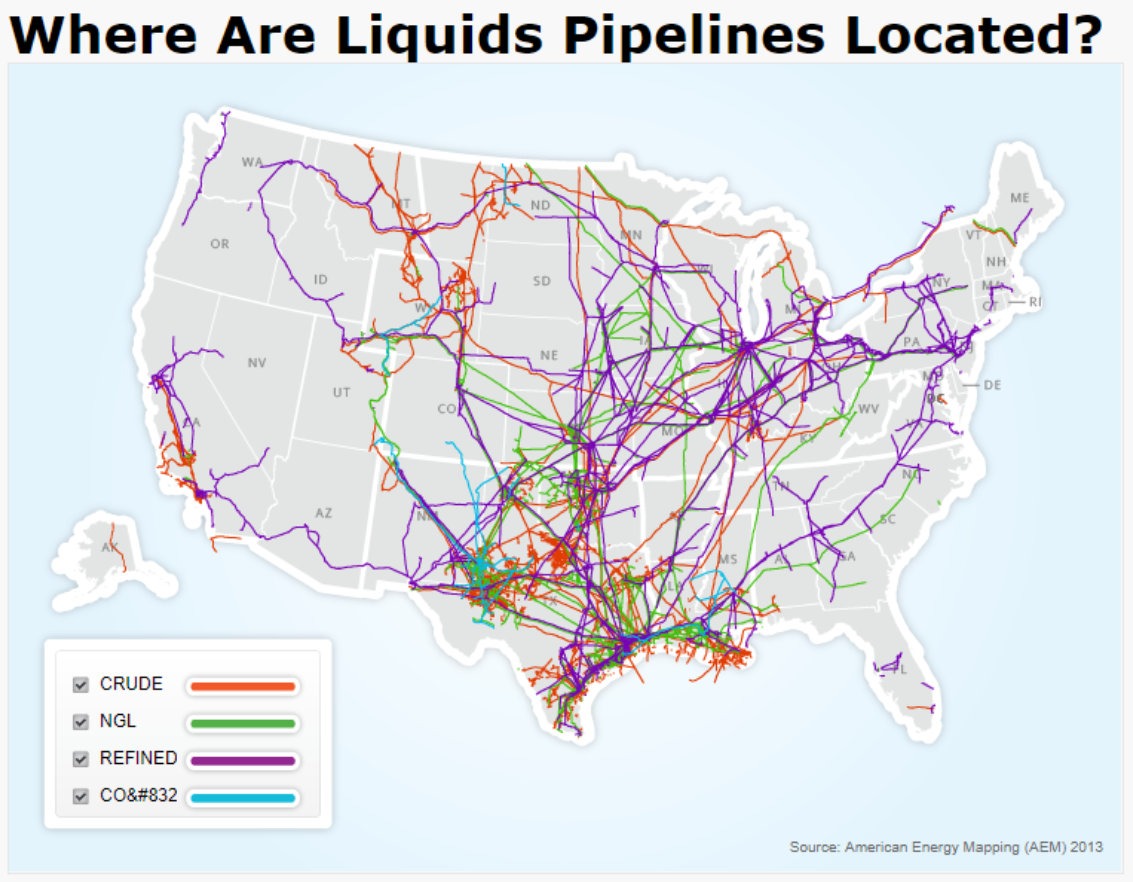
A Visual Representation of Energy Flow: The Illinois Pipeline Map
The Illinois pipeline map is a valuable tool for visualizing the intricate web of pipelines crisscrossing the state. It provides a comprehensive overview of the various pipeline systems, their locations, and the commodities they transport. This map serves as a vital reference point for various stakeholders, including:
- Energy Companies: Pipeline maps enable energy companies to plan and optimize their operations, ensuring efficient transportation of resources and minimizing potential disruptions.
- Government Agencies: Regulatory bodies use pipeline maps to monitor compliance with safety regulations, assess environmental impacts, and ensure the efficient allocation of resources.
- Community Members: Residents can use pipeline maps to understand the location of pipelines in their vicinity, fostering awareness and facilitating informed discussions regarding potential risks and benefits.
- Researchers and Analysts: Academics and industry experts rely on pipeline maps to analyze energy trends, assess the impact of pipeline infrastructure on economic development, and conduct environmental impact studies.
Delving Deeper: Types of Pipelines and Commodities Transported
Illinois’ pipeline network comprises various types of pipelines, each designed to transport specific commodities:
- Crude Oil Pipelines: These pipelines carry raw, unprocessed crude oil extracted from wells to refineries for processing. Illinois is a major hub for crude oil transportation, connecting production areas in the Midwest with refineries along the Gulf Coast and elsewhere.
- Natural Gas Pipelines: Natural gas pipelines transport methane, a clean-burning fossil fuel used for heating homes, generating electricity, and powering industrial processes. Illinois is a major consumer of natural gas, and its pipeline network ensures a steady supply to meet the state’s energy demands.
- Refined Products Pipelines: These pipelines carry refined petroleum products, such as gasoline, diesel fuel, kerosene, and jet fuel, from refineries to distribution terminals and ultimately to consumers. Illinois’ vast network of refined product pipelines ensures the efficient delivery of these essential fuels throughout the state.
- Propane Pipelines: Propane, a versatile fuel used for heating, cooking, and powering vehicles, is transported through dedicated pipelines to various distribution points across Illinois.
- Carbon Dioxide Pipelines: These pipelines transport carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that can be captured from industrial processes and used for enhanced oil recovery or other applications. While less common, carbon dioxide pipelines are gaining importance in the context of climate change mitigation efforts.
Navigating the Map: Key Features and Considerations
The Illinois pipeline map is a dynamic resource, continuously evolving as new pipelines are constructed and existing ones are modified. Understanding the key features of the map is essential for effective interpretation:
- Pipeline Ownership: Each pipeline is identified by its owner, allowing for the identification of specific companies responsible for the operation and maintenance of the infrastructure.
- Pipeline Diameter: The diameter of the pipeline indicates its capacity, revealing the volume of commodities it can transport.
- Pipeline Material: The material used for construction, such as steel or plastic, influences the pipeline’s durability and safety.
- Pipeline Routing: The map showcases the path of each pipeline, revealing its connection to other infrastructure and its proximity to populated areas.
- Pipeline Status: The map often indicates the operational status of each pipeline, whether it is active, under construction, or decommissioned.
Beyond the Map: Understanding the Importance of Pipeline Safety
While the Illinois pipeline map provides valuable insights into the state’s energy infrastructure, it is crucial to recognize the importance of pipeline safety. Pipeline accidents can have devastating consequences, impacting human health, the environment, and the economy. To mitigate these risks, several measures are in place:
- Stringent Regulations: Federal and state agencies implement comprehensive regulations governing the construction, operation, and maintenance of pipelines, ensuring compliance with safety standards.
- Regular Inspections: Pipelines undergo periodic inspections to detect potential leaks, corrosion, and other issues that could compromise safety.
- Advanced Monitoring Systems: Modern pipelines are equipped with sophisticated monitoring systems that detect and alert operators to any anomalies or potential problems.
- Emergency Response Plans: Pipeline operators are required to develop and maintain detailed emergency response plans to address potential accidents and minimize their impact.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Illinois Pipelines
1. What are the benefits of pipelines?
Pipelines offer several advantages over other modes of transportation:
- Efficiency: Pipelines are the most efficient way to transport large volumes of liquids and gases over long distances.
- Reliability: Pipelines are generally more reliable than other modes of transportation, as they are less susceptible to weather disruptions.
- Safety: Modern pipelines are designed and operated with stringent safety measures in place, minimizing the risk of accidents.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Pipelines are often the most cost-effective way to transport large volumes of commodities.
2. What are the environmental concerns associated with pipelines?
Pipelines can have potential environmental impacts, including:
- Habitat Fragmentation: Pipeline construction can disrupt natural habitats and fragment wildlife corridors.
- Water Contamination: Leaks or spills from pipelines can contaminate water sources, posing risks to human health and ecosystems.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Pipeline operations can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change.
3. How are pipeline safety regulations enforced?
Pipeline safety is regulated by both federal and state agencies. The Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (PHMSA) sets national standards for pipeline construction, operation, and maintenance. Illinois also has its own pipeline safety regulations, which may be more stringent than federal standards.
4. What are the risks associated with pipelines?
Pipelines, while generally safe, pose potential risks:
- Leaks and Spills: Leaks or spills can occur due to corrosion, mechanical failure, or external damage.
- Explosions: Under certain conditions, leaks can ignite, leading to explosions.
- Environmental Damage: Leaks and spills can contaminate water sources and harm wildlife.
5. How can I learn more about pipelines in my area?
You can access information about pipelines in your area through various resources:
- Illinois Pipeline Map: The Illinois pipeline map provides a comprehensive overview of the state’s pipeline network.
- Pipeline Operator Websites: Pipeline operators often provide information about their pipelines, including safety records and environmental impact assessments.
- State and Federal Agencies: The Illinois Department of Natural Resources and the PHMSA offer information about pipeline regulations and safety.
Tips for Engaging with Pipeline Issues
- Stay Informed: Stay informed about pipeline issues in your community and the state by following news reports, attending public meetings, and contacting your elected officials.
- Participate in Public Comment Periods: When proposed pipeline projects are under review, participate in public comment periods to express your concerns and suggestions.
- Support Pipeline Safety Initiatives: Support organizations that advocate for pipeline safety and environmental protection.
- Engage in Dialogue: Engage in respectful dialogue with others who hold different perspectives on pipeline issues, fostering understanding and finding common ground.
Conclusion: A Vital Infrastructure for a Modern Society
Illinois’ pipeline network is a testament to the state’s pivotal role in the national energy landscape. This intricate web of pipelines, transporting essential resources, fuels homes, businesses, and industries, driving economic growth and ensuring the well-being of communities. By understanding the complexities of this infrastructure, its benefits, and its potential risks, we can foster informed discussions about energy policy, environmental protection, and public safety, ensuring that Illinois’ pipelines continue to serve as a vital artery for the state’s prosperity.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Network: A Comprehensive Look at Illinois’ Pipeline Infrastructure. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!