Unraveling the Power of SWOT Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Planning
Related Articles: Unraveling the Power of SWOT Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Planning
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Power of SWOT Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Planning. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Power of SWOT Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Planning
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Power of SWOT Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Planning
- 3.1 Understanding the Fundamentals of SWOT Analysis
- 3.2 The Power of SWOT Analysis: Unveiling Strategic Insights
- 3.3 Applying SWOT Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.4 FAQs about SWOT Analysis
- 3.5 Tips for Effective SWOT Analysis
- 3.6 Conclusion: Unleashing the Potential of Strategic Planning
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Power of SWOT Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Planning
In the dynamic world of business, strategic planning is paramount for success. To navigate the complexities of competition and market fluctuations, organizations rely on a robust framework for understanding their strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This framework, known as SWOT analysis, provides a structured approach for identifying critical factors that influence an organization’s current state and future trajectory.
Understanding the Fundamentals of SWOT Analysis
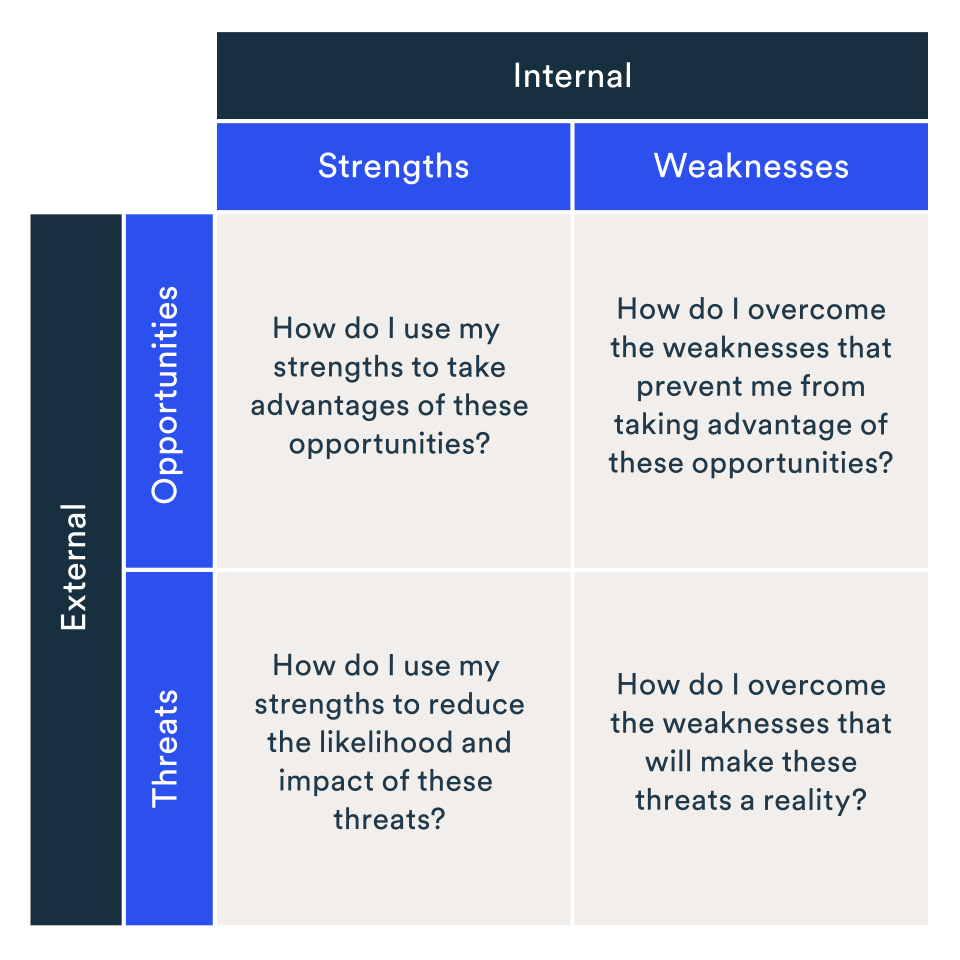
SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool that helps organizations identify their internal strengths and weaknesses, and external opportunities and threats. By systematically evaluating these four key elements, organizations can gain valuable insights into their competitive landscape and develop informed strategies for achieving their objectives.
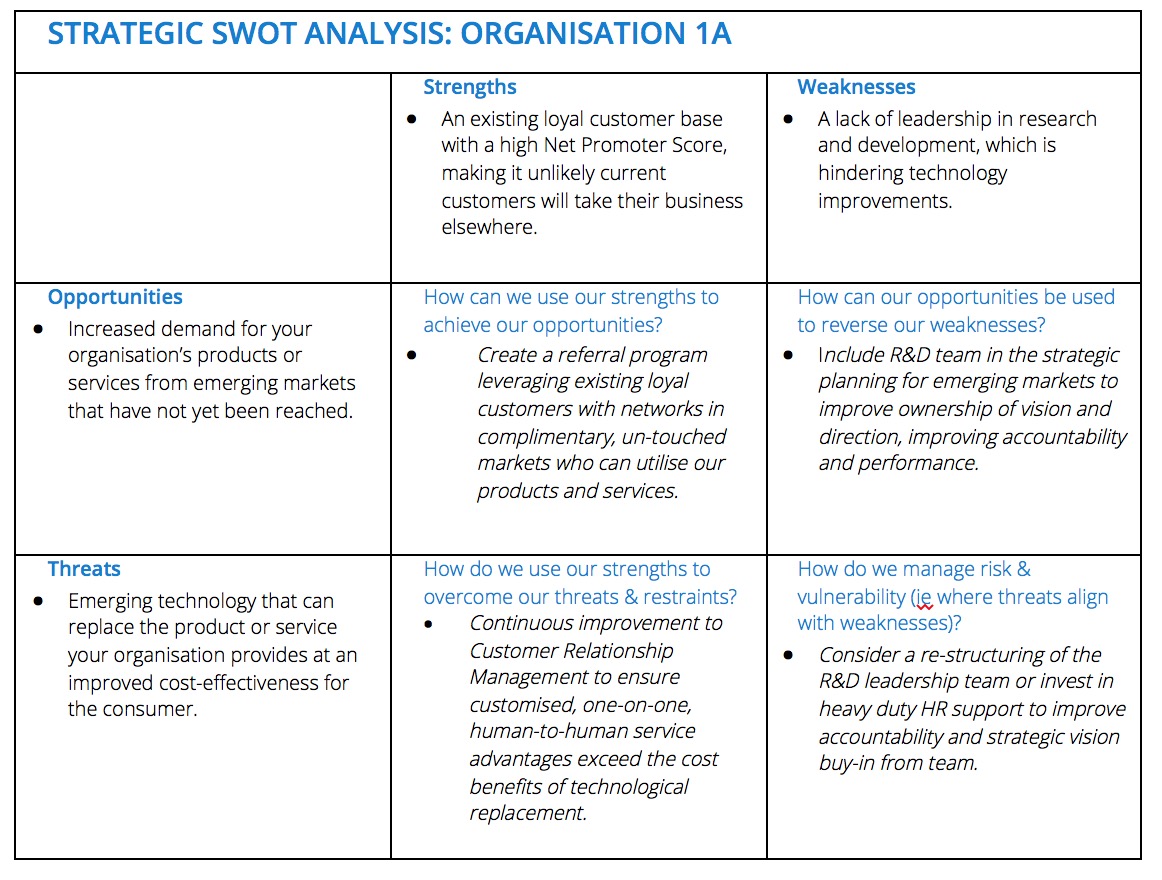
1. Strengths: Strengths represent the internal capabilities and advantages that an organization possesses. These can include factors such as:
- Strong brand reputation: A well-established and positive brand image can attract customers and foster loyalty.
- Experienced workforce: A team of skilled and knowledgeable employees can contribute to operational efficiency and innovation.
- Financial stability: Adequate financial resources provide flexibility and the ability to invest in growth initiatives.
- Proprietary technology: Unique or advanced technology can provide a competitive edge in the market.
2. Weaknesses: Weaknesses refer to internal limitations or shortcomings that hinder an organization’s performance. These can include:
- Outdated technology: Antiquated systems can limit efficiency and competitiveness.
- Lack of skilled personnel: A shortage of qualified employees can hamper productivity and innovation.
- High debt levels: Excessive debt can restrict financial flexibility and jeopardize long-term stability.
- Weak brand image: A negative or unclear brand perception can deter customers and hinder market penetration.
3. Opportunities: Opportunities represent external factors that can be leveraged for growth and expansion. These can include:
- Emerging markets: New markets with high growth potential can offer significant expansion opportunities.
- Technological advancements: New technologies can create opportunities for innovation and product development.
- Favorable government policies: Supportive regulations and incentives can boost business operations.
- Changing consumer preferences: Shifting consumer tastes and trends can create new markets and demand for specific products or services.
4. Threats: Threats refer to external factors that pose challenges or risks to an organization’s success. These can include:
- Increased competition: New entrants or existing competitors can erode market share and profitability.
- Economic downturns: Recessions or financial crises can impact consumer spending and reduce demand for goods and services.
- Changing regulations: New laws or regulations can impose burdens on businesses and affect their operations.
- Technological disruption: Rapid advancements in technology can quickly obsolete existing products or services.
The Power of SWOT Analysis: Unveiling Strategic Insights
SWOT analysis serves as a powerful tool for strategic planning by providing a comprehensive framework for understanding an organization’s internal and external environment. By identifying strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, organizations can gain valuable insights that inform strategic decision-making.
1. Identifying Competitive Advantages: SWOT analysis helps organizations pinpoint their unique strengths and identify how these can be leveraged to gain a competitive advantage. This understanding allows for the development of strategies that exploit strengths to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate threats.
2. Addressing Weaknesses and Threats: By recognizing internal weaknesses and external threats, organizations can prioritize efforts to address these vulnerabilities. This may involve investing in training programs to enhance skills, upgrading technology to improve efficiency, or developing contingency plans to mitigate potential risks.
3. Exploring Growth Opportunities: SWOT analysis helps organizations identify promising opportunities for growth and expansion. This can involve developing new products or services, entering new markets, or forming strategic partnerships.
4. Developing Actionable Strategies: The insights gained from SWOT analysis provide a foundation for developing actionable strategies that address key challenges and capitalize on opportunities. This includes setting clear objectives, allocating resources effectively, and implementing initiatives to achieve desired outcomes.
Applying SWOT Analysis: A Step-by-Step Guide
Conducting a comprehensive SWOT analysis involves a systematic process that ensures all relevant factors are considered. Here’s a step-by-step guide for conducting an effective SWOT analysis:
1. Define the Scope: Clearly define the scope of the analysis, specifying the specific organization, product, or service under consideration.
2. Gather Information: Collect relevant data from various sources, including internal reports, market research, customer feedback, industry publications, and competitor analysis.
3. Identify Strengths and Weaknesses: Analyze the organization’s internal capabilities and limitations, focusing on factors such as financial resources, human capital, technology, and brand reputation.
4. Identify Opportunities and Threats: Analyze the external environment, considering factors such as market trends, technological advancements, economic conditions, and regulatory changes.
5. Prioritize Factors: Rank the identified strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in order of importance, considering their potential impact on the organization’s success.
6. Develop Strategies: Based on the prioritized factors, develop actionable strategies that address key challenges and leverage opportunities.
7. Implement and Monitor: Implement the chosen strategies and closely monitor their effectiveness. Regularly review and adjust strategies as needed to adapt to changing circumstances.
FAQs about SWOT Analysis
1. What is the purpose of SWOT analysis?
The purpose of SWOT analysis is to provide a comprehensive understanding of an organization’s internal and external environment, enabling the development of informed strategies for achieving its objectives.
2. Who should use SWOT analysis?
SWOT analysis is a valuable tool for any organization, regardless of size or industry. It is particularly beneficial for:
- Startups: Identifying market opportunities and developing a competitive edge.
- Small businesses: Evaluating internal strengths and weaknesses to improve operations.
- Large corporations: Analyzing market trends and formulating strategic growth initiatives.
3. How often should a SWOT analysis be conducted?
SWOT analysis should be conducted periodically, ideally on an annual basis, or more frequently in highly dynamic industries or during periods of significant change.
4. What are some common pitfalls of SWOT analysis?
- Oversimplification: SWOT analysis should not be overly simplistic, as it requires a thorough understanding of complex factors.
- Bias: Personal opinions and biases can influence the analysis, leading to inaccurate conclusions.
- Lack of action: SWOT analysis should not be a purely theoretical exercise; it should lead to actionable strategies.
Tips for Effective SWOT Analysis
- Engage stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders, including employees, customers, and industry experts, to gather diverse perspectives.
- Be specific and measurable: Use quantifiable data and specific examples to support your findings.
- Consider both short-term and long-term implications: Analyze the potential impact of factors on the organization’s present and future success.
- Prioritize actions: Focus on the most critical strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that will have the greatest impact.
Conclusion: Unleashing the Potential of Strategic Planning
SWOT analysis is a powerful tool for organizations seeking to navigate the complexities of the business world. By understanding their internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats, organizations can develop informed strategies that maximize their potential for success. By applying the principles of SWOT analysis and embracing a proactive approach to strategic planning, organizations can navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and achieve sustainable growth in a dynamic and competitive landscape.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Power of SWOT Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide to Strategic Planning. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!