Unraveling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Acquiring Topographic Maps
Related Articles: Unraveling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Acquiring Topographic Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Acquiring Topographic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unraveling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Acquiring Topographic Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unraveling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Acquiring Topographic Maps
- 3.1 Online Resources: A Digital Gateway to Topographic Maps
- 3.2 Traditional Sources: A Tangible Approach to Topographic Maps
- 3.3 FAQs: Navigating the Terrain of Topographic Map Acquisition
- 3.4 Tips for Selecting the Right Topographic Map
- 3.5 Conclusion: Embracing the Terrain with Topographic Maps
- 4 Closure
Unraveling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Acquiring Topographic Maps
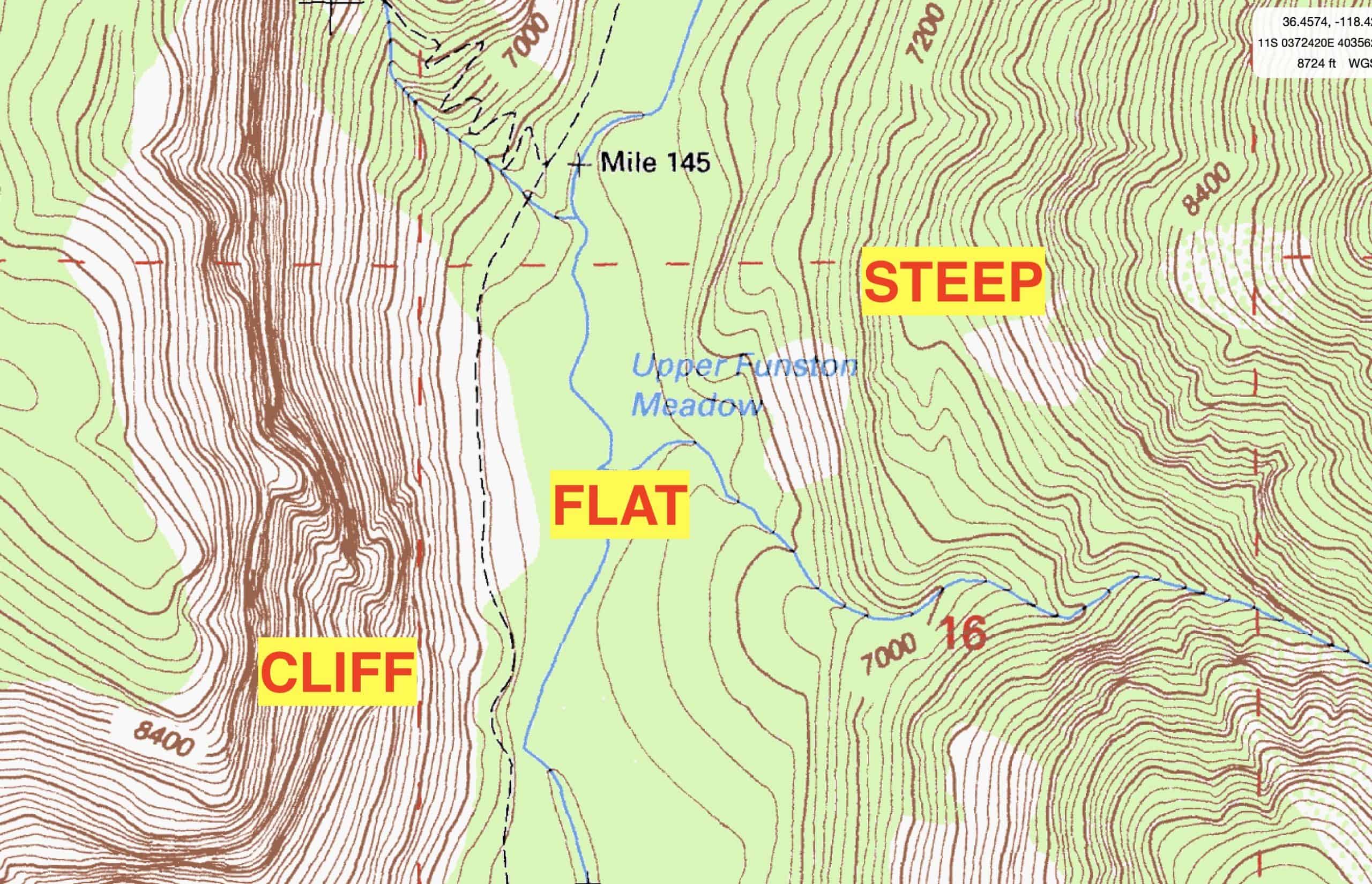
Topographic maps, with their intricate lines and detailed contours, hold the key to understanding the earth’s surface. They offer a precise and visual representation of elevation, terrain features, and geographical elements, serving as invaluable tools for a wide range of applications. Whether you are an avid hiker, a seasoned surveyor, a curious student, or a professional involved in construction or environmental management, knowing where to access these invaluable maps is crucial. This comprehensive guide delves into the various avenues available for acquiring topographic maps, providing a clear roadmap for navigating the world of terrain data.
Online Resources: A Digital Gateway to Topographic Maps
The internet has revolutionized map accessibility, offering a plethora of platforms where topographic maps can be obtained quickly and conveniently. These resources cater to diverse needs, providing options for both free and paid map services.
1. Government Agencies:
-
United States Geological Survey (USGS): The USGS, a leading source for topographic data, provides access to a vast collection of maps through its website, The National Map. This platform allows users to download maps in various formats, including PDF, GeoTIFF, and Shapefile, enabling customization and integration with other geographic information systems (GIS). The USGS also offers a wide range of other geospatial data, such as aerial imagery, elevation data, and land cover information.
-
National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA): The NGA, responsible for providing geospatial intelligence to the U.S. government, makes some of its topographic maps available to the public through its website. These maps, often designed for military purposes, offer detailed information on terrain features, infrastructure, and other key geographic elements.
-
Other National Agencies: Many countries maintain their own national mapping agencies, offering similar resources and services. For instance, the Ordnance Survey in the United Kingdom, the Institut Géographique National (IGN) in France, and the Geological Survey of Canada provide access to topographic maps of their respective territories.
2. Commercial Mapping Services:
-
Esri ArcGIS Online: Esri, a leading provider of geographic information systems (GIS) software, offers a cloud-based mapping platform, ArcGIS Online, that includes access to a wide range of topographic maps. Users can explore, analyze, and share maps with others, leveraging advanced tools for spatial analysis and visualization.
-
MapQuest: While primarily known for its street maps, MapQuest also offers topographic maps for various regions. These maps are often integrated with other features, such as elevation profiles and satellite imagery, providing a comprehensive view of the terrain.
-
Google Earth: Google Earth, a popular virtual globe platform, provides access to topographic maps as part of its basemap options. Users can explore the terrain in three dimensions, zooming in and out to view detailed features.
3. Specialized Mapping Platforms:
-
OpenStreetMap: This collaborative, open-source mapping project allows users to contribute and access topographic maps worldwide. The data is freely available and can be downloaded or accessed through various online tools, including the OpenStreetMap website and dedicated mapping applications.
-
TopoFusion: This online platform offers a comprehensive collection of topographic maps, aerial imagery, and other geospatial data. Users can access maps in various formats, including PDF, GeoTIFF, and Shapefile, and utilize advanced tools for analysis and visualization.
Traditional Sources: A Tangible Approach to Topographic Maps
While digital resources dominate the landscape of map acquisition, traditional sources still hold relevance, offering unique benefits and a tangible experience.
1. Physical Map Stores:
-
Specialty Map Stores: These stores, often found in cities with a strong outdoor recreation or travel culture, offer a curated selection of topographic maps. They provide knowledgeable staff who can assist in finding the right maps for specific needs and destinations.
-
Bookstores: Many large bookstores carry a selection of topographic maps, particularly those focusing on popular hiking and camping destinations.
2. Government Agencies:
-
USGS Map Sales: The USGS offers a wide range of topographic maps for purchase through its website and physical stores. These maps are available in various formats, including paper, digital, and custom print-on-demand options.
-
Other National Agencies: Similar to online resources, many national mapping agencies offer physical maps for purchase through their offices or online stores.
FAQs: Navigating the Terrain of Topographic Map Acquisition
1. What is the best way to find topographic maps for a specific location?
The best approach depends on your needs and preferences. For online resources, start with government agency websites like the USGS, NGA, or their international counterparts. Commercial mapping services like Esri ArcGIS Online, MapQuest, and Google Earth can provide a wider range of options, including detailed maps and aerial imagery. If you prefer physical maps, visit specialty map stores or bookstores, or explore government agency map sales outlets.
2. What are the different formats available for topographic maps?
Topographic maps are available in various formats, including:
- Paper maps: Traditional paper maps offer a tangible experience and are suitable for field use.
- Digital maps: These maps are available in various formats, such as PDF, GeoTIFF, and Shapefile, allowing for easy viewing, printing, and integration with other software.
- Online maps: Interactive online maps provide a dynamic experience, allowing for zooming, panning, and overlaying additional data.
3. Are there any free topographic map resources available?
Yes, several free resources offer topographic maps. Government agencies like the USGS and NGA provide free access to a wide range of maps through their websites. Additionally, OpenStreetMap offers a collaborative, open-source mapping platform where users can contribute and access free maps worldwide.
4. How can I find topographic maps for specific activities, such as hiking or camping?
Many online resources and map stores specialize in maps for outdoor recreation. Websites like AllTrails and Gaia GPS offer detailed maps for hiking and backpacking trails, while specialty map stores often carry maps designed for specific regions and activities.
5. What are the key features to look for in a topographic map?
Topographic maps should include the following key features:
- Contour lines: These lines represent elevation changes, providing a visual representation of the terrain.
- Elevation points: These points indicate specific elevations on the map, providing reference points for determining altitude.
- Geographic features: Maps should include features like rivers, lakes, roads, and buildings, providing context and orientation.
- Scale: The map’s scale indicates the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground.
- Legend: The legend explains the symbols and markings used on the map, ensuring understanding of the map’s information.
Tips for Selecting the Right Topographic Map
- Define your purpose: Identify the specific activity or application for which you need the map. This will help you determine the required level of detail, scale, and features.
- Consider the region: Choose maps specifically designed for the region you are exploring. Maps tailored to specific areas offer more detailed information on local features and points of interest.
- Evaluate the map’s scale: The scale indicates the ratio between distances on the map and real-world distances. Choose a scale that provides the appropriate level of detail for your needs.
- Check the map’s date: Ensure the map is up-to-date, as terrain features and infrastructure can change over time.
- Explore multiple sources: Compare maps from different sources to find the best fit for your requirements and budget.
Conclusion: Embracing the Terrain with Topographic Maps
Navigating the world of topographic maps requires a strategic approach, utilizing diverse resources and understanding the nuances of each option. Whether you are seeking detailed digital maps for professional applications or traditional paper maps for outdoor adventures, the avenues for acquiring these valuable tools are plentiful. By leveraging the power of online platforms, government agencies, specialized map stores, and traditional resources, you can unlock the secrets of the terrain and gain a deeper understanding of the Earth’s intricate landscape. With the right map in hand, you are equipped to explore, analyze, and navigate the world with confidence.
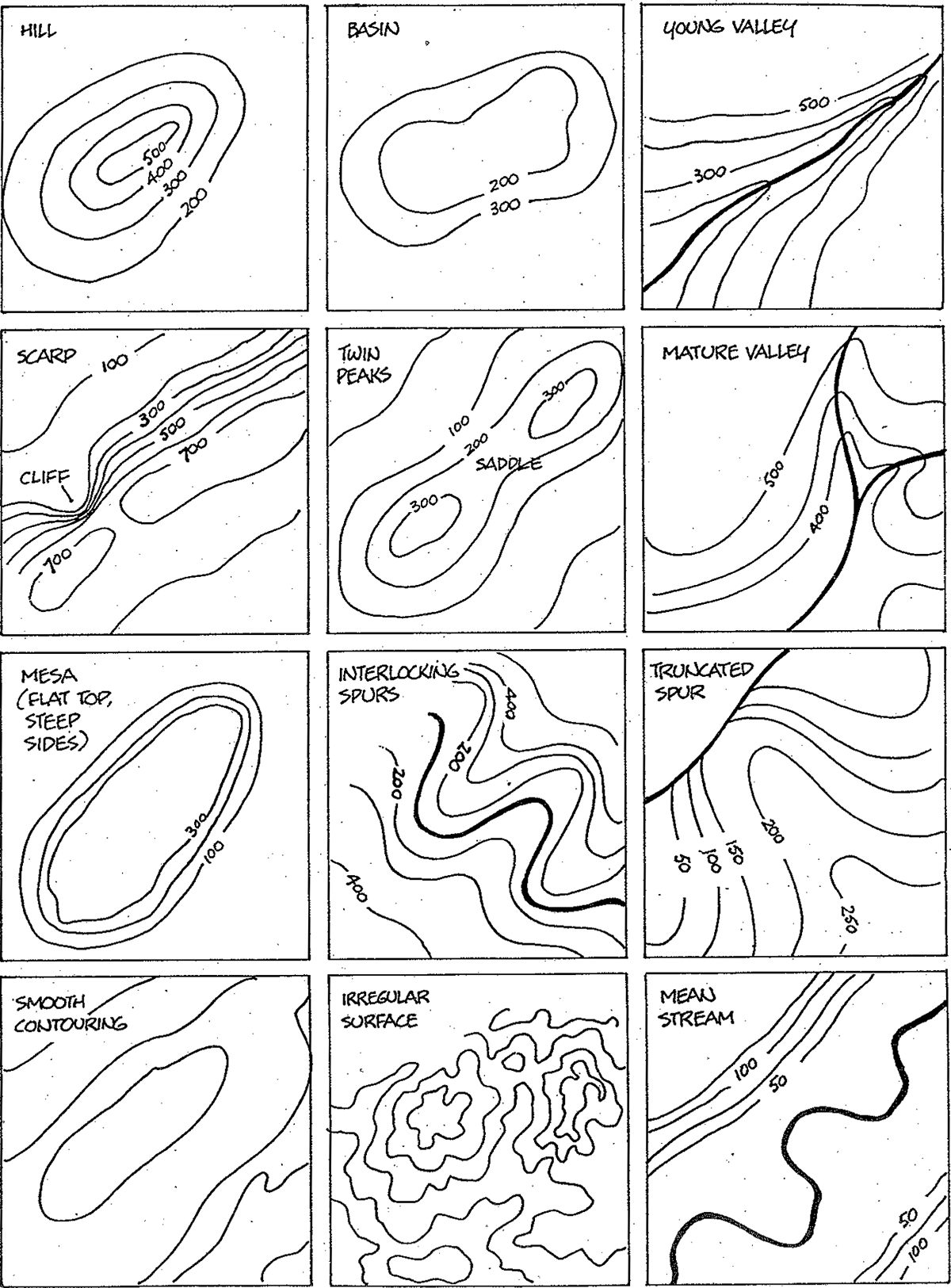



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Terrain: A Comprehensive Guide to Acquiring Topographic Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!