Unveiling India: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Subcontinent’s Geography
Related Articles: Unveiling India: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Subcontinent’s Geography
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling India: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Subcontinent’s Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling India: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Subcontinent’s Geography
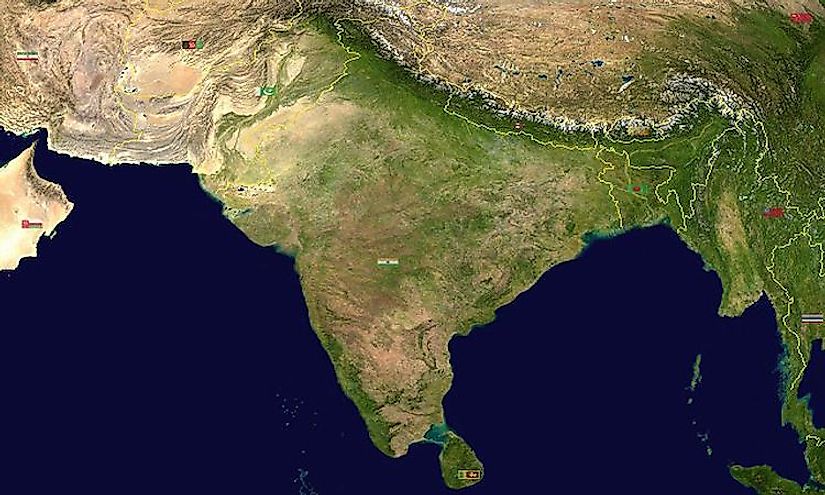
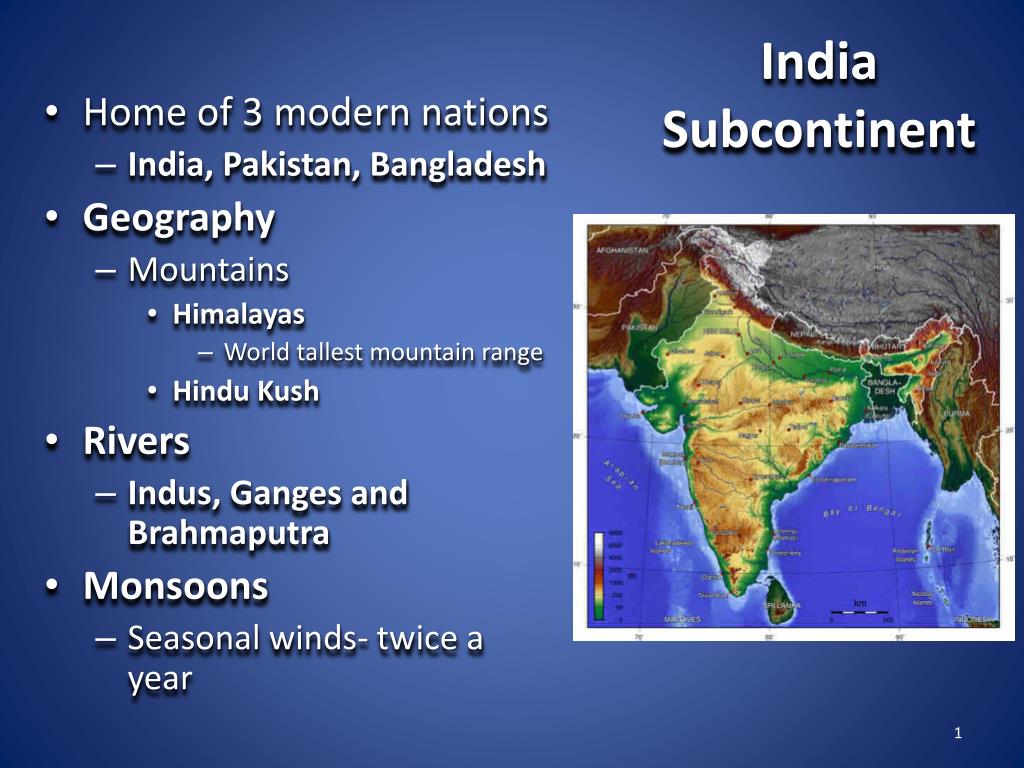
India, a vast and diverse nation, holds a captivating allure for travelers, historians, and geographers alike. Its intricate tapestry of cultures, landscapes, and languages is woven together by a complex geography that is best understood through the lens of a map. This article delves into the significance of understanding India’s geographical features, exploring its diverse regions and the unique characteristics that define each.
The Importance of a Map: A Visual Journey Through India’s Landscape
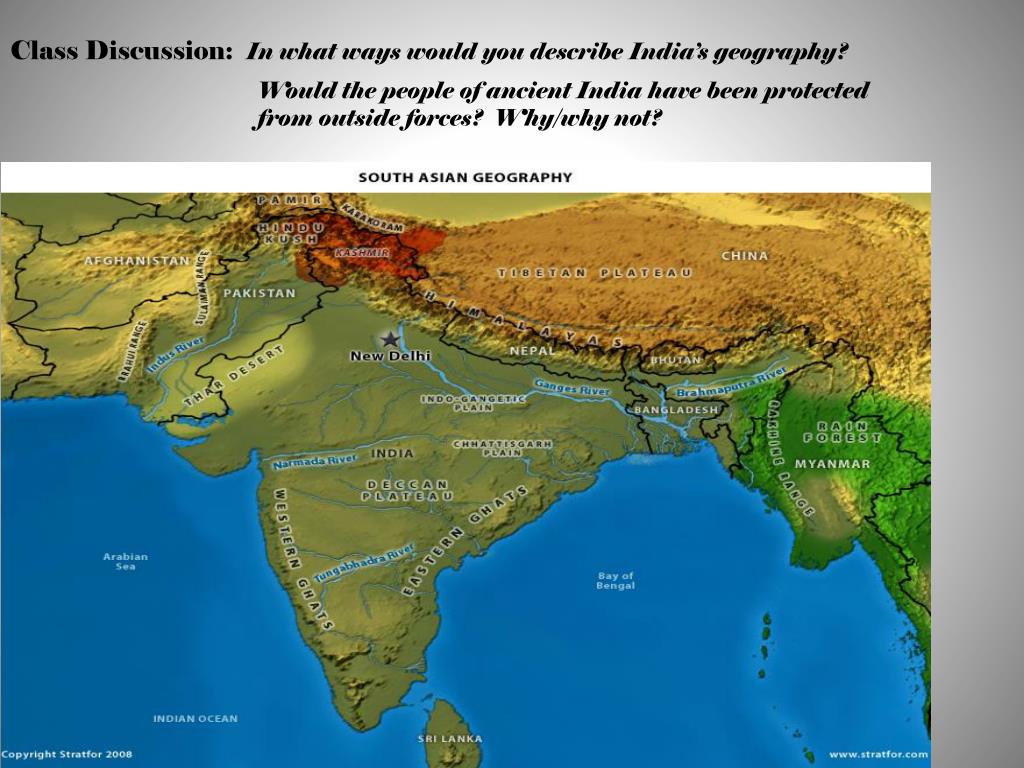
A map serves as a powerful tool for navigating the intricacies of India’s geography. It provides a visual representation of the country’s physical features, from the snow-capped Himalayas to the sun-kissed beaches of the Indian Ocean. By examining a map, one can gain a deeper understanding of the following:
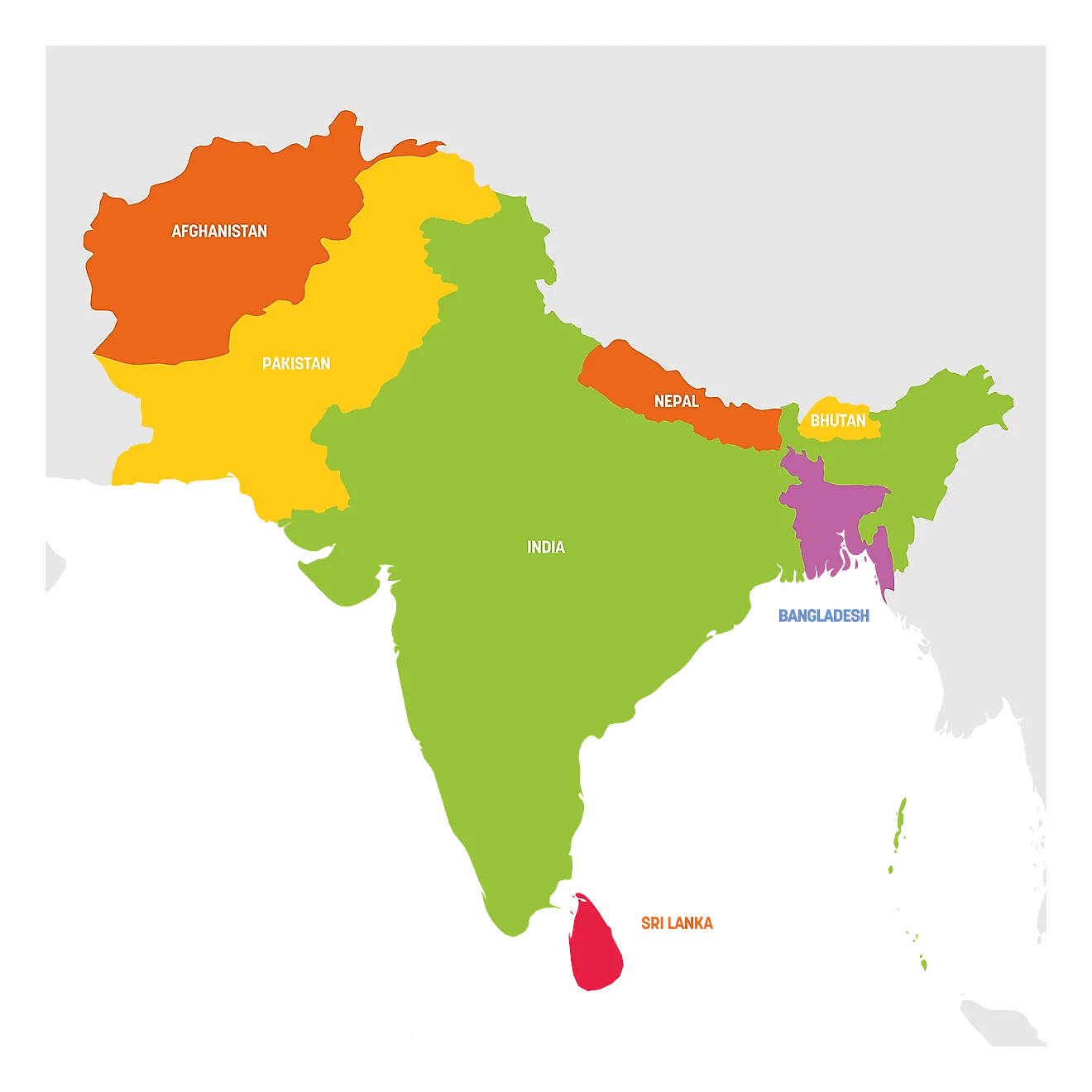
- Geographical Boundaries: India’s borders with neighboring countries like Pakistan, China, Nepal, and Bangladesh are clearly defined on a map, providing a sense of the country’s spatial context.
- Major Landforms: The map reveals the dominance of the Himalayan mountain range in the north, the vast plains of the Ganges River, the Deccan Plateau in the south, and the coastal regions along the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea.
- River Systems: India’s intricate network of rivers, including the Ganges, Brahmaputra, Indus, and Godavari, are depicted on the map, highlighting their vital role in agriculture, transportation, and the cultural life of the nation.
- Climate Zones: The map reveals the distinct climate zones of India, ranging from the tropical monsoon climates in the south to the temperate climates in the Himalayas.
- Major Cities and Urban Centers: The map showcases the distribution of India’s major cities, from bustling metropolises like Mumbai and Delhi to smaller urban centers, providing insights into the country’s population distribution and economic activity.
Exploring India’s Diverse Regions: A Geographic Mosaic
India’s vast geography is characterized by a rich diversity of regions, each with its own distinct identity shaped by its unique geographical features, cultural heritage, and economic activities.
1. The Himalayan Region:
- Location: Northern India, bordering Pakistan, China, Nepal, and Bhutan.
- Landforms: The towering Himalayas, home to the world’s highest peaks, including Mount Everest.
- Climate: Cold and snowy in the winter, with mild summers.
- Economic Activities: Tourism, agriculture (tea, fruits), hydropower generation.
- Culture: Rich cultural heritage, influenced by Tibetan Buddhism and Hindu traditions.
2. The Northern Plains:
- Location: Between the Himalayas and the Deccan Plateau.
- Landforms: Fertile alluvial plains, formed by the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Indus rivers.
- Climate: Tropical monsoon climate, with hot and humid summers and mild winters.
- Economic Activities: Agriculture (wheat, rice, sugarcane), textiles, manufacturing.
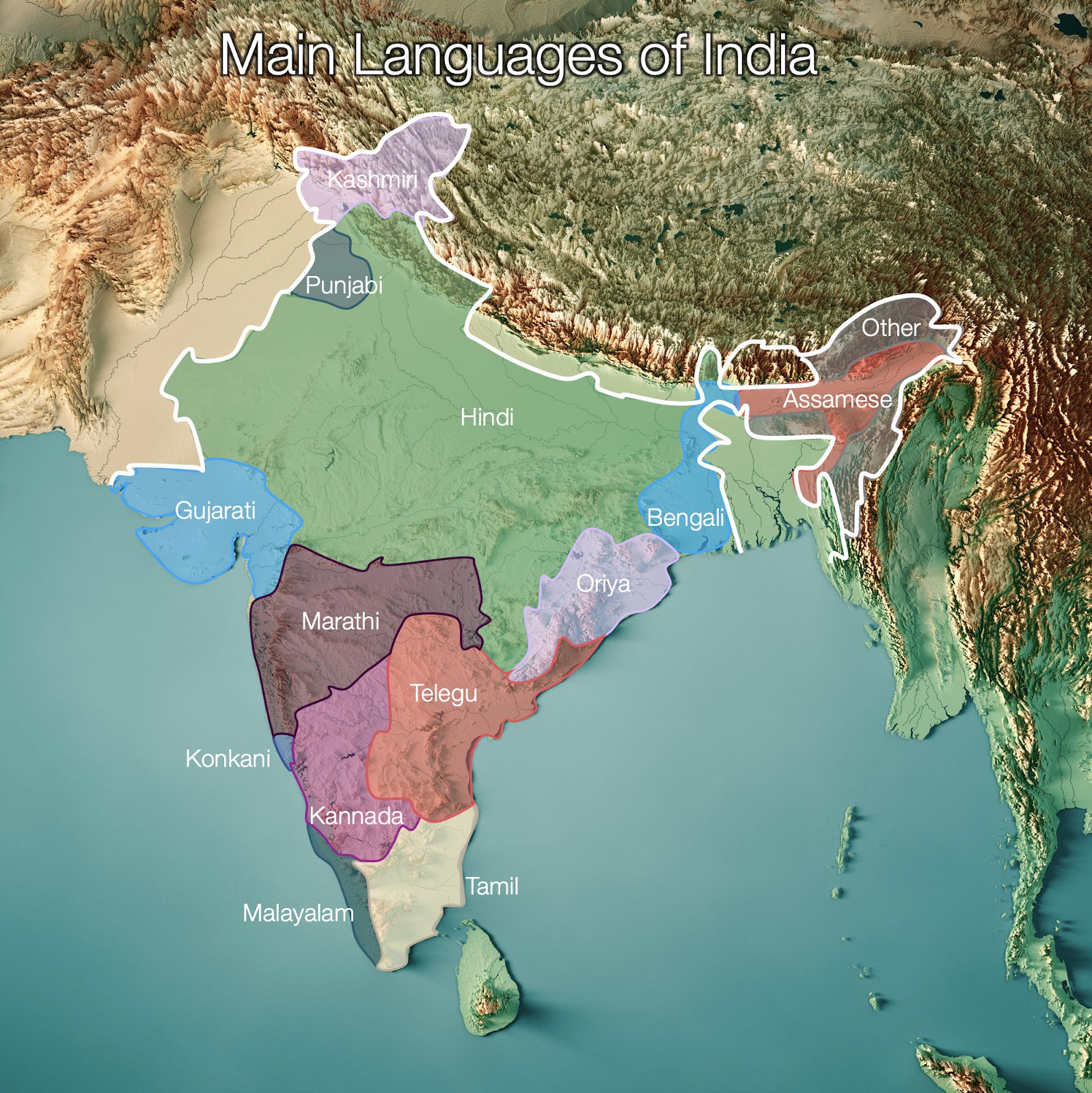
- Culture: Diverse cultural heritage, influenced by Hinduism, Sikhism, and Islam.
3. The Deccan Plateau:
- Location: Central and southern India.
- Landforms: A vast plateau, with rolling hills and valleys.
- Climate: Dry and semi-arid, with hot summers and mild winters.
- Economic Activities: Agriculture (cotton, pulses), mining (iron ore, manganese), IT industry.
- Culture: Rich cultural heritage, influenced by Dravidian languages and traditions.
4. The Coastal Regions:
- Location: Along the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea.
- Landforms: Coastal plains, beaches, deltas, and estuaries.
- Climate: Tropical monsoon climate, with high humidity and heavy rainfall.
- Economic Activities: Fishing, tourism, shipping, agriculture (rice, coconut).
- Culture: Diverse cultural heritage, influenced by maritime trade and coastal communities.
5. The Islands:
- Location: The Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Lakshadweep Islands in the Arabian Sea.
- Landforms: Volcanic islands, coral reefs, and beaches.
- Climate: Tropical monsoon climate, with high humidity and heavy rainfall.
- Economic Activities: Tourism, fishing, coconut cultivation.
- Culture: Unique cultural heritage, influenced by indigenous tribes and maritime traditions.
Understanding India’s Geography: Key Benefits
A comprehensive understanding of India’s geography offers numerous benefits for individuals and organizations:
- Informed Decision-Making: By understanding the geographical factors influencing various aspects of life in India, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions regarding travel, business, and development initiatives.
- Resource Management: Recognizing the distribution of natural resources, such as water, minerals, and forests, enables effective resource management and sustainable development practices.
- Disaster Preparedness: Understanding the geographical factors contributing to natural disasters, such as floods, droughts, and earthquakes, enhances disaster preparedness and mitigation strategies.
- Cultural Appreciation: A deeper understanding of India’s geography fosters appreciation for its diverse cultures and the unique adaptations developed by communities in response to their environment.
- Tourism Planning: A map helps travelers plan their itineraries, choosing destinations based on their interests and preferences, exploring the diverse landscapes and cultural experiences that India offers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the highest point in India?
A: The highest point in India is Mount Kangchenjunga, located in the Himalayas, with a height of 8,586 meters (28,169 feet).
Q2. What are the major rivers in India?
A: India has a vast network of rivers, including the Ganges, Brahmaputra, Indus, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri. These rivers are vital for agriculture, transportation, and cultural life.
Q3. What are the main climate zones in India?
A: India has diverse climate zones, ranging from the tropical monsoon climate in the south to the temperate climates in the Himalayas. These zones are influenced by the monsoon winds, latitude, and altitude.
Q4. What are the major cities in India?
A: India has numerous major cities, including Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata, Bengaluru, Chennai, Hyderabad, and Ahmedabad. These cities are major centers of commerce, industry, and culture.
Q5. How can I use a map to plan a trip to India?
A: A map can help you plan your trip by identifying destinations based on your interests, such as historical sites, natural wonders, or cultural experiences. It can also help you determine the best routes for travel and plan your accommodation.
Tips for Using a Map to Explore India
- Choose a reliable and detailed map: Use a map that provides clear information about geographical features, cities, transportation routes, and other relevant details.
- Focus on your interests: Identify destinations that align with your interests, such as historical sites, natural wonders, or cultural experiences.
- Consider the best time to visit: Research the climate and weather conditions in different regions of India to plan your trip during the most suitable time.
- Explore the map beyond major cities: Discover smaller towns and villages to experience the authentic culture and local life of India.
- Use the map to navigate and find your way around: Utilize the map to understand the layout of cities and towns, find specific locations, and plan your routes.
Conclusion
A map is an indispensable tool for understanding India’s vast and complex geography. It provides a visual representation of the country’s diverse landscapes, climate zones, major cities, and river systems, offering valuable insights into the unique characteristics of each region. By exploring India’s geography through the lens of a map, individuals and organizations can gain a deeper appreciation for the country’s rich cultural heritage, diverse ecosystems, and the interconnectedness of its people. Using a map as a guide, one can embark on a journey of discovery, exploring the captivating beauty and fascinating complexities of this remarkable nation.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling India: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding the Subcontinent’s Geography. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!