Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of Indonesia
Related Articles: Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of Indonesia
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of Indonesia. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of Indonesia
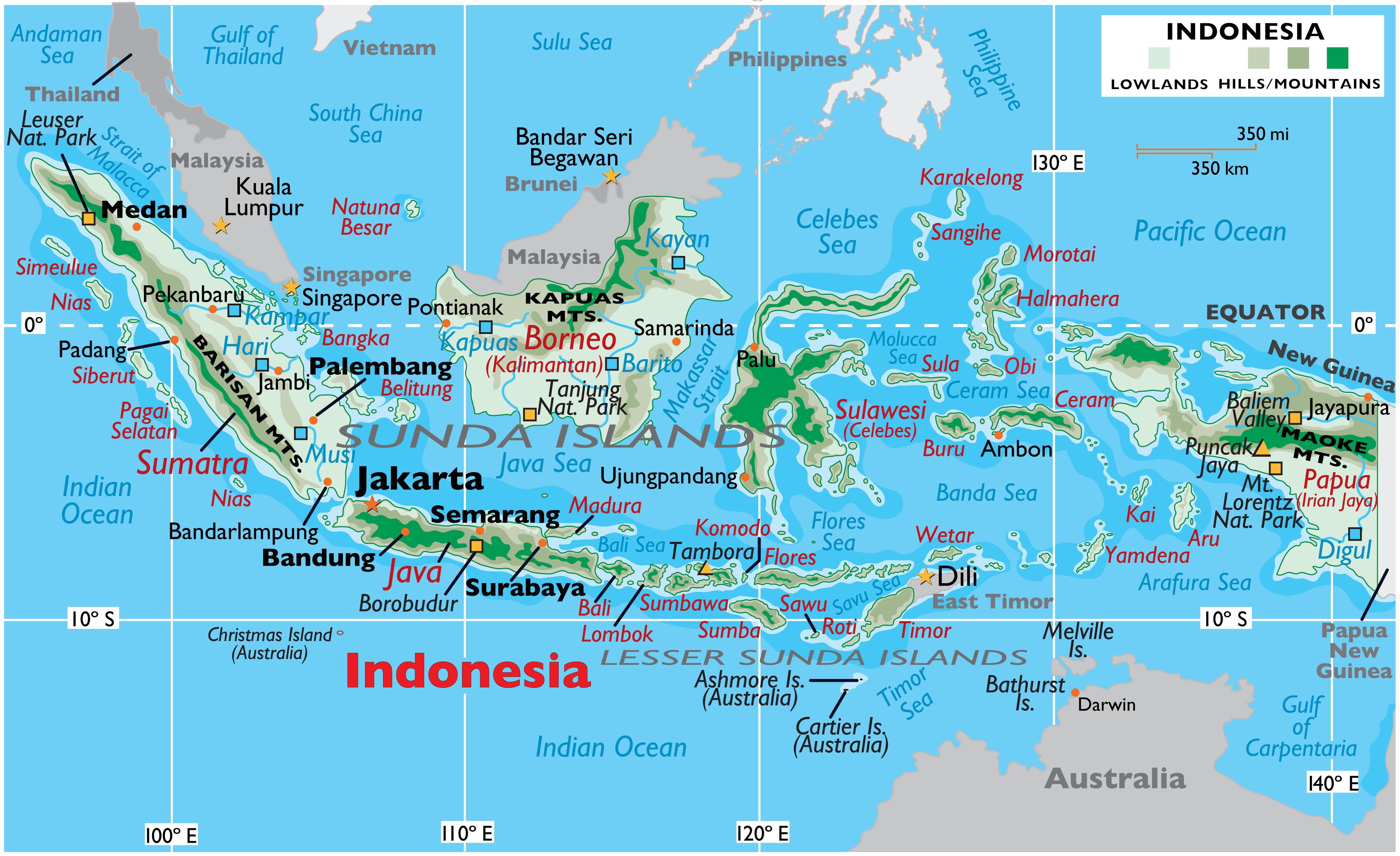
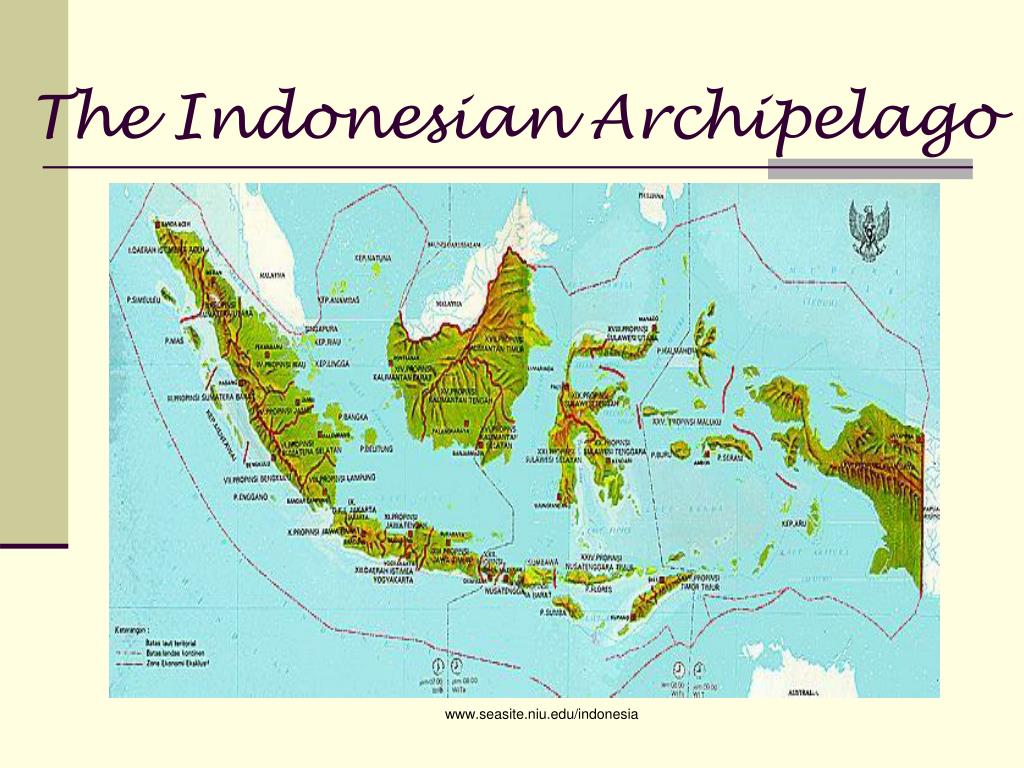
Indonesia, a nation of over 17,000 islands, is a geographical marvel. Its sprawling archipelago, stretching across the equator, boasts a diverse landscape of volcanic peaks, fertile plains, dense rainforests, and pristine beaches. Understanding the geographical layout of Indonesia is crucial for appreciating its rich cultural tapestry, diverse ecosystems, and complex history. This article provides a detailed overview of the Indonesian archipelago, highlighting its key features, geographic significance, and the impact on its people and environment.
A Nation of Islands:
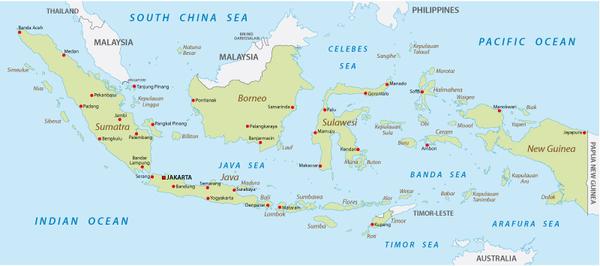
Indonesia’s geographical identity is defined by its sprawling archipelago. It is the largest archipelago nation in the world, with over 17,000 islands, of which only around 6,000 are inhabited. This vast expanse of land and water stretches across the equator, encompassing a significant portion of Southeast Asia and Oceania.
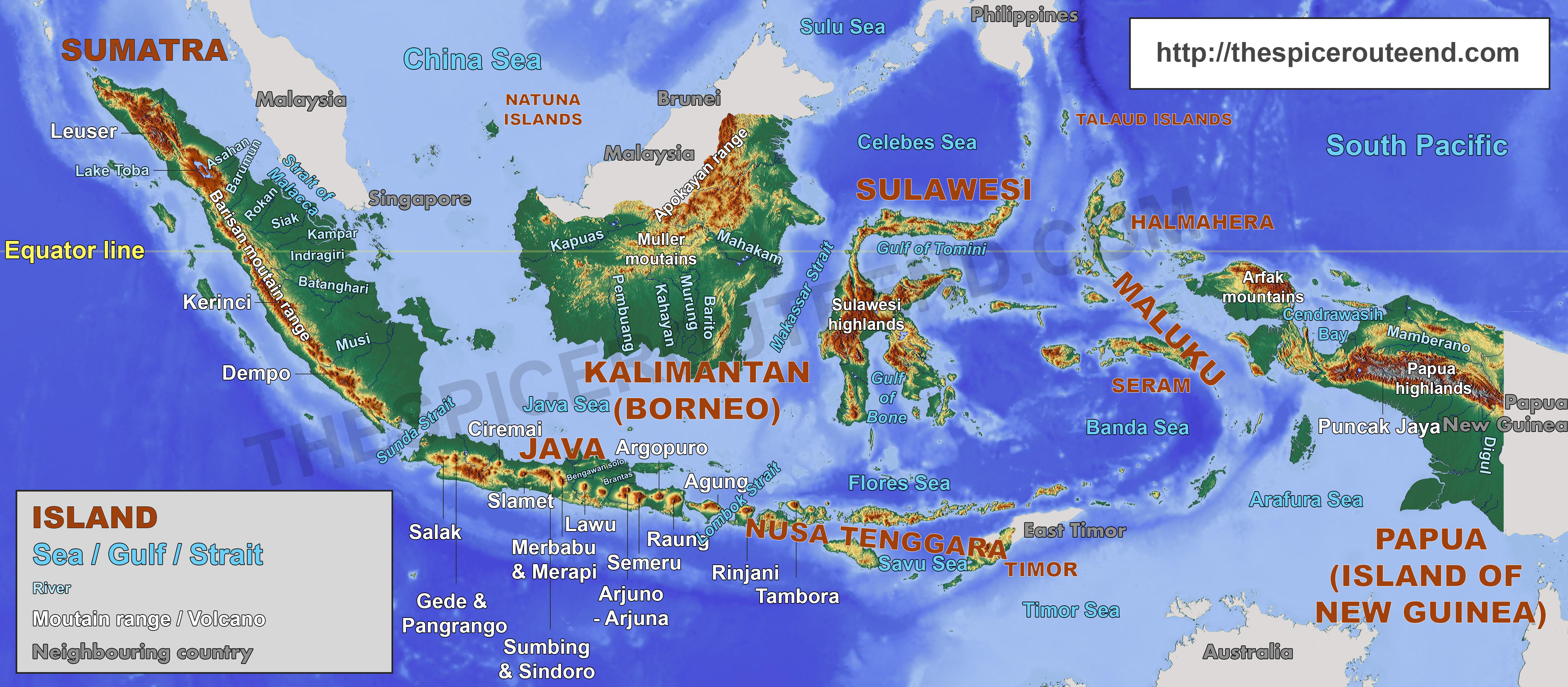
The Five Major Islands:
Indonesia’s geographical landscape is dominated by five major islands:
- Sumatra: The westernmost of the major islands, Sumatra is known for its dense rainforests, active volcanoes, and rich biodiversity. It is home to the iconic orangutan, Sumatran rhinoceros, and a vast array of flora and fauna.
- Java: The most populous island in Indonesia, Java is the heart of the nation’s culture, economy, and history. It is characterized by fertile volcanic plains, bustling cities, and ancient temples.
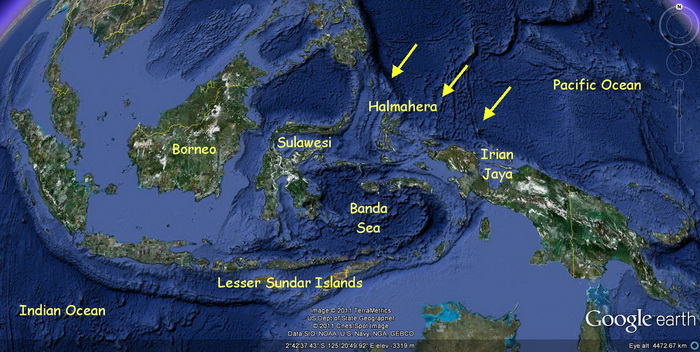
- Kalimantan (Borneo): The third-largest island in the world, Kalimantan is shared between Indonesia, Malaysia, and Brunei. It is known for its vast rainforests, rich mineral deposits, and indigenous communities.
- Sulawesi: This island, shaped like a human hand, is known for its unique biodiversity, including the elusive dwarf buffalo and the endemic Sulawesi crested macaque.
- Irian Jaya (New Guinea): The easternmost island, Irian Jaya is shared between Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. It is characterized by rugged mountains, dense rainforests, and a diverse indigenous population.
Beyond the Major Islands:
While the five major islands dominate Indonesia’s geography, the archipelago encompasses a vast array of smaller islands, each with its own distinct character and beauty. These include:
- The Lesser Sunda Islands: This chain of islands, stretching east from Java, includes Bali, Lombok, Flores, and Timor. They are known for their diverse landscapes, from volcanic mountains to pristine beaches, and their rich cultural heritage.
- The Moluccas (Spice Islands): This group of islands, located in the eastern part of the archipelago, was once the center of the spice trade. They are known for their lush rainforests, active volcanoes, and unique biodiversity.
- The Riau Islands: This group of islands, located off the coast of Sumatra, is known for its beautiful beaches, clear waters, and rich marine life.
Geographical Significance:
Indonesia’s geographical position has had a profound impact on its history, culture, and economy.
- Strategic Location: Situated at the crossroads of Asia and Oceania, Indonesia’s strategic location has made it a vital trading hub throughout history. The archipelago’s numerous islands and harbors have facilitated maritime trade routes, connecting Indonesia to various civilizations and cultures.
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Indonesia is home to a staggering level of biodiversity, with an estimated 10% of the world’s plant and animal species found within its borders. Its diverse ecosystems, from rainforests to coral reefs, support a vast array of life, making it a critical area for conservation.
- Natural Resources: Indonesia is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, timber, minerals, and agricultural products. These resources have played a significant role in the country’s economic development, although their exploitation has also led to environmental challenges.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Indonesia’s geography also presents challenges, including:
- Natural Disasters: The archipelago is vulnerable to natural disasters, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, tsunamis, and floods. These events can cause significant damage to infrastructure, property, and human life.
- Environmental Degradation: Deforestation, pollution, and unsustainable resource extraction pose significant threats to Indonesia’s environment. These challenges require effective conservation efforts and sustainable development practices.
- Connectivity: Connecting the vast archipelago poses logistical challenges, particularly for transportation and communication. The government is working to improve infrastructure, including roads, ports, and airports, to enhance connectivity and facilitate economic development.
FAQs:
Q: What is the total land area of Indonesia?
A: The total land area of Indonesia is approximately 1,904,569 square kilometers (735,358 square miles).
Q: What is the population of Indonesia?
A: The population of Indonesia is estimated to be over 273 million, making it the fourth most populous country in the world.
Q: What are the major religions practiced in Indonesia?
A: The majority of Indonesians are Muslim, followed by Christians, Hindus, and Buddhists.
Q: What are some of the major cities in Indonesia?
A: Some of the major cities in Indonesia include Jakarta (the capital), Surabaya, Bandung, Medan, and Semarang.
Q: What is the official language of Indonesia?
A: The official language of Indonesia is Bahasa Indonesia.
Tips for Understanding the Geography of Indonesia:
- Use a map: A map is essential for understanding the layout of the archipelago.
- Explore online resources: Websites such as Google Maps, Wikipedia, and the Indonesian Ministry of Tourism provide valuable information and interactive maps.
- Read books and articles: There are numerous books and articles available that delve into the geography of Indonesia.
- Watch documentaries: Documentaries on Indonesia’s geography, wildlife, and culture can provide a visual understanding of the archipelago.
Conclusion:
Indonesia’s geography is a defining feature of the nation, shaping its history, culture, and economy. The sprawling archipelago, with its diverse landscapes, rich biodiversity, and strategic location, presents both opportunities and challenges. Understanding the geographical layout of Indonesia is crucial for appreciating its unique character, navigating its complexities, and contributing to its sustainable development.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Archipelago: A Comprehensive Guide to the Geography of Indonesia. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!