Unveiling the Klamath Basin: A Vital Ecosystem in the Pacific Northwest
Related Articles: Unveiling the Klamath Basin: A Vital Ecosystem in the Pacific Northwest
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Klamath Basin: A Vital Ecosystem in the Pacific Northwest. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Klamath Basin: A Vital Ecosystem in the Pacific Northwest

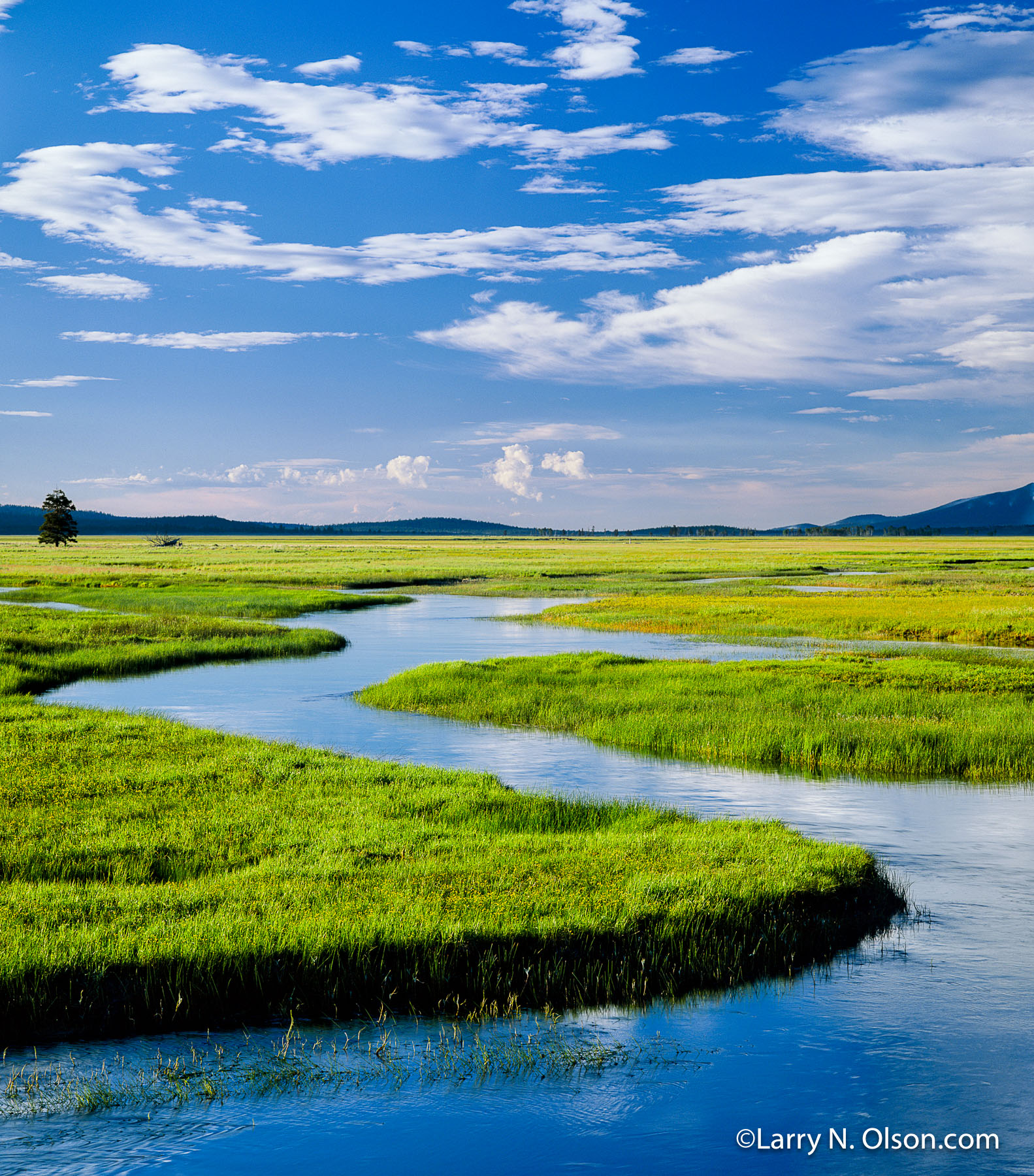
The Klamath Basin, nestled in the high desert of southern Oregon and northern California, is a captivating landscape of volcanic peaks, lush wetlands, and sparkling lakes. This region, encompassing a vast area of 15,000 square miles, is a critical ecosystem that sustains a diverse array of life, from migratory birds to indigenous communities. Understanding the Klamath Basin’s intricate geography through its map is crucial for appreciating its ecological significance and the challenges it faces.
A Tapestry of Landscapes:
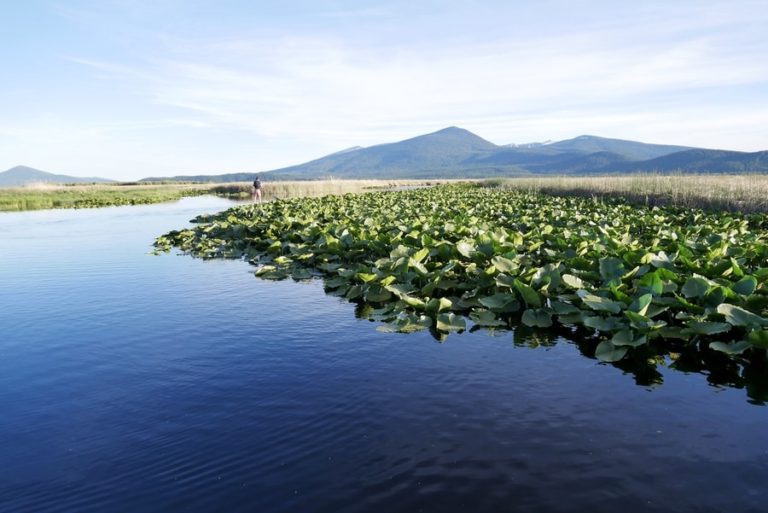
The Klamath Basin map reveals a complex interplay of landforms that contribute to its unique character. The heart of the basin is defined by Upper Klamath Lake, a vast body of water fed by the Klamath River and its tributaries. This lake, along with smaller lakes like Agency Lake and Goose Lake, forms the foundation of the basin’s wetland ecosystem.
To the east, the Cascade Range rises majestically, its slopes covered in dense forests of ponderosa pine and Douglas fir. These forests serve as a vital watershed, providing water to the basin’s lakes and rivers. To the west, the Siskiyou Mountains, known for their rugged terrain and diverse plant life, mark the boundary between Oregon and California.
A Lifeline for Wildlife and People:
The Klamath Basin’s diverse landscapes are a testament to its ecological richness. The wetlands provide critical habitat for numerous migratory bird species, including the iconic bald eagle, the majestic trumpeter swan, and the graceful sandhill crane. The lakes and rivers support a thriving fishery, with species like kokanee salmon and rainbow trout drawing anglers from across the region.
The basin is also home to a variety of mammals, including black bears, mule deer, and elk. The forests, with their rich biodiversity, serve as a haven for numerous insect species and amphibians. The Klamath Basin’s ecological value extends beyond its wildlife, as it provides essential water resources for agriculture and human communities.
Navigating the Challenges:
Despite its ecological importance, the Klamath Basin faces a number of challenges, including:
- Water scarcity: The basin’s water resources are increasingly strained due to competing demands from agriculture, urban development, and environmental needs.
- Habitat loss: Decades of land use practices, including agricultural development and logging, have led to significant habitat loss and fragmentation.
- Climate change: Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns are impacting the basin’s water availability and ecosystem health.
- Pollution: Agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and urban wastewater contribute to water quality issues in the basin.
The Klamath Basin Map: A Tool for Understanding and Action:
The Klamath Basin map is a powerful tool for understanding the intricate relationships between the region’s various components. It allows us to visualize the interconnectedness of water resources, wildlife habitats, and human settlements. By studying the map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the basin’s ecological significance and the challenges it faces.
Understanding the Klamath Basin Map: FAQs
Q: What are the key geographical features of the Klamath Basin?
A: The Klamath Basin is defined by Upper Klamath Lake, the Klamath River, and its tributaries, the Cascade Range to the east, and the Siskiyou Mountains to the west.
Q: Why is the Klamath Basin considered an important ecological region?
A: The basin’s diverse landscapes support a wide variety of wildlife, including migratory birds, fish, mammals, and amphibians. It also provides vital water resources for agriculture and human communities.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the Klamath Basin?
A: Water scarcity, habitat loss, climate change, and pollution are major challenges impacting the basin’s ecosystem and communities.
Q: How can we use the Klamath Basin map to address these challenges?
A: By understanding the relationships between the basin’s different components, we can develop sustainable solutions for water management, habitat restoration, and pollution control.
Tips for Using the Klamath Basin Map:
- Identify the major geographical features: Locate Upper Klamath Lake, the Klamath River, the Cascade Range, and the Siskiyou Mountains.
- Examine the distribution of different habitats: Observe the location of wetlands, forests, grasslands, and agricultural lands.
- Consider the flow of water: Trace the path of the Klamath River and its tributaries, understanding how water moves through the basin.
- Analyze human settlements: Identify major cities, towns, and agricultural areas, and their proximity to water resources.
Conclusion:
The Klamath Basin map is a valuable resource for understanding this vital ecosystem and the challenges it faces. By studying the map, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of the basin’s landscapes, wildlife, and human communities. This knowledge empowers us to develop sustainable solutions for managing water resources, protecting wildlife habitats, and ensuring the long-term health of this remarkable region. As we navigate the complexities of the Klamath Basin, the map serves as a constant reminder of our responsibility to preserve this precious ecosystem for future generations.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Klamath Basin: A Vital Ecosystem in the Pacific Northwest. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!