Unveiling the Layers of Iowa: A Comprehensive Guide to the Iowa Geologic Map
Related Articles: Unveiling the Layers of Iowa: A Comprehensive Guide to the Iowa Geologic Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Layers of Iowa: A Comprehensive Guide to the Iowa Geologic Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Layers of Iowa: A Comprehensive Guide to the Iowa Geologic Map
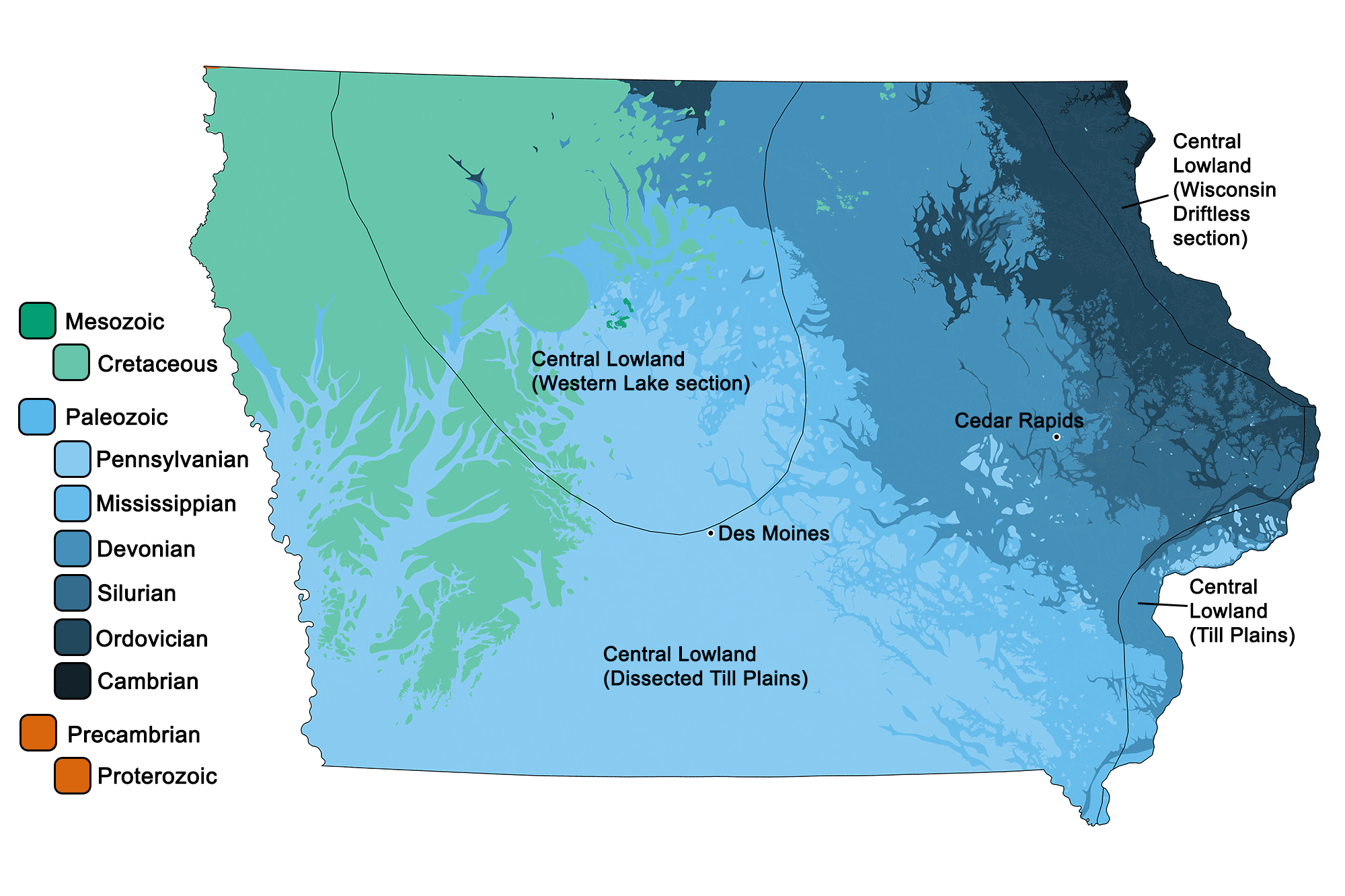
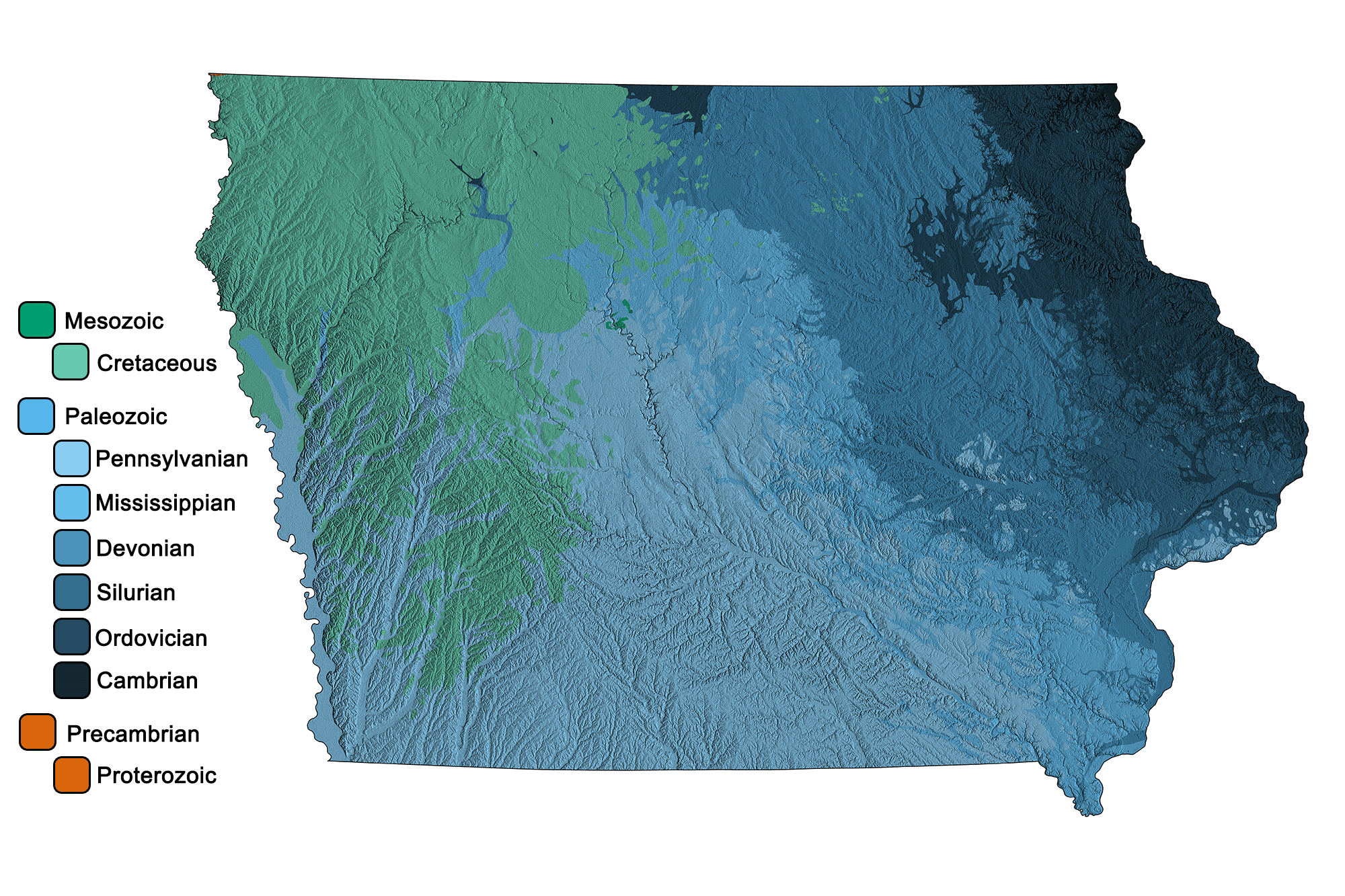
The Iowa Geological Survey, a division of the Iowa Department of Natural Resources, has produced a comprehensive geologic map that serves as a vital tool for understanding the state’s diverse geological history and its impact on various aspects of life in Iowa. This map is not merely a static representation of rocks and formations; it is a window into the dynamic processes that have shaped Iowa’s landscape over millions of years.
Deciphering the Landscape: A Journey Through Time
The Iowa geologic map is a visual testament to the intricate interplay of geological forces that have shaped the state. It reveals a tapestry of rock units, each representing a distinct chapter in Iowa’s geological history. These units, ranging from ancient Precambrian bedrock to relatively recent Quaternary deposits, provide insights into:
-
Formation Processes: The map highlights the various geological processes that have shaped Iowa, including:
- Sedimentation: Deposition of sediments from ancient seas and rivers, creating layers of sandstone, limestone, and shale.
- Volcanism: Eruptions of volcanic ash and lava flows, leaving behind distinctive rock formations.
- Glaciation: The advance and retreat of massive ice sheets, carving valleys, depositing glacial till, and shaping the landscape.
- Erosion: The relentless forces of wind and water, sculpting hills, canyons, and riverbeds.
- Time Scales: The map acts as a chronological timeline, showcasing the age and relative order of rock formations. It allows scientists to trace the evolution of the landscape over millions of years.
-
Resource Potential: The map identifies areas with potential for various natural resources, including:
- Groundwater: The map reveals the location and depth of aquifers, crucial for water supply.
- Fossil Fuels: Areas rich in coal, oil, and natural gas deposits can be identified.
- Construction Materials: Sand, gravel, and limestone, essential for building and infrastructure, can be located.
- Environmental Hazards: The map highlights areas prone to geological hazards like landslides, sinkholes, and seismic activity.
Beyond the Map: Applications and Importance
The Iowa geologic map serves as a foundation for numerous scientific and practical applications, impacting various sectors of Iowa’s economy and society.
- Geological Research: The map provides a framework for researchers studying the state’s geology, paleontology, and environmental history. It aids in understanding the formation of mineral deposits, the evolution of ecosystems, and the impact of climate change.
- Water Resource Management: The map is essential for identifying and protecting groundwater resources, crucial for agriculture, industry, and drinking water. It helps in managing water quality and developing sustainable water use strategies.
- Land Use Planning: The map assists in planning land use and development, considering geological factors like soil stability, bedrock depth, and potential hazards. It helps in minimizing environmental impacts and ensuring sustainable development.
- Infrastructure Development: The map is vital for planning and constructing roads, bridges, dams, and other infrastructure projects. It helps in selecting suitable construction materials, avoiding geological hazards, and optimizing project design.
- Natural Resource Exploration: The map guides exploration efforts for minerals, oil, gas, and other natural resources. It identifies areas with potential for resource extraction, facilitating sustainable development and economic growth.
- Environmental Protection: The map helps in identifying and mitigating environmental risks, such as groundwater contamination, soil erosion, and landslides. It aids in developing strategies for environmental protection and remediation.
Understanding the Map: A Key to Knowledge
The Iowa geologic map is a powerful tool, but its effectiveness depends on understanding its symbols, legends, and data representation.
- Colors and Patterns: Different colors and patterns represent various rock units, indicating their age, composition, and origin.
- Symbols: Symbols are used to denote specific geological features, such as faults, folds, and mineral deposits.
- Legends: The legend explains the meaning of colors, patterns, and symbols used on the map.
- Scale: The scale indicates the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground.
- Data Sources: The map includes information from various sources, including field observations, laboratory analyses, and aerial photography.
Frequently Asked Questions About the Iowa Geologic Map
1. Where can I find the Iowa geologic map?
The Iowa Geological Survey offers various formats of the map, including printed versions, digital downloads, and online interactive maps. These resources can be accessed through the Iowa Geological Survey’s website.
2. What is the most recent version of the Iowa geologic map?
The Iowa Geological Survey continually updates the map based on new research and data. The most recent version is available on their website, along with information about its updates and revisions.
3. How can I use the Iowa geologic map for my research or project?
The Iowa Geological Survey provides guidance on using the map for various purposes, including research, education, and planning. They offer workshops, webinars, and online resources to help users interpret the map’s data effectively.
4. Is the Iowa geologic map available in different formats?
Yes, the map is available in various formats, including printed versions, digital downloads, and online interactive maps. Users can choose the format that best suits their needs and preferences.
5. Can I contribute data to the Iowa geologic map?
The Iowa Geological Survey welcomes contributions from researchers, students, and the public. They provide guidelines and procedures for submitting data to enhance the map’s accuracy and completeness.
Tips for Utilizing the Iowa Geologic Map Effectively
- Start with the legend: Familiarize yourself with the map’s symbols, colors, and patterns to understand the data represented.
- Consider the scale: The map’s scale determines the level of detail it can show. Choose a scale appropriate for your research or project.
- Consult multiple sources: Combine the geologic map with other relevant data, such as topographic maps, aerial imagery, and soil surveys, for a comprehensive understanding.
- Seek expert guidance: If you require assistance in interpreting the map or using its data, consult with experts at the Iowa Geological Survey or other relevant organizations.
- Stay informed about updates: The Iowa Geological Survey regularly updates the map. Stay informed about the latest versions and revisions to ensure you are using the most accurate data.
Conclusion
The Iowa geologic map is a valuable resource for understanding the state’s geological history, its impact on various aspects of life, and its potential for future development. By utilizing the map effectively, researchers, planners, and the public can gain valuable insights into the state’s geology, resources, and environmental challenges. It serves as a cornerstone for responsible land use, resource management, and environmental protection, ensuring a sustainable future for Iowa.
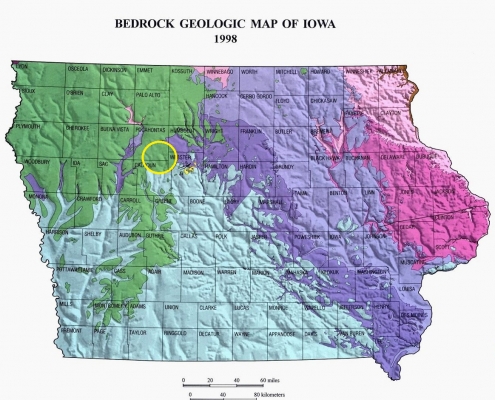


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/IAgeomap-58b5aa303df78cdcd892eb00.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Layers of Iowa: A Comprehensive Guide to the Iowa Geologic Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!