Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Streamlining Efficiency and Enhancing Collaboration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Streamlining Efficiency and Enhancing Collaboration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Streamlining Efficiency and Enhancing Collaboration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Streamlining Efficiency and Enhancing Collaboration
In the contemporary business landscape, marked by relentless change and increasing complexity, organizations are constantly seeking ways to optimize operations, enhance efficiency, and foster collaboration. Enter process mapping, a potent tool that provides a visual representation of workflows, enabling organizations to understand, analyze, and improve their processes.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of process mapping, exploring its core concepts, benefits, and practical applications. It aims to equip readers with a thorough understanding of how process mapping can be leveraged to drive organizational success.
Defining Process Mapping: A Visual Language for Business Processes
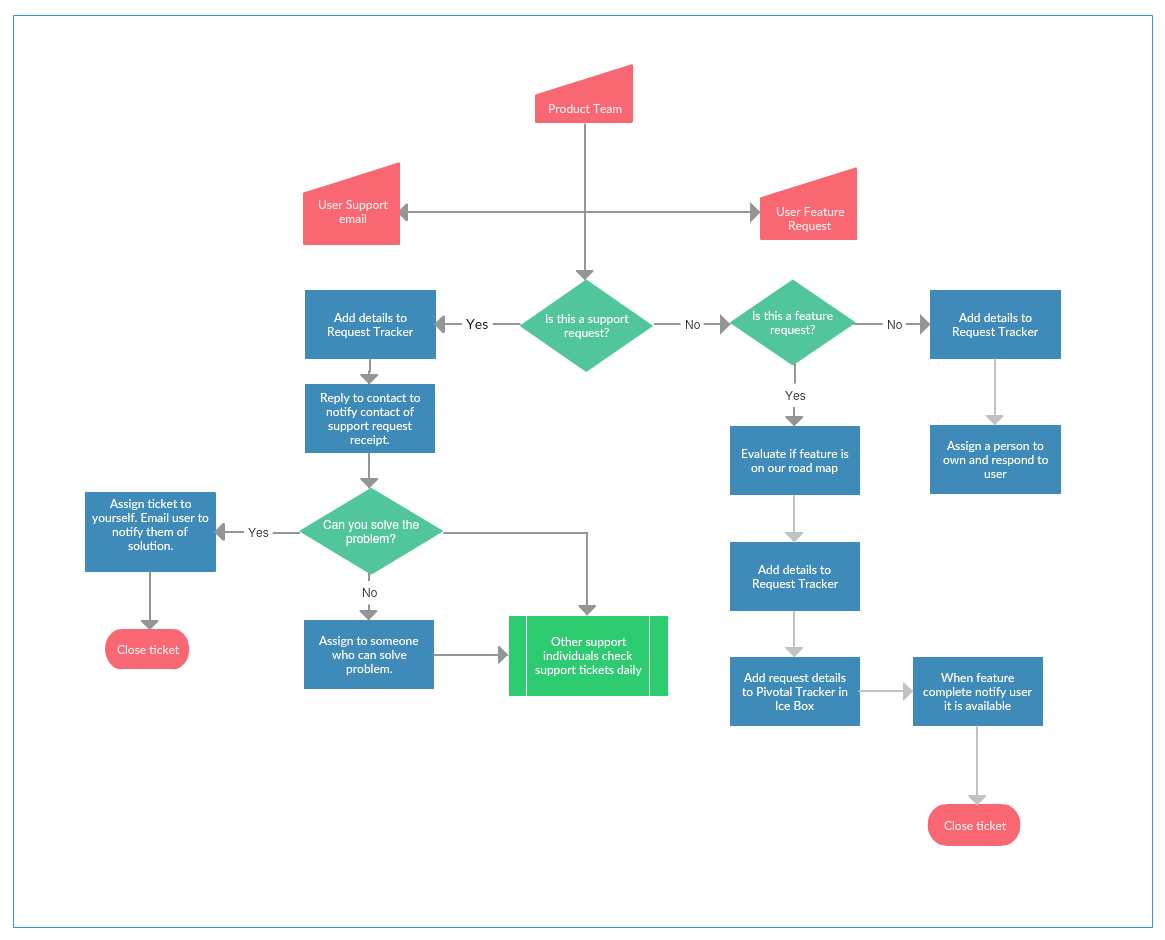
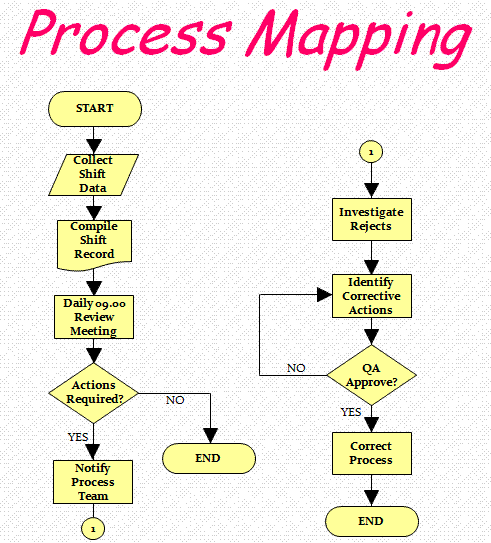
Process mapping, often referred to as workflow mapping or process flowcharting, is a visual representation of a sequence of activities or steps involved in a particular process. It utilizes standardized symbols and notations to depict the flow of work, decision points, and potential bottlenecks within a process.
The Building Blocks of Process Mapping: Symbols and Notations
Process mapping employs a standardized set of symbols and notations to ensure clarity and consistency in representing processes. These symbols, often defined by industry standards like BPMN (Business Process Model and Notation) or SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers), represent various elements within a process, such as:
- Start/End: Denotes the beginning and end of a process.
- Task/Activity: Represents a specific action or step within the process.
- Decision: Indicates a point where a choice needs to be made.
- Flow: Shows the direction of the process flow.
- Connector: Links different parts of the process diagram.
Types of Process Maps: Tailoring the Visualization to Your Needs
Process maps can be categorized based on their level of detail and purpose. Some common types include:
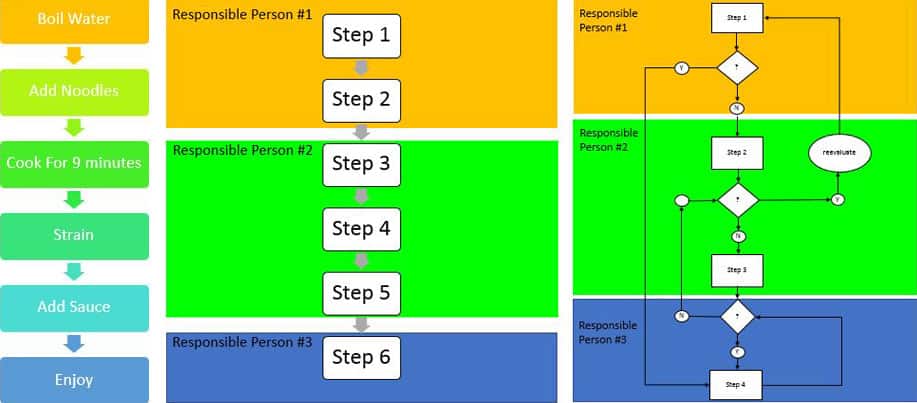
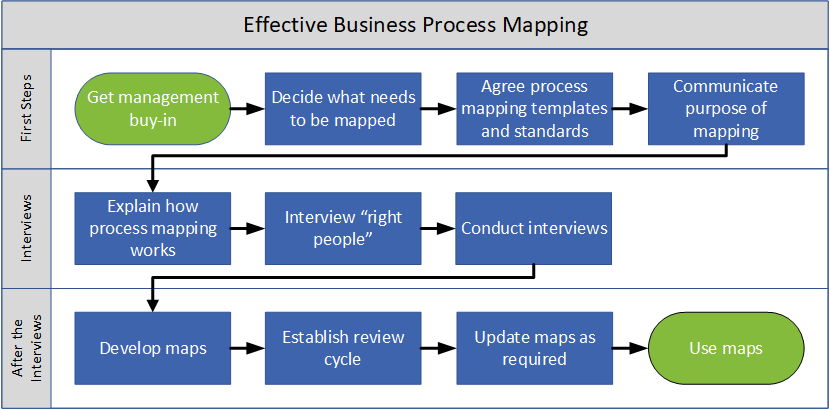
- High-Level Process Map: Provides a broad overview of a process, focusing on major activities and decision points.
- Detailed Process Map: Depicts a specific process in detail, outlining every step and decision.
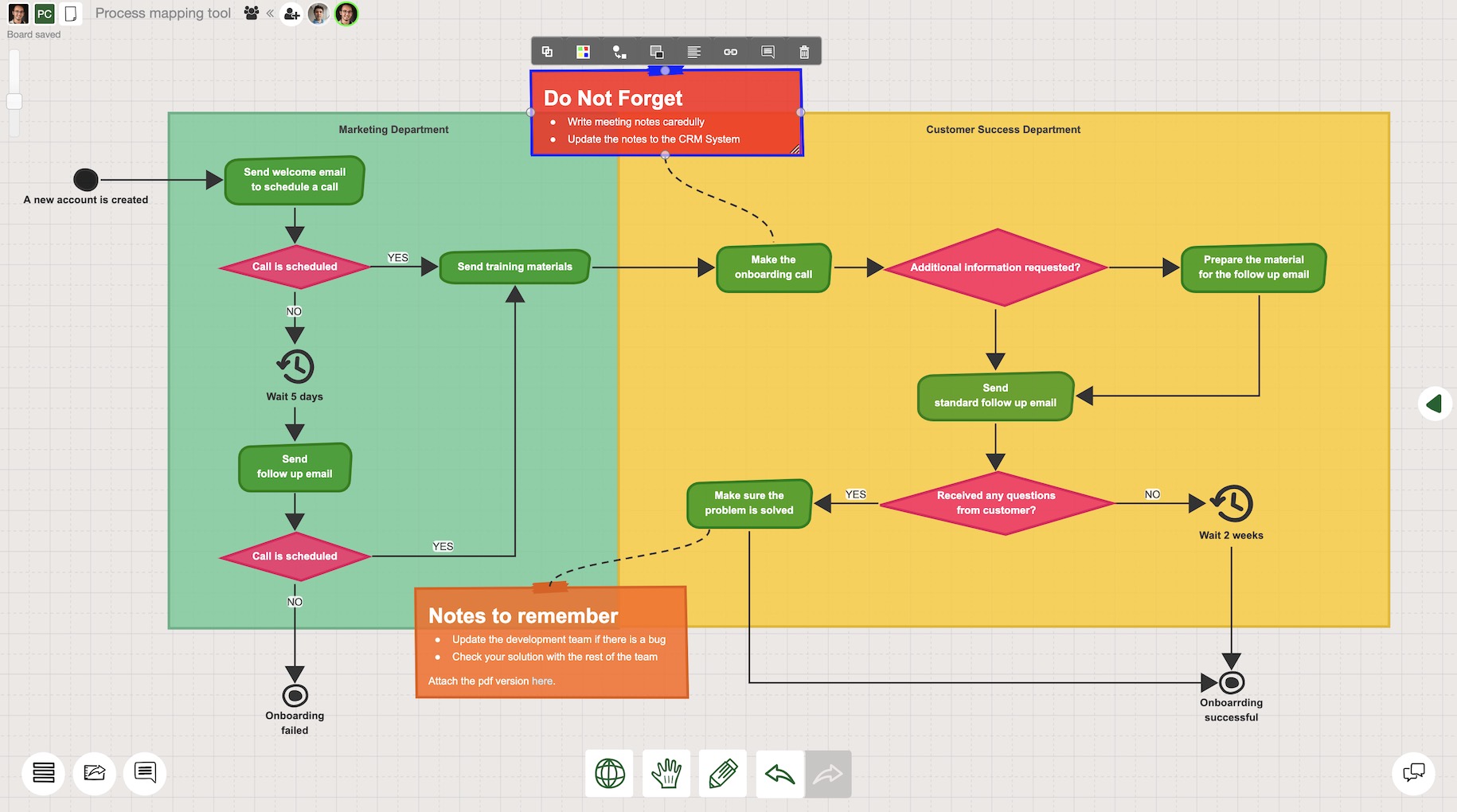
- Swimlane Process Map: Divides a process into lanes representing different departments or roles involved.
- Cross-Functional Process Map: Illustrates how multiple departments or teams collaborate within a process.
The Advantages of Embracing Process Mapping: Unlocking Efficiency and Clarity
Process mapping offers a multitude of benefits for organizations of all sizes and industries:
- Improved Understanding: Process maps provide a clear and concise visual representation of how work is done, fostering a shared understanding of the process among stakeholders.
- Enhanced Efficiency: By identifying bottlenecks and redundancies, process maps enable organizations to streamline workflows and eliminate unnecessary steps, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Reduced Errors: Visualizing the process allows for identification of potential error points, enabling organizations to implement preventative measures and minimize mistakes.
- Improved Communication: Process maps serve as a common language for communication across departments, facilitating collaboration and alignment.
- Simplified Training: Clear process maps facilitate training new employees and onboarding new team members, ensuring consistent and effective execution of processes.
- Increased Accountability: By defining roles and responsibilities within a process, process maps promote accountability and clarity of ownership.
- Facilitated Innovation: Process mapping provides a foundation for identifying areas for improvement and exploring innovative solutions to optimize processes.
The Practical Applications of Process Mapping: From Operations to Customer Service
Process mapping finds widespread applications across various organizational functions, including:
- Operations: Mapping production processes, supply chain management, and logistics can optimize resource allocation, reduce lead times, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
- Customer Service: Visualizing customer service workflows helps identify areas for improvement in response times, resolution rates, and customer satisfaction.
- Sales and Marketing: Mapping sales processes and marketing campaigns can optimize lead generation, sales conversion rates, and customer acquisition strategies.
- Human Resources: Process mapping can streamline recruitment, onboarding, and performance management processes, enhancing employee experience and productivity.
- Finance and Accounting: Visualizing financial processes, such as budgeting, forecasting, and reporting, can improve accuracy, transparency, and compliance.
- IT and Software Development: Mapping software development processes can facilitate project management, agile development practices, and quality assurance.
The Process Mapping Toolkit: Essential Software Solutions
While manual process mapping is possible, utilizing specialized software tools can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the process. These tools offer features such as:
- Drag-and-Drop Functionality: Enables easy creation and modification of process diagrams.
- Predefined Symbols and Templates: Provides a library of standardized symbols and templates for various process types.
- Collaboration Features: Allows multiple users to work on process maps simultaneously, fostering teamwork and shared ownership.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Offers insights into process performance, identifying bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Integration with Other Systems: Connects process maps with other business systems, providing a comprehensive view of operations.
Frequently Asked Questions: Addressing Common Concerns and Doubts
Q: What are the key steps involved in creating a process map?
A: The process of creating a process map typically involves the following steps:
- Define the Process: Clearly identify the process to be mapped, including its purpose, scope, and stakeholders.
- Gather Data: Collect information about the process, including inputs, outputs, activities, decision points, and potential bottlenecks.
- Create the Diagram: Use a process mapping tool or manual methods to create a visual representation of the process, employing standardized symbols and notations.
- Validate and Review: Ensure the accuracy and completeness of the process map by reviewing it with stakeholders and making necessary adjustments.
- Implement and Monitor: Put the process map into practice, monitor its effectiveness, and make ongoing improvements based on data and feedback.
Q: What are the challenges associated with process mapping?
A: Implementing process mapping effectively can present some challenges:
- Resistance to Change: Some stakeholders may resist changes to existing processes, requiring effective communication and change management strategies.
- Data Accuracy and Completeness: Gathering accurate and complete process data can be challenging, requiring careful planning and collaboration.
- Maintaining Process Maps: Regularly updating process maps to reflect changes and improvements is crucial for their continued relevance and effectiveness.
- Choosing the Right Tool: Selecting the appropriate process mapping software can be a challenge, requiring careful consideration of features, functionality, and budget constraints.
Q: How can process mapping be used for continuous improvement?
A: Process mapping is a powerful tool for driving continuous improvement by:
- Identifying Bottlenecks: Process maps highlight areas where work is slowed down or delayed, enabling organizations to address these bottlenecks and improve efficiency.
- Eliminating Redundancies: By visualizing the process, redundancies and unnecessary steps can be identified and eliminated, streamlining workflows and reducing waste.
- Optimizing Resources: Process maps provide insights into resource allocation, enabling organizations to optimize resource utilization and minimize costs.
- Enhancing Collaboration: Process mapping fosters communication and collaboration among stakeholders, facilitating the identification and implementation of improvements.
Tips for Successful Process Mapping: Maximizing Impact and Efficiency
- Start Small: Begin with mapping a simple process to gain experience and build momentum before tackling more complex processes.
- Involve Stakeholders: Engage all relevant stakeholders in the process mapping process to ensure buy-in and ownership.
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Ensure the process map is easily understood by everyone involved, using clear and concise language and avoiding technical jargon.
- Regularly Review and Update: Process maps are living documents and should be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect changes in processes and workflows.
- Utilize Process Mapping Software: Leverage specialized process mapping software to enhance efficiency, collaboration, and data analysis capabilities.
Conclusion: Embracing Process Mapping for a More Efficient and Collaborative Future
Process mapping is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance organizational efficiency, collaboration, and innovation. By providing a clear visual representation of workflows, process maps enable organizations to understand, analyze, and improve their processes, leading to increased productivity, reduced errors, and enhanced customer satisfaction. As organizations navigate the ever-changing business landscape, embracing process mapping can be a key differentiator, empowering them to achieve their goals and thrive in a competitive environment.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Process Mapping: A Comprehensive Guide to Streamlining Efficiency and Enhancing Collaboration. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!