Unveiling the Power of Unmarked Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Exploration and Learning
Related Articles: Unveiling the Power of Unmarked Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Exploration and Learning
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Power of Unmarked Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Exploration and Learning. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Power of Unmarked Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Exploration and Learning

In an era dominated by digital maps and GPS navigation, the concept of an unmarked map might seem antiquated. However, the simplicity and potential of a blank canvas, in this case, a map devoid of labels and markings, offer a unique and rewarding experience for learners of all ages.
This article delves into the world of unmarked maps, exploring their significance, benefits, and applications, while dispelling any misconceptions surrounding their use. We will examine how these seemingly bare maps can serve as powerful tools for fostering geographical understanding, encouraging critical thinking, and promoting deeper engagement with the world around us.
Understanding the Essence of an Unmarked Map
An unmarked map, often referred to as a blank map, is a visual representation of a geographical area devoid of any labels, names, or other markings. It presents a clean slate, allowing users to actively engage in the process of filling in the missing information. This seemingly simple act of adding details transforms the map from a passive visual into an interactive learning tool.
Benefits of Utilizing Unmarked Maps
The absence of pre-existing information on an unmarked map unlocks a multitude of benefits for individuals seeking to enhance their geographical knowledge and critical thinking skills. These benefits include:
1. Active Engagement and Deeper Learning:
Unmarked maps encourage active engagement and participation. By filling in the missing details, individuals are forced to actively recall and apply their knowledge, leading to a deeper understanding of the subject matter. This process fosters a more meaningful learning experience compared to passively absorbing information from a pre-labeled map.
2. Enhanced Spatial Reasoning and Visualization:
The act of placing geographical features on an unmarked map enhances spatial reasoning and visualization skills. By mentally constructing the relationships between different locations and understanding their relative positions, users develop a stronger spatial awareness. This ability to mentally navigate and visualize geographical concepts is crucial for various applications, including map reading, navigation, and spatial analysis.
3. Fostering Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving:
Unmarked maps encourage critical thinking and problem-solving. By analyzing the available information, such as latitude and longitude lines, users must deduce the locations of various features. This process requires logical reasoning, pattern recognition, and the ability to interpret clues, all of which contribute to the development of critical thinking skills.
4. Promoting Creativity and Independence:
The freedom to fill in an unmarked map encourages creativity and independence. Users are not bound by pre-determined information and can explore different ways to represent geographical features. This allows them to develop their own understanding of the world and express their creativity in a visual format.
5. Facilitating Collaborative Learning:
Unmarked maps can be used effectively in collaborative learning environments. By working together to fill in the missing details, individuals can share their knowledge, learn from each other, and develop a shared understanding of the subject matter. This collaborative process enhances communication, teamwork, and problem-solving skills.
Applications of Unmarked Maps
Unmarked maps find applications in various contexts, catering to diverse learning needs and objectives:
1. Educational Settings:
Unmarked maps are widely used in educational settings to enhance geography lessons, history classes, and social studies curricula. They provide a hands-on learning experience that encourages active participation and promotes deeper understanding of geographical concepts.
2. Travel Planning and Exploration:
Unmarked maps can be invaluable tools for travel planning and exploration. By plotting out desired destinations, routes, and points of interest, travelers can gain a better understanding of their itinerary and potential challenges. This process fosters a sense of adventure and encourages a more mindful approach to travel.
3. Research and Data Visualization:
Unmarked maps are used in research and data visualization to present and analyze geographical data. By adding specific data points and markers, researchers can create visually compelling representations of trends, patterns, and relationships within a geographical context.
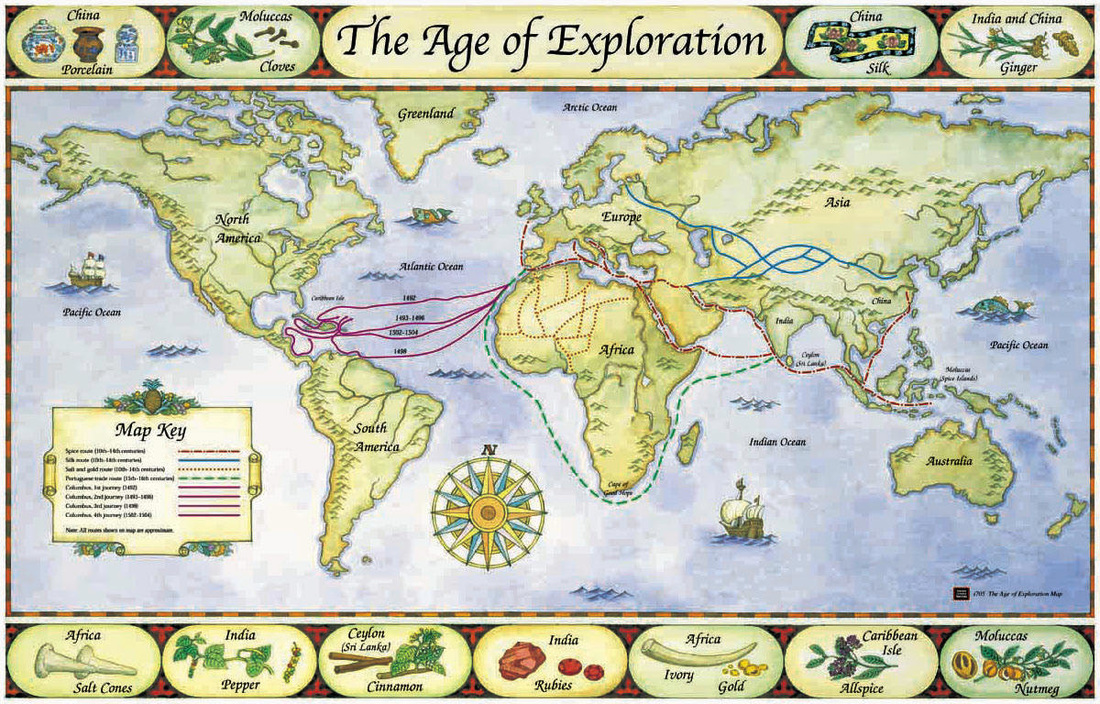
4. Historical Analysis and Mapping:
Unmarked maps play a crucial role in historical analysis and mapping. By reconstructing past events and geographical configurations, historians can gain insights into historical processes and understand the spatial dynamics of the past.
5. Urban Planning and Development:
Unmarked maps are used in urban planning and development to visualize proposed projects, analyze existing infrastructure, and assess the potential impact of development on the surrounding environment.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Despite their numerous benefits, unmarked maps often face misconceptions that hinder their widespread adoption. These misconceptions include:
1. Unmarked Maps are Only for Beginners:
This is a misconception. While unmarked maps can be beneficial for beginners, they also offer valuable learning opportunities for experienced individuals. The process of filling in a blank map can help reinforce existing knowledge, deepen understanding, and challenge individuals to think critically about geographical concepts.
2. Unmarked Maps are Too Difficult to Use:
This is not necessarily true. With proper guidance and resources, anyone can learn to use unmarked maps effectively. The initial challenge of filling in the missing details can be overcome with practice and the application of critical thinking skills.
3. Unmarked Maps are Outdated and Irrelevant in the Digital Age:
This is a misjudgment. While digital maps offer convenience and instant access to information, unmarked maps provide a unique and valuable learning experience that cannot be replicated by digital tools. The act of actively engaging with the map and filling in the missing details fosters a deeper understanding and appreciation of geographical concepts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are some examples of resources that can be used to fill in an unmarked map?
A: Numerous resources can be used to fill in an unmarked map, including:
- Textbooks and reference books: These resources provide detailed information about geographical features, their locations, and relevant historical or cultural contexts.
- Atlases: Atlases offer comprehensive maps and detailed descriptions of geographical features, including physical features, political boundaries, and demographic information.
- Online databases and mapping tools: Online databases like Google Maps, OpenStreetMap, and other mapping tools provide a wealth of information and interactive features that can be used to fill in an unmarked map.
- Photographs and satellite imagery: These visual resources can provide valuable insights into the appearance and location of geographical features.
Q: How can I encourage students to use unmarked maps in the classroom?
A: Here are some tips for incorporating unmarked maps into classroom learning:
- Start with simple maps: Begin with smaller, more familiar areas, such as the classroom or the school neighborhood.
- Provide clear instructions and guidance: Explain the purpose of the exercise and provide students with clear instructions on how to fill in the missing details.
- Encourage collaboration and discussion: Encourage students to work together, share their knowledge, and discuss their findings.
- Use a variety of activities: Integrate unmarked maps into various activities, such as map quizzes, geography games, and research projects.
- Provide feedback and support: Offer constructive feedback and support students as they navigate the process of filling in unmarked maps.
Q: What are some tips for using unmarked maps for travel planning?
A: Here are some tips for incorporating unmarked maps into travel planning:
- Choose the right map scale: Select a map scale that is appropriate for the size of the area you are planning to visit.
- Identify key destinations and points of interest: Mark your desired destinations and points of interest on the map.
- Plot your route and consider alternative routes: Plan your route and consider alternative routes in case of unexpected road closures or delays.
- Research transportation options: Identify available transportation options, such as public transportation, car rentals, or walking routes.
- Mark potential challenges and safety concerns: Consider potential challenges, such as weather conditions, traffic congestion, or areas with limited access.
Conclusion
Unmarked maps, despite their apparent simplicity, offer a wealth of educational and practical benefits. By engaging in the active process of filling in the missing details, individuals can develop a deeper understanding of geographical concepts, enhance spatial reasoning skills, and cultivate critical thinking abilities.
From classrooms to travel planning and research applications, unmarked maps serve as powerful tools for fostering geographical literacy, encouraging exploration, and promoting a more engaged and informed understanding of the world around us. Embracing the power of blank canvases, in this case, unmarked maps, opens a world of possibilities for learning, exploration, and critical thinking.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Power of Unmarked Maps: A Comprehensive Guide to Geographical Exploration and Learning. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!