Unveiling the Significance of the IRC Climate Zone Map: A Guide to Building Efficiency and Sustainability
Related Articles: Unveiling the Significance of the IRC Climate Zone Map: A Guide to Building Efficiency and Sustainability
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Significance of the IRC Climate Zone Map: A Guide to Building Efficiency and Sustainability. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Significance of the IRC Climate Zone Map: A Guide to Building Efficiency and Sustainability
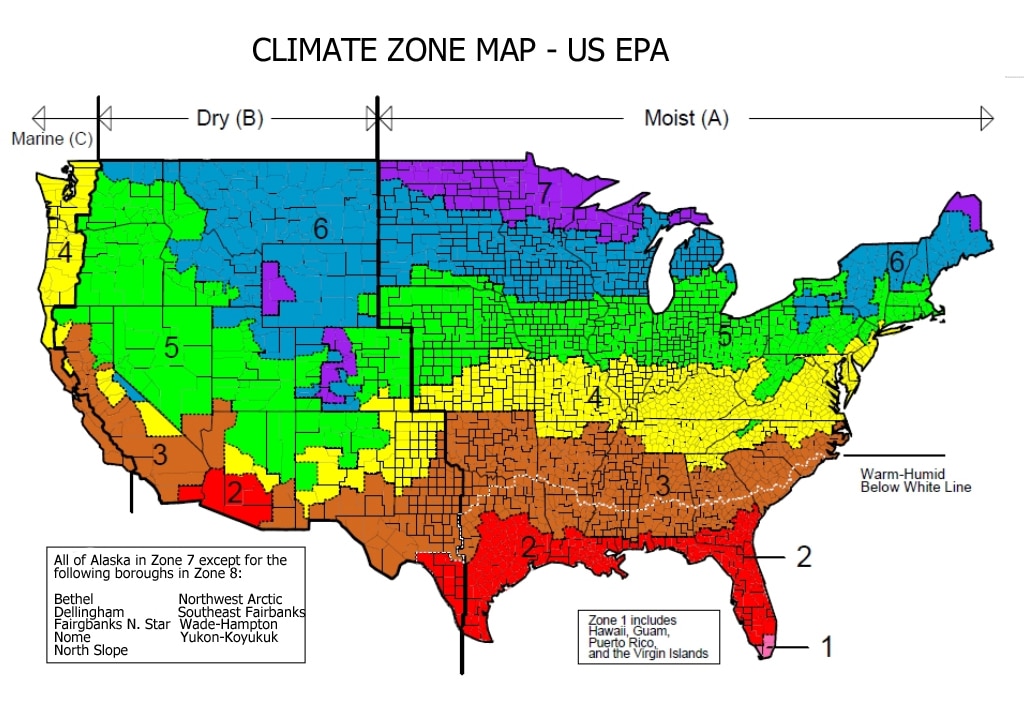
The International Residential Code (IRC) Climate Zone Map is a vital tool in the realm of building design and construction. This map, developed and maintained by the International Code Council (ICC), serves as a comprehensive guide for determining appropriate building practices and energy efficiency standards based on the specific climate conditions of a given region.
Understanding the IRC Climate Zone Map: A Foundation for Building Efficiency
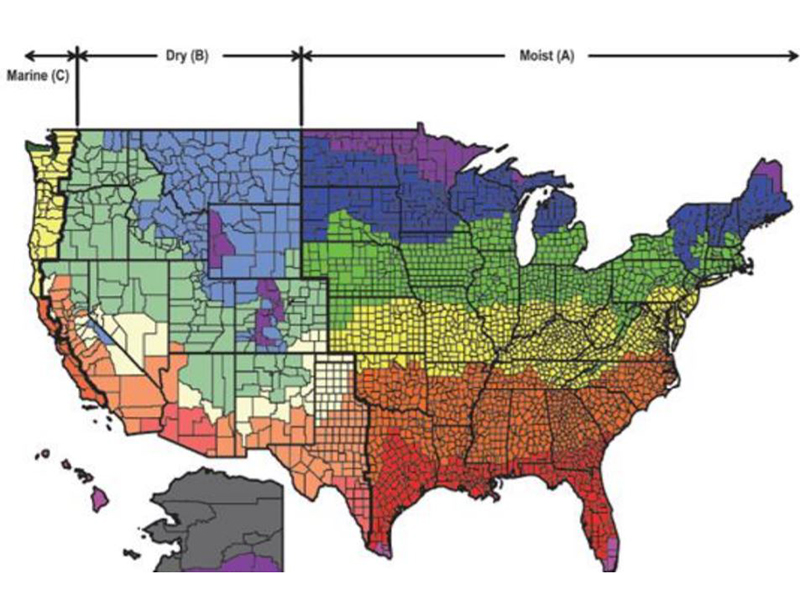
The IRC Climate Zone Map is a visual representation of the United States and its territories, divided into 16 distinct climate zones. These zones are categorized based on factors such as:
- Heating Degree Days (HDD): A measure of how much heating is required during the winter months.
- Cooling Degree Days (CDD): A measure of how much cooling is required during the summer months.
- Design Temperature: The lowest or highest temperature expected in a particular region, used for calculating heating and cooling loads.
- Climate Data: This includes factors like humidity, precipitation, and wind patterns, all of which influence building design and performance.
Each climate zone represents a specific set of climate characteristics, and the IRC provides building code requirements tailored to each zone. This ensures that buildings are designed and constructed to meet the unique demands of their environment, ultimately contributing to energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and overall sustainability.
Decoding the Climate Zones: A Detailed Breakdown
The IRC Climate Zone Map utilizes a numerical system to identify each zone, ranging from 1A to 8. The zones are further subdivided into subzones (A, B, C) within certain regions, reflecting specific climate variations.
- Zones 1A and 1B: These represent the coldest regions of the United States, characterized by extremely low temperatures and high HDDs. Buildings in these zones require robust insulation and efficient heating systems to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures.
- Zones 2A, 2B, and 3: These zones experience moderately cold winters and moderate HDDs. Building codes in these zones emphasize adequate insulation and efficient heating systems, but they may be less stringent than in colder regions.
- Zones 4A, 4B, 5A, and 5B: These zones represent a transition between colder and warmer climates, with moderate HDDs and CDDs. Building codes in these zones focus on balancing heating and cooling requirements, incorporating features like proper ventilation and shading to optimize energy performance.
- Zones 6A, 6B, 7, and 8: These zones experience hot and humid summers with high CDDs. Building codes in these zones emphasize features like proper ventilation, shading, and high-efficiency cooling systems to ensure comfortable indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption.
The Impact of the IRC Climate Zone Map: Benefits and Applications
The IRC Climate Zone Map plays a crucial role in promoting energy efficiency and sustainability in building design and construction. Its benefits are multifaceted:
- Energy Savings: By tailoring building codes to specific climate conditions, the map ensures that buildings are designed and constructed to minimize energy consumption for heating and cooling. This translates into significant energy savings for building occupants and reduced environmental impact.
- Improved Comfort: By considering the unique climate characteristics of each region, the map helps ensure that buildings provide comfortable indoor temperatures year-round. This enhances the quality of life for building occupants and promotes a healthier living environment.
- Reduced Building Costs: By optimizing building design and construction practices for specific climate zones, the map can help reduce overall building costs. This is achieved through the use of appropriate materials, efficient systems, and minimized energy consumption.
- Environmental Protection: The map’s focus on energy efficiency and sustainability directly contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change.
Beyond Building Codes: The Wider Implications of the IRC Climate Zone Map
The IRC Climate Zone Map’s influence extends beyond building codes, impacting various aspects of building design and construction:
- Material Selection: The map guides the selection of appropriate building materials, such as insulation, windows, and roofing, to optimize energy performance in specific climate zones.
- HVAC System Design: The map informs the design and sizing of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to ensure efficient operation and optimal indoor comfort.
- Solar Design: The map helps determine the optimal orientation and size of solar panels for maximum energy production in different climate zones.
- Landscaping and Site Design: The map encourages the use of landscaping and site design elements that enhance building performance and reduce energy consumption, such as shade trees and green roofs.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about the IRC Climate Zone Map
Q: How do I find my climate zone?
A: The IRC Climate Zone Map is readily available online through various resources, including the International Code Council website. You can locate your specific climate zone by entering your address or zip code.
Q: What are the key differences between climate zones?
A: Each climate zone is characterized by unique climate characteristics, including HDDs, CDDs, and design temperatures. These differences influence building code requirements and design considerations.
Q: How does the IRC Climate Zone Map affect building costs?
A: While some initial costs may be associated with implementing energy-efficient building practices, the long-term savings in energy consumption and maintenance often outweigh these costs.
Q: Is the IRC Climate Zone Map applicable to all types of buildings?
A: The IRC Climate Zone Map primarily focuses on residential buildings. However, its principles can be applied to other building types, such as commercial and industrial structures.
Q: How often is the IRC Climate Zone Map updated?
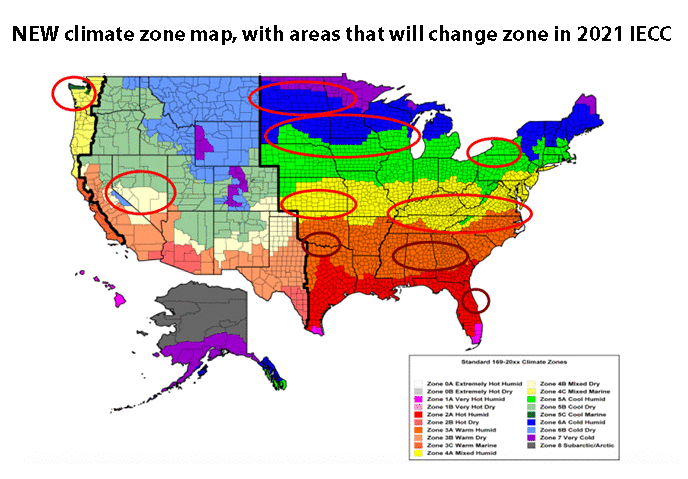
A: The IRC Climate Zone Map is updated periodically to reflect changes in climate data and building technology.
Tips for Utilizing the IRC Climate Zone Map Effectively
- Consult with a qualified professional: Seek guidance from an architect, engineer, or building contractor experienced in using the IRC Climate Zone Map to ensure optimal design and construction practices.
- Understand the specific requirements: Carefully review the building code requirements for your climate zone to ensure compliance and maximize energy efficiency.
- Consider energy-efficient materials: Utilize insulation, windows, and roofing materials that are appropriate for your climate zone and meet energy efficiency standards.
- Optimize HVAC systems: Design and install HVAC systems that are properly sized and efficient for your climate zone, minimizing energy consumption.
- Incorporate sustainable design features: Consider implementing sustainable design features like shading, ventilation, and green roofs to enhance building performance and reduce environmental impact.
Conclusion: A Blueprint for Sustainable Building Practices
The IRC Climate Zone Map serves as a valuable tool for promoting energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and environmental sustainability in building design and construction. By providing a framework for tailoring building practices to specific climate conditions, the map empowers architects, engineers, and builders to create buildings that are not only functional but also environmentally responsible. As we strive for a more sustainable future, the IRC Climate Zone Map will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the built environment and ensuring that buildings are designed and constructed to meet the challenges of a changing climate.
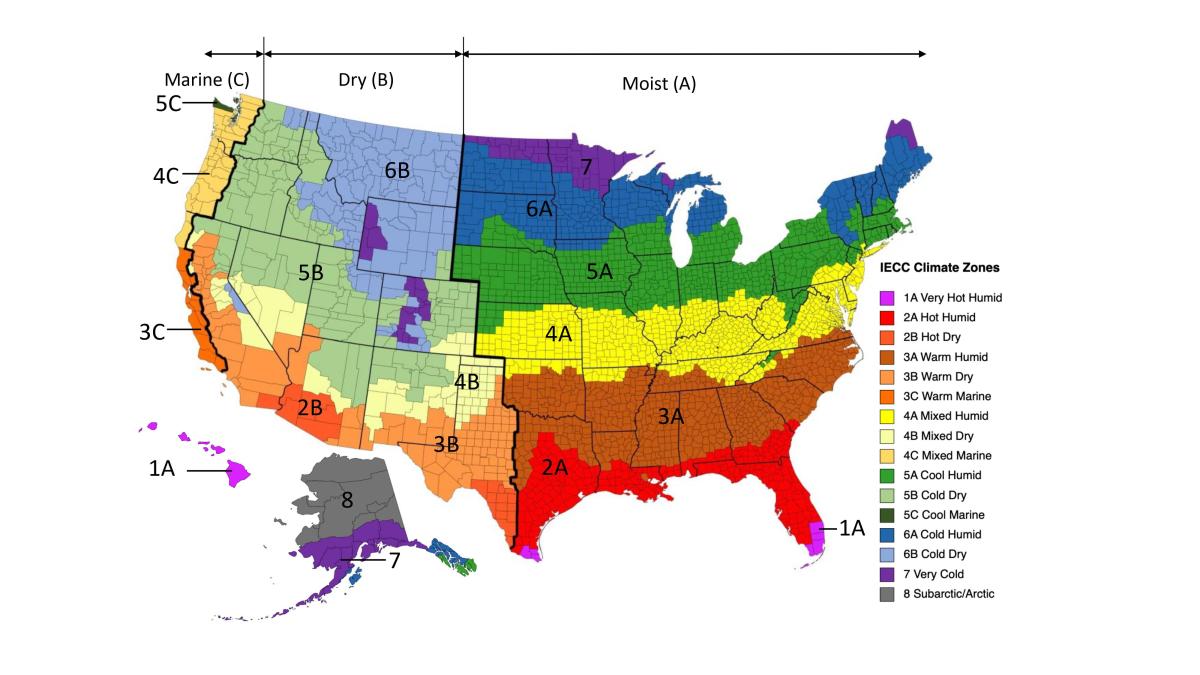

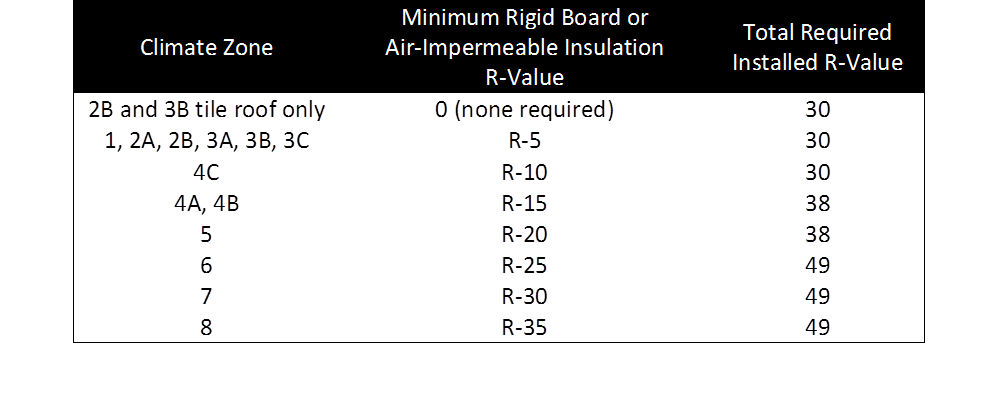
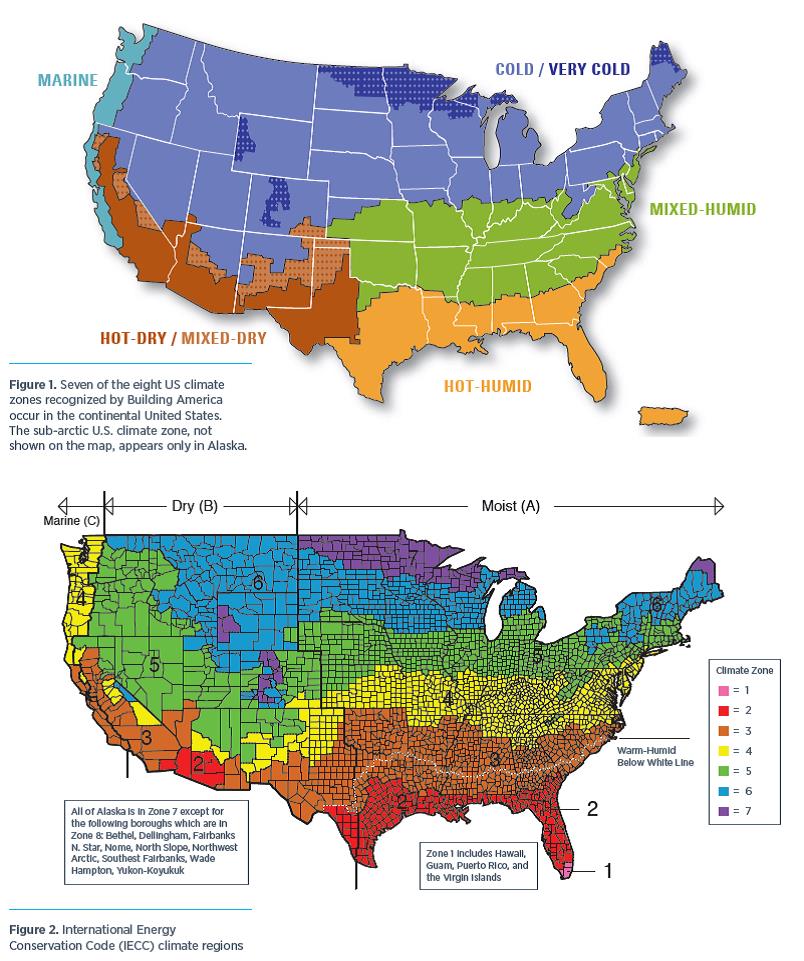
![CHAPTER 11 [RE] ENERGY EFFICIENCY 2015 International Residential Code](https://cdn-codes.iccsafe.org/bundles/document/new_document_images/553/Ch_11_Fig_N1101_7_(R301_1).jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Significance of the IRC Climate Zone Map: A Guide to Building Efficiency and Sustainability. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!