Unveiling the Sunshine State: A Comprehensive Guide to Florida’s Geography
Related Articles: Unveiling the Sunshine State: A Comprehensive Guide to Florida’s Geography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Sunshine State: A Comprehensive Guide to Florida’s Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Sunshine State: A Comprehensive Guide to Florida’s Geography
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Sunshine State: A Comprehensive Guide to Florida’s Geography
- 3.1 A Glimpse into Florida’s Geographic Canvas
- 3.2 Understanding the Importance of Florida’s Geography
- 3.3 Navigating Florida’s Map: Essential Tips
- 3.4 FAQs about Florida’s Geography
- 3.5 Conclusion: Florida’s Geography – A Tapestry of Diversity
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Sunshine State: A Comprehensive Guide to Florida’s Geography
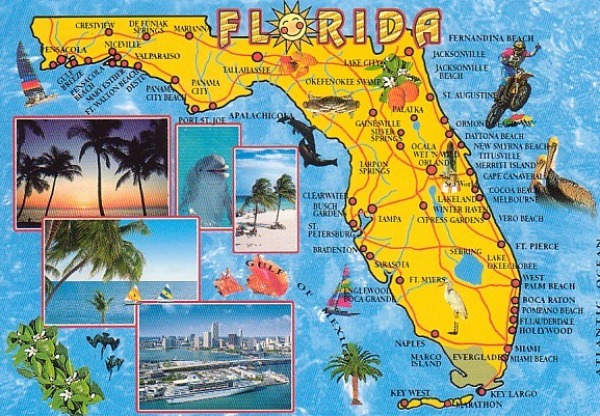
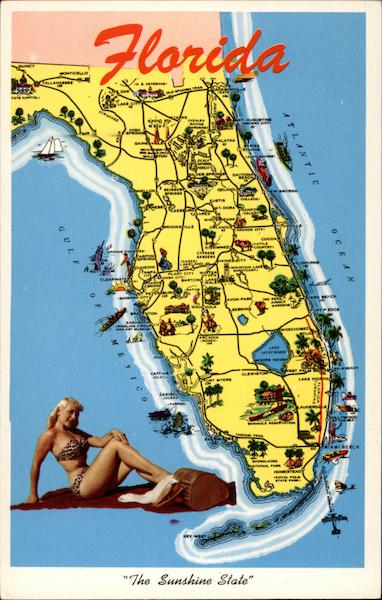
Florida, the "Sunshine State," is a peninsula jutting out from the southeastern United States, renowned for its vibrant culture, diverse ecosystems, and captivating coastline. Understanding Florida’s geography through its map is essential for appreciating its unique character and navigating its varied landscapes. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of Florida’s map, exploring its physical features, regional distinctions, and the significance of its geographical characteristics.
A Glimpse into Florida’s Geographic Canvas
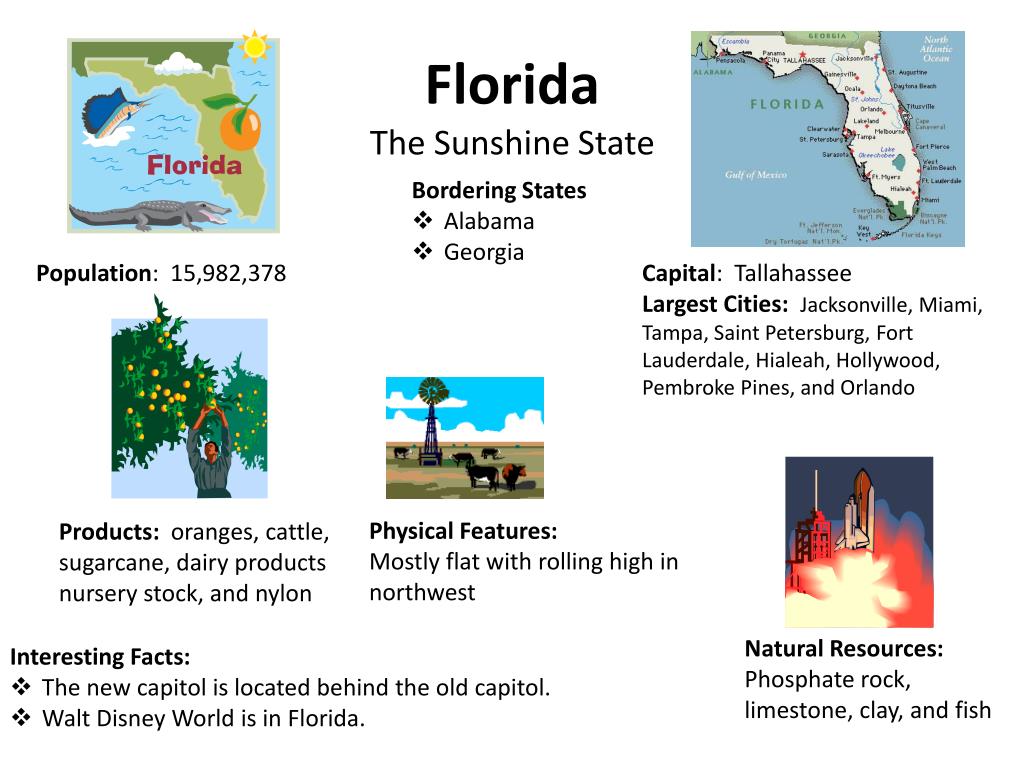
Florida’s map reveals a state shaped like a long, slender finger pointing towards the Caribbean Sea. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and the Gulf of Mexico to the west, with Alabama and Georgia forming its northern boundaries. The state’s distinctive shape is a result of its geological history, formed over millions of years by the interplay of tectonic plates, sea level changes, and erosion.
The Panhandle and the Peninsula:
- The Panhandle: The northernmost part of Florida, often referred to as the Panhandle, extends westward from the state’s northern border, forming a narrow strip of land bordering Alabama and the Gulf of Mexico. It is characterized by rolling hills, pine forests, and a coastline dotted with bays and inlets.
- The Peninsula: The southern portion of Florida, known as the Peninsula, stretches southward from the Panhandle, encompassing the majority of the state’s landmass. It is renowned for its vast wetlands, diverse flora and fauna, and a stunning coastline featuring barrier islands, beaches, and mangrove forests.
Regions and Their Distinctive Features:
Florida’s map can be further dissected into distinct regions, each with its own unique characteristics:
- The Florida Keys: A chain of islands stretching southwest from the southern tip of the peninsula, the Keys are renowned for their turquoise waters, coral reefs, and laid-back island lifestyle.
- South Florida: Encompassing the southernmost portion of the peninsula, South Florida is home to bustling metropolitan areas like Miami, Fort Lauderdale, and West Palm Beach, known for their vibrant culture, international flair, and luxurious beaches.
- Central Florida: A region encompassing Orlando, a major tourist hub known for its theme parks, and the Space Coast, home to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center. Central Florida also boasts vast natural areas, including the Everglades National Park.
- North Florida: The northern region of the peninsula, North Florida, is known for its historic cities like Jacksonville, its rolling hills, and its diverse ecosystems, including the Apalachicola National Forest.
- The Panhandle: As mentioned earlier, the Panhandle is characterized by its coastal beauty, its forests, and its charming small towns.
Understanding the Importance of Florida’s Geography
The map of Florida reveals the state’s complex and interconnected geography, which plays a crucial role in shaping its environment, economy, and culture.
Coastal Influence:
- Tourism and Recreation: Florida’s extensive coastline, stretching over 1,200 miles, is a major draw for tourists, providing endless opportunities for swimming, sunbathing, fishing, boating, and other water activities.
- Economic Hub: The tourism industry, fueled by Florida’s coastal allure, is a major contributor to the state’s economy.
- Environmental Impacts: Florida’s coastline is susceptible to the effects of climate change, including rising sea levels and more frequent and intense hurricanes.
Wetlands and Water Resources:
- The Everglades: This vast wetland ecosystem, spanning southern Florida, is crucial for the state’s water supply, wildlife habitat, and flood control.
- Water Management: Florida’s unique geography presents challenges in managing its water resources, especially in light of population growth and the impacts of climate change.
Climate and Weather:
- Subtropical Climate: Florida’s location within the subtropical zone results in warm temperatures year-round, with distinct wet and dry seasons.
- Hurricane Season: The state is prone to hurricanes during the summer and fall months, posing significant risks to coastal communities.
Navigating Florida’s Map: Essential Tips
- Understanding Scale: Pay attention to the map’s scale to get an accurate sense of distances and relative sizes of different regions.
- Key Features: Identify important features like major cities, highways, rivers, lakes, and national parks.
- Regional Distinctions: Recognize the distinct characteristics of each region, including its climate, landscape, and cultural attractions.
- Online Resources: Utilize online mapping tools, such as Google Maps, to explore Florida’s geography in detail, including street views, satellite imagery, and interactive features.
FAQs about Florida’s Geography
Q: What are the highest points in Florida?
A: Florida’s highest point is Britton Hill in Walton County, at 345 feet above sea level. The state’s highest point within the peninsula is Sugarloaf Mountain in Lake County, at 312 feet above sea level.
Q: What are the major rivers in Florida?
A: Some of the major rivers in Florida include the St. Johns River, the Suwannee River, the Apalachicola River, and the Peace River.
Q: What is the largest city in Florida?
A: Jacksonville is the largest city in Florida by land area, while Miami is the most populous.
Q: What are the most popular tourist destinations in Florida?
A: Some of the most popular tourist destinations in Florida include Miami Beach, Orlando, the Florida Keys, and the Everglades National Park.
Q: What are the major industries in Florida?
A: Florida’s economy is driven by tourism, agriculture, aerospace, and healthcare.
Q: What are the major environmental challenges facing Florida?
A: Florida faces significant environmental challenges, including climate change, water pollution, and habitat loss.
Conclusion: Florida’s Geography – A Tapestry of Diversity
The map of Florida is a testament to the state’s unique and diverse geography. It reveals a land shaped by coastal influences, wetlands, and a subtropical climate. Understanding the intricate relationships between these elements is crucial for appreciating Florida’s natural beauty, its economic vitality, and the challenges it faces. By exploring Florida’s map, we gain a deeper understanding of the state’s character, its vibrant culture, and its rich tapestry of landscapes.
![Learn Why is Florida Called the Sunshine State [stats and facts explained]](https://foreignusa.com/wp-content/uploads/why-is-florida-the-sunshine-state.jpg)
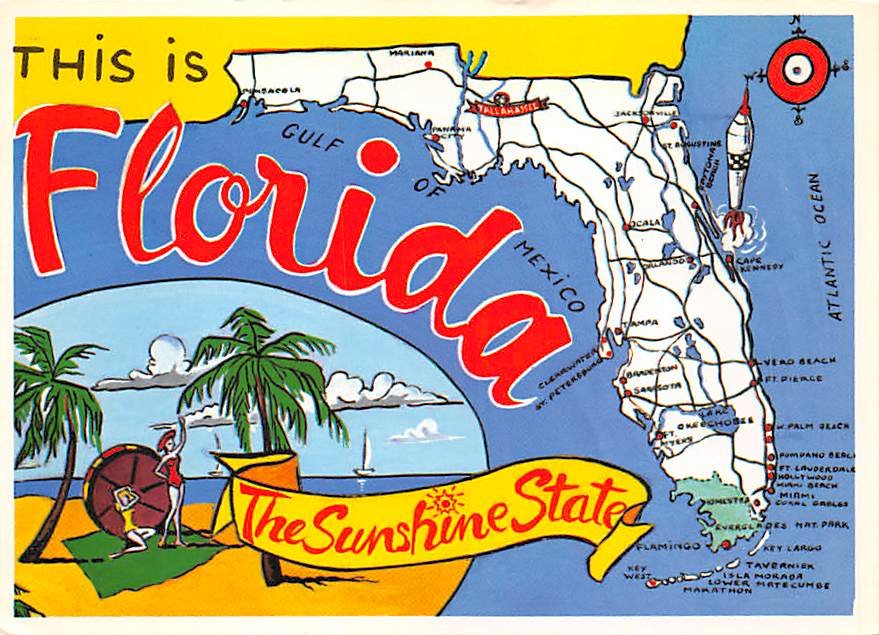
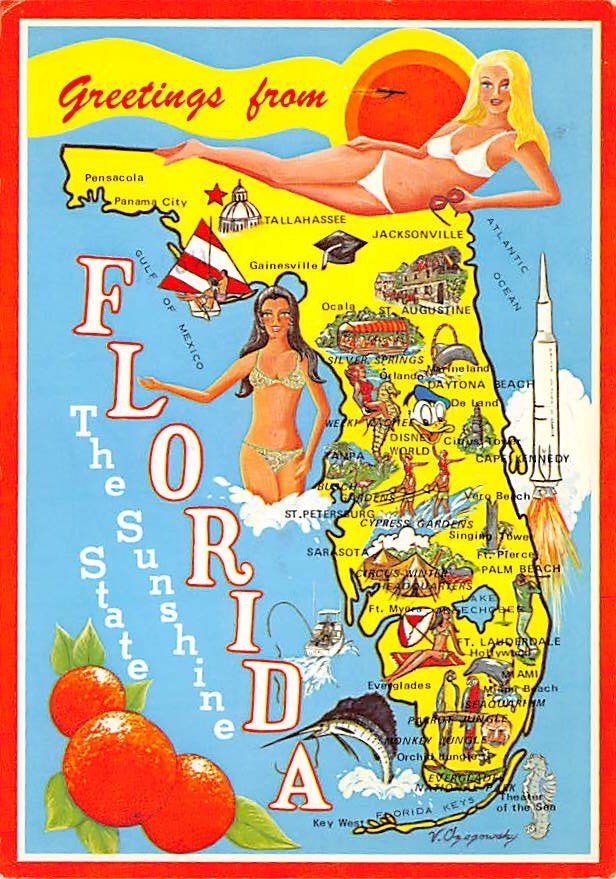



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Sunshine State: A Comprehensive Guide to Florida’s Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!