Unveiling the Tapestry of Humanity: A Comprehensive Look at World Population Distribution
Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Humanity: A Comprehensive Look at World Population Distribution
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Tapestry of Humanity: A Comprehensive Look at World Population Distribution. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unveiling the Tapestry of Humanity: A Comprehensive Look at World Population Distribution
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unveiling the Tapestry of Humanity: A Comprehensive Look at World Population Distribution
- 3.1 A Glimpse into the Past: Historical Trends and Drivers
- 3.2 Mapping the World’s People: Geographical Patterns and Factors
- 3.3 Beyond the Map: The Importance of Understanding Population Distribution
- 3.4 FAQs: Demystifying World Population Distribution
- 3.5 Tips for Understanding and Interpreting Population Distribution Maps:
- 3.6 Conclusion: A Tapestry of Humanity in Constant Evolution
- 4 Closure
Unveiling the Tapestry of Humanity: A Comprehensive Look at World Population Distribution
The Earth, a vibrant tapestry woven with diverse cultures, languages, and ecosystems, harbors a vast and ever-evolving population. Understanding the distribution of this population across the globe is crucial for comprehending global dynamics, addressing societal challenges, and shaping the future of humanity. This article delves into the intricacies of world population distribution, exploring its historical evolution, geographical patterns, and underlying factors, while highlighting its significance for various fields.
A Glimpse into the Past: Historical Trends and Drivers
The journey of human population distribution is a captivating narrative, shaped by historical events, technological advancements, and environmental factors.
- Early Human Migration: Early humans, driven by the search for food and resources, migrated across continents, populating diverse landscapes. The development of agriculture, around 10,000 years ago, led to the establishment of settled communities and increased population density in fertile regions.
- The Rise of Cities: The emergence of cities, driven by trade and urbanization, further concentrated populations in specific geographical locations. Ancient civilizations like Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley civilization thrived in fertile river valleys, attracting large populations.
- Colonialism and Global Trade: European colonialism, starting in the 15th century, significantly impacted population distribution. The transatlantic slave trade, forced migration, and the introduction of new diseases led to demographic shifts in various regions.
- Industrial Revolution and Technological Advancements: The Industrial Revolution, beginning in the 18th century, spurred rapid technological advancements, leading to increased agricultural productivity, improved sanitation, and a decline in mortality rates. This resulted in a dramatic population increase, particularly in Europe and North America.
These historical events, along with ongoing demographic trends, have shaped the current landscape of world population distribution.
Mapping the World’s People: Geographical Patterns and Factors
World population distribution maps, visual representations of population density across the globe, offer a powerful tool for understanding global demographics. Analyzing these maps reveals distinct geographical patterns and underlying factors influencing population distribution:
1. Population Concentration:
- Coastal Regions: Coastal areas, with access to water resources, trade routes, and fertile land, tend to be densely populated. Examples include the eastern coast of the United States, Southeast Asia, and the Mediterranean region.
- River Valleys: Fertile river valleys, providing water for agriculture and transportation, have historically attracted large populations. The Nile River Valley in Egypt, the Ganges River Valley in India, and the Yangtze River Valley in China are prime examples.
- Urban Centers: Cities, as centers of economic activity, innovation, and cultural exchange, attract large populations. Megacities like Tokyo, New York City, and London are global hubs of human activity.
2. Factors Influencing Distribution:
- Climate: Temperate climates, with moderate rainfall and temperatures, are generally more suitable for human habitation and agriculture, contributing to higher population density.
- Topography: Flat, easily accessible terrain facilitates agriculture, transportation, and settlement, promoting population growth. Mountainous regions, on the other hand, tend to have lower population densities due to challenging terrain and limited resources.
- Natural Resources: The availability of natural resources, including water, minerals, and fertile land, plays a significant role in attracting populations.
- Economic Opportunities: Regions with thriving economies, offering employment and income opportunities, tend to attract migrants and experience population growth.
- Political Stability: Areas with stable political systems and strong governance attract populations seeking security and prosperity.
3. Regional Variations:
- Asia: Asia, with its vast landmass and diverse ecosystems, is home to the largest population on Earth. China and India, with their long histories of agriculture and urbanization, have the highest population densities.
- Africa: Africa, with its rapid population growth and diverse cultural landscape, is experiencing a significant demographic shift. The continent’s high birth rates and urbanization are contributing to increased population density in urban areas.
- Europe: Europe, historically a region of high population density, is experiencing a decline in population growth due to low birth rates and aging populations. However, some areas, particularly in Western Europe, continue to attract migrants.
- North America: North America, with its vast agricultural land and urban centers, has a relatively high population density. The United States, with its economic opportunities and diverse population, attracts migrants from around the globe.
- South America: South America, with its diverse geography and growing economies, is experiencing population growth. Brazil, with its vast Amazon rainforest and urban centers, is one of the most populous countries in the region.
Beyond the Map: The Importance of Understanding Population Distribution
Understanding world population distribution is not merely an academic exercise. It has profound implications for various fields, including:
1. Resource Management:
- Food Security: Population distribution maps can help identify areas facing food shortages and guide policies for sustainable agriculture and food production.
- Water Resources: Understanding water availability and demand based on population density is crucial for managing water resources effectively and ensuring equitable access.
- Energy Production and Consumption: Mapping population distribution can help determine energy needs and optimize energy infrastructure development.
2. Urban Planning and Development:
- Infrastructure Development: Population distribution data is essential for planning and developing infrastructure, including transportation, housing, and public services, to meet the needs of growing urban populations.
- Disaster Management: Understanding population distribution helps in preparing for and responding to natural disasters, ensuring effective evacuation plans and resource allocation.
- Environmental Sustainability: Population density and distribution are crucial factors in urban planning and development, aiming for sustainable cities that minimize environmental impact.
3. Healthcare and Public Health:
- Disease Prevention and Control: Population distribution data can help identify areas at risk for disease outbreaks and guide public health interventions.
- Access to Healthcare: Understanding population distribution patterns helps in allocating healthcare resources effectively and ensuring equitable access to medical services.
- Population Health Monitoring: Population distribution data is essential for tracking population health trends, identifying disparities, and developing targeted public health programs.
4. Economic Development and Policy:
- Labor Force Planning: Understanding population distribution helps in forecasting labor force needs and developing strategies for workforce development.
- Investment and Trade: Population distribution data can guide investment decisions, targeting areas with high growth potential and demand for goods and services.
- Social Welfare Programs: Population distribution data helps in designing and implementing social welfare programs, ensuring they reach the intended beneficiaries.
5. Political and Social Dynamics:
- Political Representation: Population distribution data is crucial for ensuring fair political representation and allocating resources based on population size.
- Social Cohesion: Understanding population distribution patterns helps in promoting social cohesion and addressing issues related to inequality and marginalization.
- Migration Patterns: Population distribution maps can help understand migration patterns, identifying areas of origin and destination, and informing policies related to migration.
FAQs: Demystifying World Population Distribution
1. What is population density, and how is it calculated?
Population density refers to the number of people living in a specific area, typically measured in people per square kilometer or square mile. It is calculated by dividing the total population of an area by its total land area.
2. How does population distribution differ from population density?
Population distribution refers to the spatial arrangement of people across a region, while population density focuses on the concentration of people within a specific area. Distribution describes where people live, while density measures how many people live in a given space.
3. What are the major factors driving population growth and decline in different regions?
Population growth is primarily driven by high birth rates, while population decline is influenced by factors like low birth rates, aging populations, and emigration. Factors influencing these trends include economic development, healthcare advancements, social norms, and government policies.
4. How can technology be used to improve our understanding of population distribution?
Technological advancements, such as remote sensing, geographic information systems (GIS), and big data analytics, are revolutionizing our understanding of population distribution. These tools allow for more accurate and detailed mapping, enabling us to analyze population dynamics in real-time and make informed decisions based on data-driven insights.
5. What are some of the challenges associated with understanding and managing population distribution?
Challenges include:
- Data Collection and Accuracy: Collecting accurate and comprehensive population data, particularly in remote or conflict-affected areas, can be challenging.
- Data Interpretation and Analysis: Interpreting and analyzing population data, considering complex factors and regional variations, requires expertise and sophisticated tools.
- Addressing Inequalities: Understanding population distribution highlights inequalities in access to resources, healthcare, and opportunities, necessitating targeted interventions and policies.
- Sustainable Development: Managing population growth and distribution sustainably requires balancing economic development, environmental protection, and social well-being.
Tips for Understanding and Interpreting Population Distribution Maps:
- Pay attention to scale: Maps often use different scales, so it’s essential to compare population densities across regions using consistent scales.
- Consider geographic context: Population distribution is influenced by geography, climate, and natural resources. Understanding the context helps in interpreting patterns.
- Look for trends and anomalies: Identify areas with high or low population densities, and explore the factors contributing to these patterns.
- Compare maps over time: Analyzing population distribution maps over time reveals historical trends and provides insights into demographic shifts.
- Integrate data from other sources: Combine population data with other relevant information, such as economic indicators, environmental data, and social statistics, for a comprehensive understanding.
Conclusion: A Tapestry of Humanity in Constant Evolution
World population distribution maps offer a powerful lens through which to understand the intricate tapestry of humanity. They reveal patterns of concentration, highlight underlying factors, and underscore the interconnectedness of human societies. By comprehending the dynamics of population distribution, we can address global challenges, foster sustainable development, and create a more equitable and prosperous world for all. As the human population continues to evolve, these maps will continue to provide crucial insights, guiding our understanding of the world and shaping our collective future.
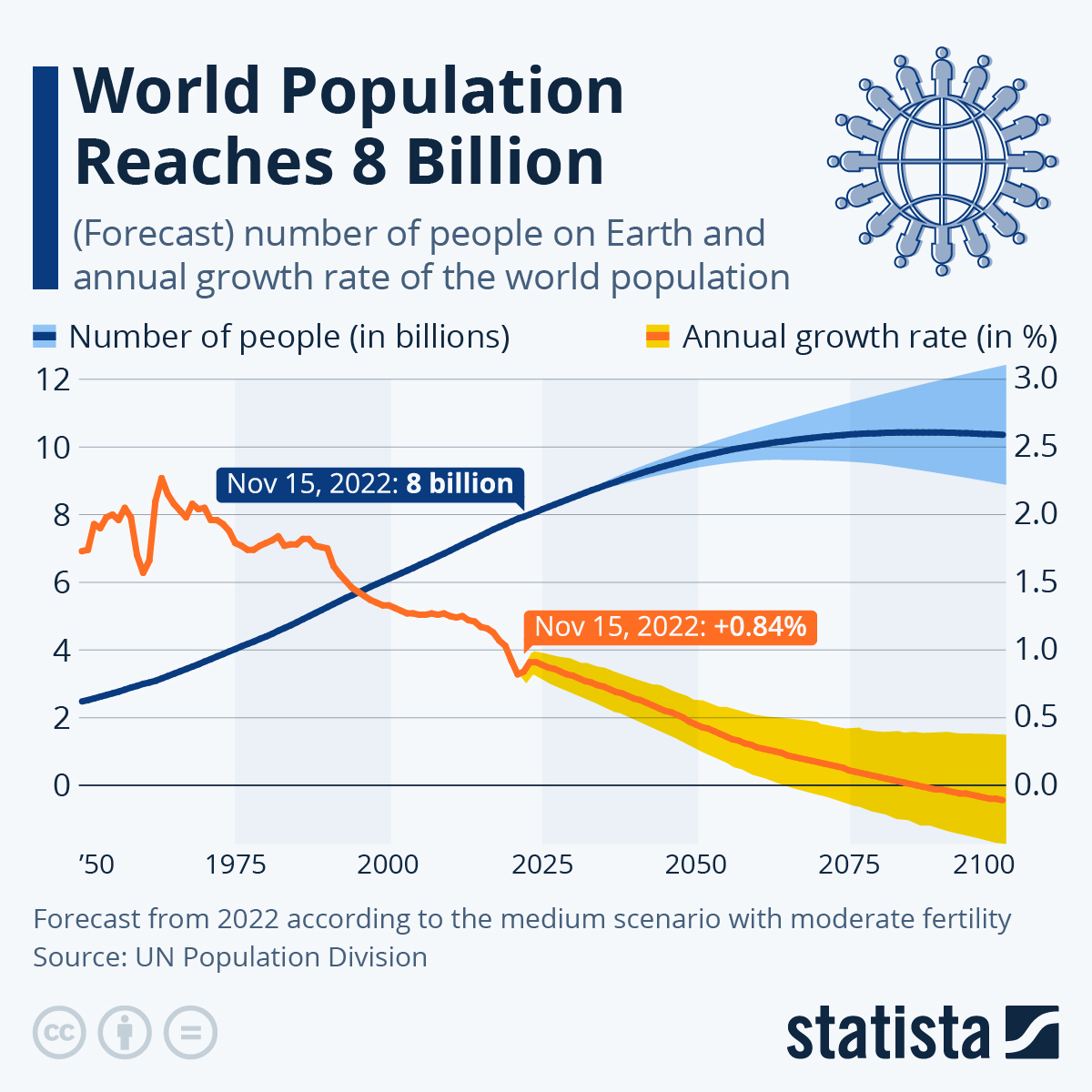






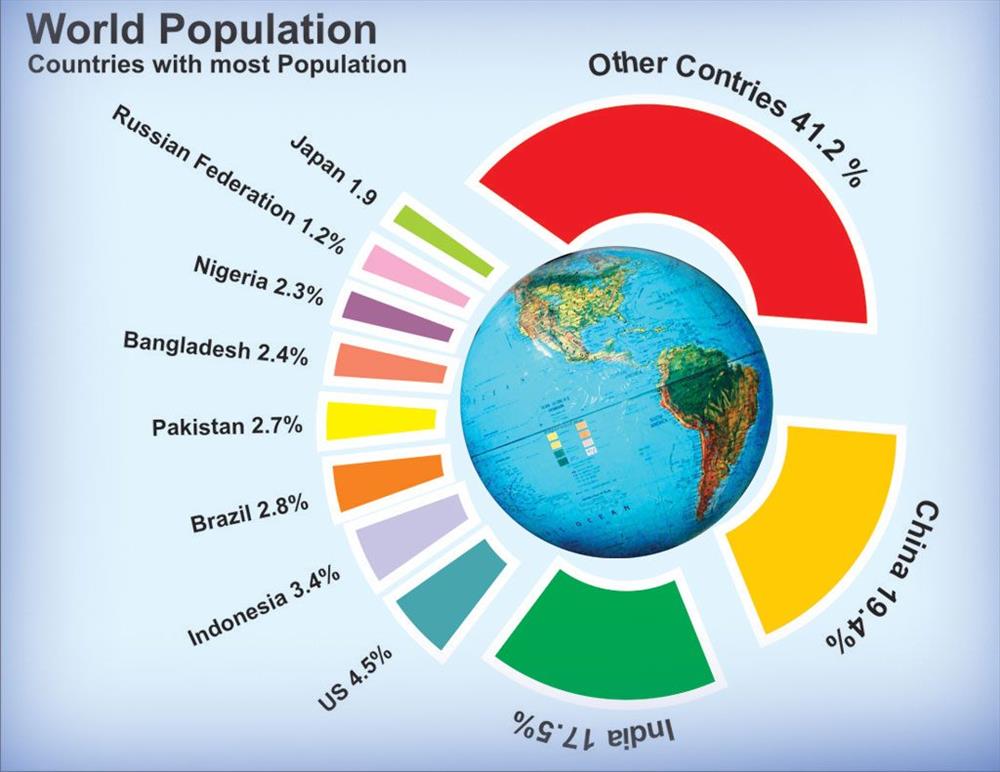
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Tapestry of Humanity: A Comprehensive Look at World Population Distribution. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!